Figure 1.
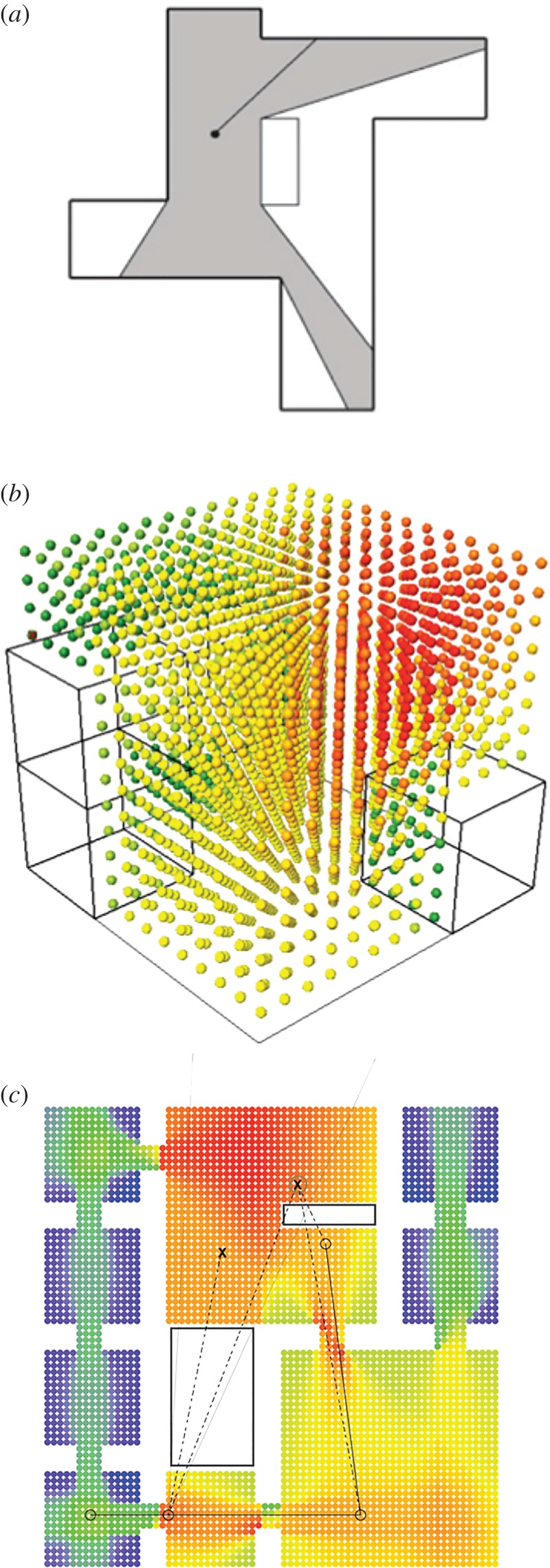
Spatial analysis and architectural computation. (a) Illustration of a traditional method of assessing connectivity, using an isovist to determine the set of all points/locations visible from a given vantage point in space and with respect to the center/starting location. In 3D visibility graph analysis [36], the isovist approach is carried out in three dimensions, comparing the connectedness between all points in space with each other, represented by the colour-coded array in (b). In (c), spatial relations of visibility and accessibility, which in traditional analysis presented challenges, are encoded into a mixed-directionality graph as a way to differentiate the intervisible lines of sight and potential walkable paths between two locations [37]. The surface-based graph analysis method we developed and applied in this study builds on the foundation from these earlier approaches to expand spatial analysis to new dimensions and contexts.
