Figure 4. NCI-H2077-R cells have a secondary NRAS mutation, rendering them more sensitive to inhibition of the MAPK pathway.
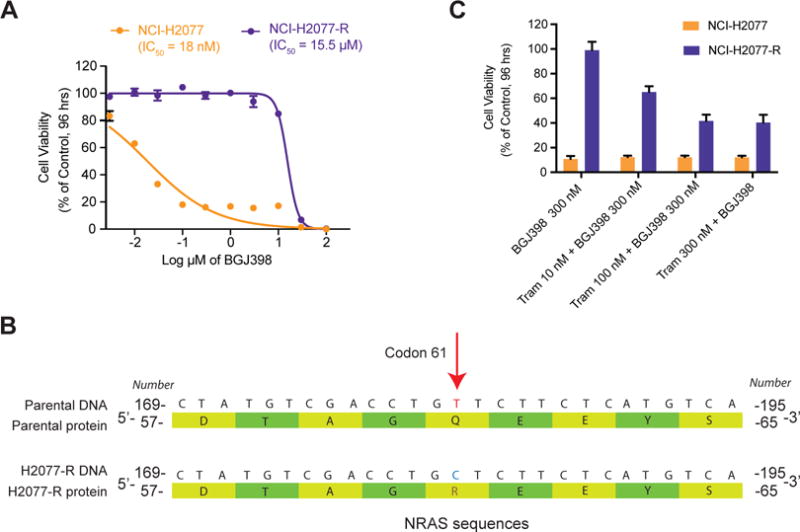
A) NCI-H2077 parental cells are sensitive to BGJ398. Treatment with increasing concentration of BGJ398 over time lead to the emergence of a resistant clone (H2077-R), which is insensitive to BGJ398.
B) Illumina sequencing analysis of 504 cancer and cancer-related genes revealed a canonical NRAS Q61R mutation in H2077-R cells (indicated by the red arrow over the sequencing reads). A schematic of the altered DNA and protein sequences is shown.
C) Cell viability assays of NCI-H2077 and H2077-R treated with BGJ398, trametinib (MEK inhibitor) or combination treatment, as indicated. Combination of non-lethal concentration of BGJ398 and increasing concentration of trametinib preferentially inhibited NCI-H2077-R cells, with modest additional effect on NCI-H2077 cells compared to BGJ398 treatment alone.
