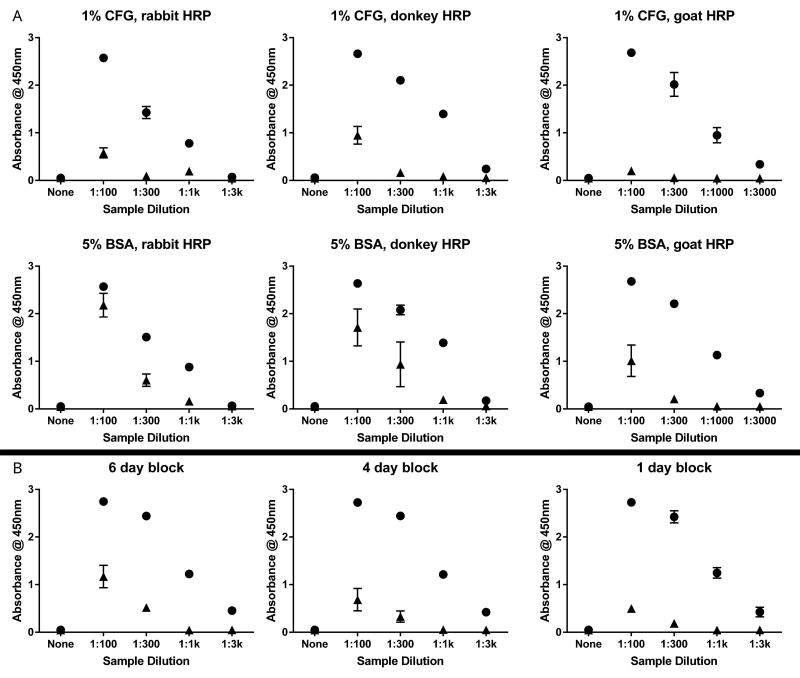
Figure 1. Optimization of ELISA for α-syn AAb detection.
Dilute serum was applied to 384-well ELISA plates either coated with recombinant α-syn or not coated. (A) Plates were blocked with either 1% cold fish gelatin (top row) or 5% bovine serum albumin (middle row) overnight at 4 °C. Binding was detected using anti-human IgG HRP-conjugates raised in rabbit (left column), donkey (middle column), or goat (right column).
(B) Plates were blocked with 1% cold fish gelatin at 4°C for either 6 days (left), 4 days (middle), or 1 day (right). Additional blocking solutions (1% bovine serum albumin, 5% milk in PBS, several commercial blocking solutions) did not demonstrate any improvement over 1% cold fish gelatin. Each data point represents three technical replicates (n=3 wells). Wells coated with α-syn denoted by closed circles. Uncoated wells denoted by closed triangles. BSA = bovine serum albumin; CFG = cold fish gelatin; HRP = horseradish peroxidase conjugate.