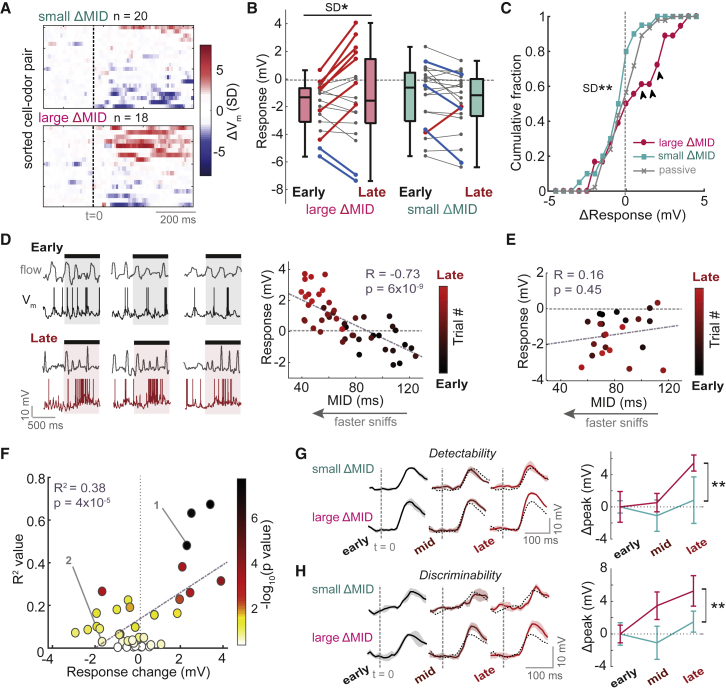
Figure 4.
Positive Response Changes Are Tightly Linked to Changes in Active Sampling
All data are from the learning dataset.
(A) Response change heatmaps (late-early average Vm response) normalized by baseline SD, for small MID change (|ΔMID| <20 ms) and large MID change (|ΔMID| >20 ms).
(B) Plot of early and late Vm responses for cell-odor pairs with large and small ΔMID separately. Thick red and blue lines indicate significant positive and negative changes, respectively (p < 0.01).
(C) Cumulative histograms of Vm response changes. Black arrowheads indicate significant differences between large ΔMID and both small ΔMID and passive histograms (STAR Methods). Large ΔMID, SD = 1.9 mV, n = 18; small ΔMID, SD = 1.1 mV; p = 0.002, Bartlett test.
(D) Left: example nasal flow and Vm traces for early and late trials for a cell-odor pair undergoing significant increase in excitation across learning. Spikes have been clipped for display. Right: scatterplot between MID and Vm response across trials for this cell-odor pair. Points have been colored according to trial number.
(E) As for (D), but for a cell undergoing a significant increase in inhibition across learning.
(F) Scatterplot between the response change across learning, and the R2 value for correlations as in (D) and (E), colored according to the p value of the correlation. Labeled points 1 and 2 refer to examples in (D) and (E), respectively.
(G) Left plots: Euclidean distance between population response vectors and baseline data (measure of response detectability; Figure S13) for cell-odor pairs recorded alongside large ΔMID and small ΔMID. Shaded area shows SD. Dashed gray line indicates odor onset. Dotted black plots show data for early trials for comparison. Right: plot to show change in peak detectability within the first 170 ms of the stimulus for early, mid-point, and late trials, relative to the mean for early trials. Error bars show SD. Two-way ANOVA; ΔMID, p = 4 × 10−12; time, p = 0.0003; interaction, p = 0.02.
(H) As for (G), but for the Euclidean distance between population response vectors for CS+ and CS− (measure of response discriminability). Large ΔMID is assigned to cells with >20 ms change for both CS+ and CS− (n = 8). Small MID change is assigned to all other cells (n = 11). Two-way ANOVA; ΔMID, p = 2 × 10−7; time, p = 0.0003; interaction, p = 0.008.