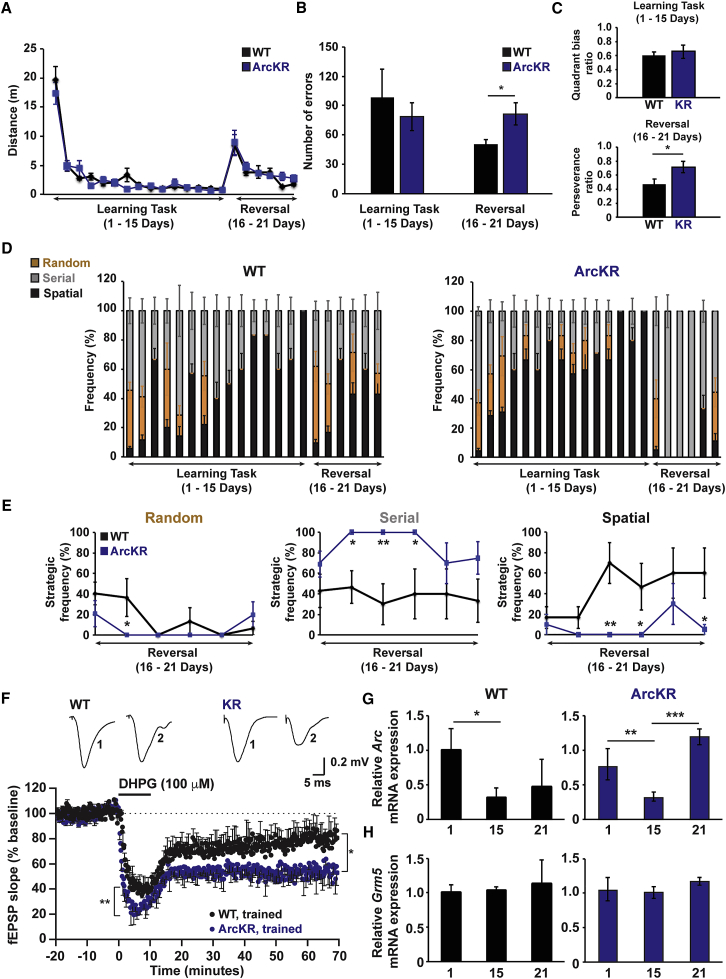
Figure 3.
ArcKR Mice Have Impaired Cognitive Flexibility
(A) Distances traveled by WT and ArcKR mice during Barnes maze training.
(B) Number of errors in WT and ArcKR mice during learning (days 1–15) and reversal phase (days 16–21).
(C) Top: average quadrant bias. Bottom: perseverance ratio for WT and ArcKR mice during learning and reversal phase.
(D) Percentage time that WT and ArcKR mice used random (brown), serial (gray), and spatial (black) search strategies (n = 5 mice for WT and ArcKR).
(E) Average frequency of strategy used in (D). Two-way ANOVA, post hoc Fisher’s LSD, ∗p ≤ 0.05, ∗∗p ≤ 0.005.
(F) Normalized mean fEPSP slope against time for Barnes maze trained WT and ArcKR mice. Baseline fEPSP slope was analyzed at 15–20 min, LTD induction was analyzed at 0–5 min after DHPG and LTD expression analyzed at 55–60 min after DHPG application. Both LTD induction (∗∗p < 0.001) and expression (WT: 78.8% ± 4.4%, n = 3, 5 slices; ArcKR: 58.1% ± 4.9%, n = 3, 7 slices, p = 0.0003) were significantly enhanced in trained ArcKR compared to WT mice. Top: representative fEPSP traces (averages of 10 fEPSPs) at the times indicated (1, 15–20 min and 2, 75–80 min).
(G) Comparison of hippocampal Arc mRNA after 1, 15, or 21 days of training in the Barnes maze. Arc mRNA was normalized to the geometric mean of 2 genes (GAPDH and GPI) and Arc in the mouse with the highest expression after 1 day of training was set to 1 for the WT mice. Each data point represents triplicate measurements from an individual mouse. (WT 1day: n = 5; WT 15 days: n = 5; WT 21 days: n = 4; ArcKR 1 day: n = 6; ArcKR 15 days: n = 7; ArcKR 21 days: n = 5). ∗p = 0.07, ∗∗p = 0.025, ∗∗∗p = 0.001.
(H) Grm5 mRNA in WT and ArcKR mice after training. Values represent mean ± SEM. Statistical comparisons were carried out with one-way ANOVA, paired and unpaired Student’s t tests.