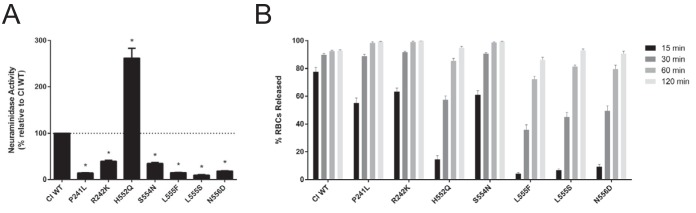
FIG 6 .
Increase in fusion promotion by mutant HN correlates with a decrease in neuraminidase activity and a decrease in RBC release. (A) Neuraminidase activity was quantified by measuring cleavage of 4-MUNANA. The observed values were normalized to expression of the HNs. Excluding H552Q (see Discussion), neuraminidase activity is decreased in all the mutant HNs compared to the wild-type clinical isolate. Results depict means plus standard deviations from three biological replicates consisting of three technical replicates each. Mutants were compared with CI wt with one-way ANOVA following log transformation of data. *, P < 0.0001. (B) Release of sialic acid-bearing RBCs by HNs at pH 7.5 and 37°C. 293T cells transiently expressing HNs were allowed to bind RBCs at 4°C for 30 min, washed, and transferred to 37°C. The percentages of RBCs released at 15, 30, 60, and 120 min were determined (y axis). All the mutants have decreased release of RBCs relative to the wild-type clinical isolate. Results depict means plus standard errors of the means (SEM) from three biological replicates consisting of two technical replicates each.