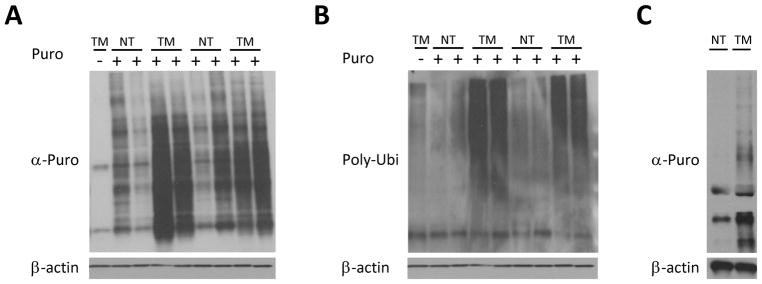
Figure 1. Protein translation is significantly increased in intestinal tumors.
A. Anti-puromycin western blot of large bowel normal tissue (NT) and tumorous tissue (TM) of 6 month old APCmin/+ mice and their sibling controls (8 mice: lanes 2–5 are females and 6–9 are males), 30 minutes after injection with 0.04 uMol/gr of Puromycin, showing significantly greater puromycin uptake in large bowel tumors of APCmin/+ mice compared to normal tissue. B. anti-Polyubiquinated (FK-2) western blot of the samples from A., showing dramatic increase in the polyubiquitinated proteins in tumors. C. Anti-puromycin western blot of large bowel normal tissue and tumor organoids from AOM-DSS mice (NT and TM respectively). Organoids were cultured in the presence of 4 uM Puromycin for 30 min, showing significantly higher puromycin uptake in tumor organoids.