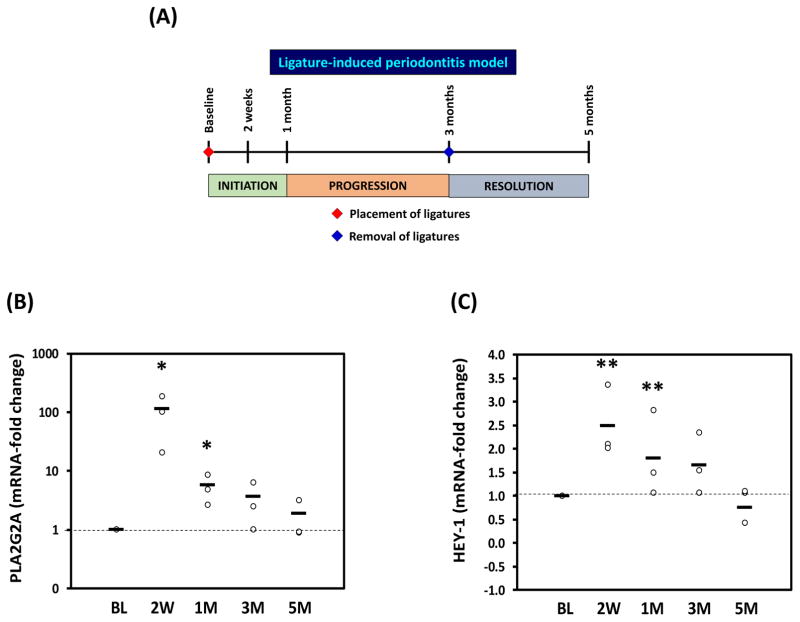
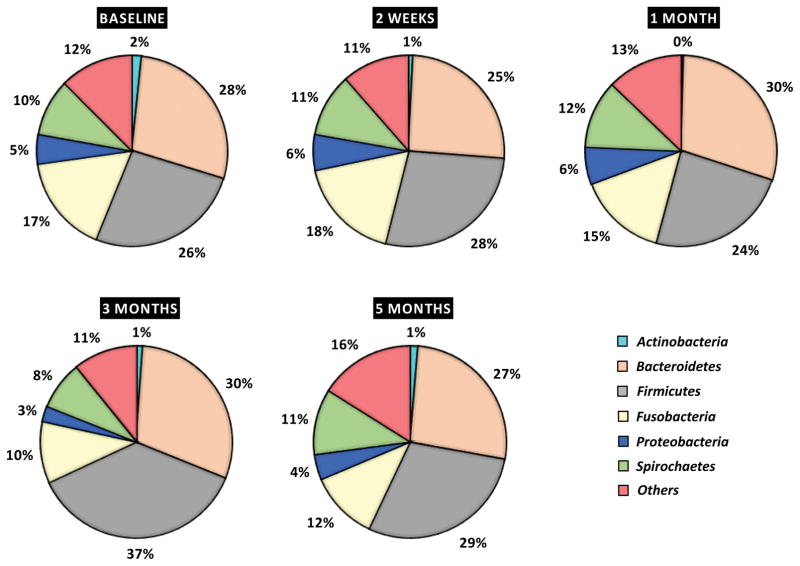
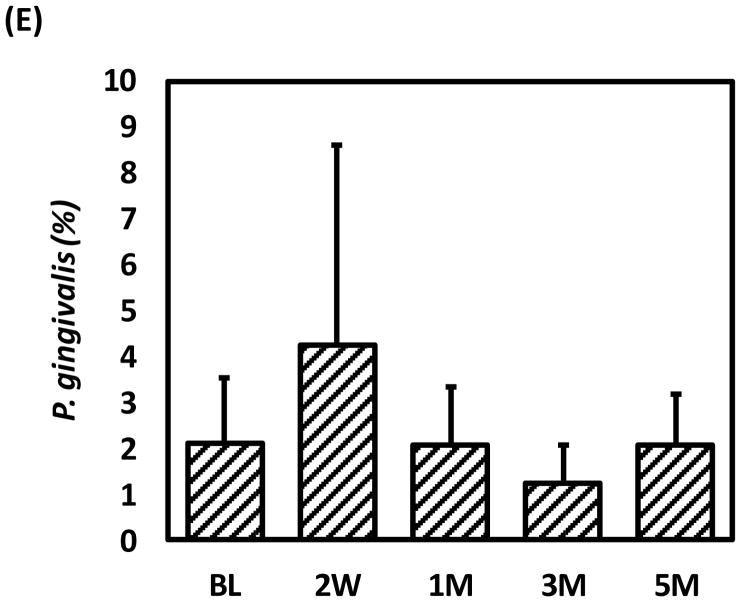
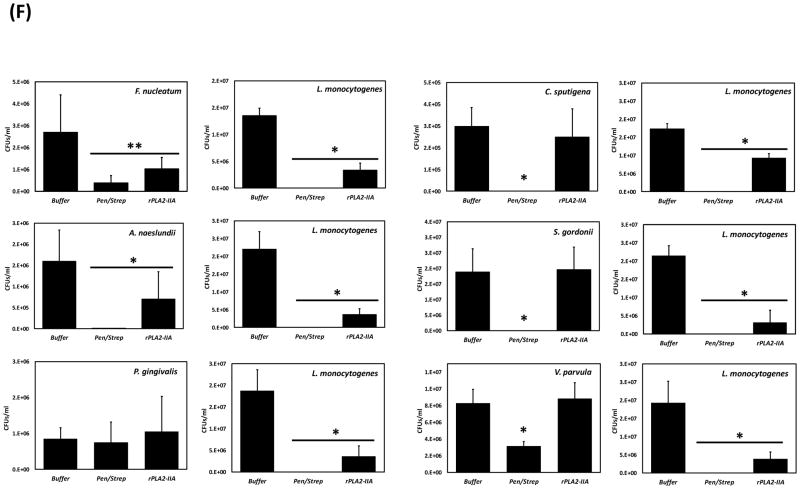
Figure 8. PLA2G2A expression, Notch-1 activation and oral microbiome changes during initiation, progression and resolution of periodontal disease in non-human primates (NHPs).
(A) The ligature-induced periodontitis model was used in nonhuman primates M. mulatta (n=9) as described in methods to determine variations in gingival gene expression by qRT-PCR during initiation (2 weeks and 1 month), progression (3 months) and resolution (2 months after removing ligatures) of periodontal disease. Fold changes in gene expression with respect to baseline levels are shown for (B) PLA2G2A and (C) HEY-1 (a marker for Notch-1 activation). Gingival biopsies (n=9) were pooled in three groups of 3 samples/each for qRT-PCR analysis. The mean of gene expression is depicted by horizontal bars in each time point. (D) Variation in abundance of the main oral bacterial Phyla and (E) P. gingivalis, was determined by 16S rRNA sequencing in oral subgingival plaque samples from NHPs. DNA from plaque samples was isolated (Magnapure LC DNA isolation kit III, Roche), barcoded and amplified using 16S universal primers for V4 region (254bp amplicon). Amplicons for each sample were purified and pooled in equimolar concentrations and sequenced using Miseq (Illumina). Sequences were clustered into phylotypes based on their sequence similarity and these binned phylotypes were assigned to their respective taxonomic classification using the Human Oral Microbiome Database (HOMD V13). (F) Antimicrobial effect of recombinant human PLA2-IIA (1μg/ml for 2h) in selected oral bacterial species (106) was evaluated by determination of colony forming units (CFUs). Bacteria exposed to 0.1 mg/ml penicillin/streptomycin (Pen/Strep) was used as a positive control and L. monocytogenes (susceptible target for PLA2-IIA) was used as control for the anti-microbial activity of PLA2-IIA in each experiment. The mean ± SD of triplicates from each treatment group from 2–3 independent experiments are shown *p≤0.01 **p≤0.05 when gene expression was compared with baseline levels, and when number of CFUs/ml of Pen/Strep or rPLA2-IIA-treated groups compared vs. Buffer.