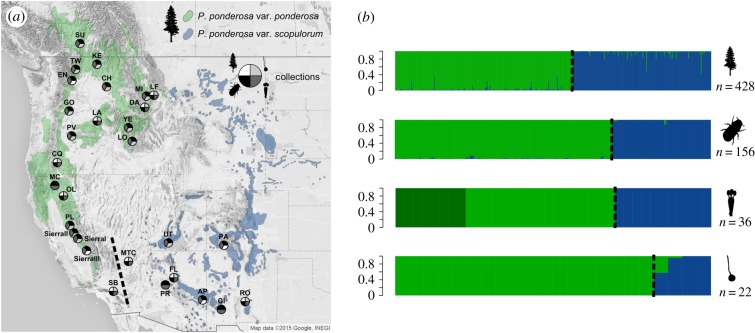
Figure 2.
Geographical distribution and codifferentiation in the tree–beetle–fungi system. (a) Ponderosa pine comprised two subspecies (var. ponderosa and var. scopulorum) thought to have formed in isolation in southern refugia during the Pleistocene. The distribution of the beetle currently follows its primary host tree, except where absent in the central and northern portion of the P. ponderosa var. scopulorum range. The northern range limits of the beetle (and fungi) in the var. scopulorum range is broadly coincident with a shift in tree defensive monoterpenes [26]. Tree, beetle and fungal collection locations are shown, and when present at a location, are represented in the pie chart. (b) Structure and Admixture results for the tree, beetle and two symbiotic fungi and the posterior probability of assignment for each individual (vertical bar) to the optimal number of genetic clusters (K) for each species.