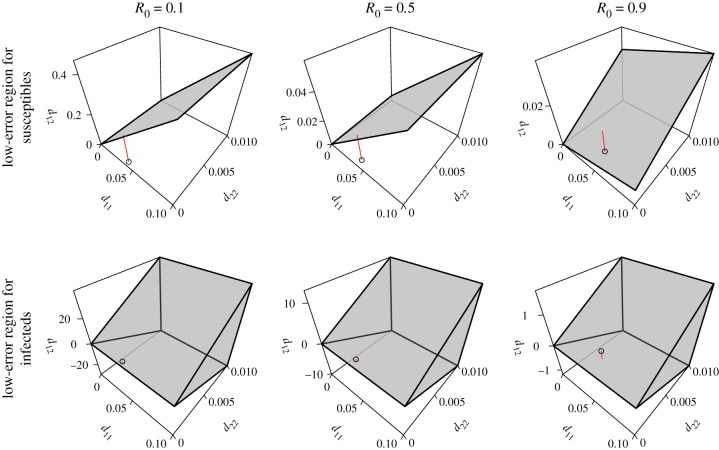
Figure 2.
In our SIR model for most R0 < 1, the set of noise parameters under which the distance to the epidemic threshold may be estimated is much larger for the number infected than for the number susceptible. Each panel plots as a prism, for a range of variances in white noise perturbations to the number of susceptible and infected (subscripts 1 and 2, respectively), the region containing the covariances for the perturbations that result in the autocorrelation of the model variable being within 0.1 of the reference that would result in a perfect distance estimate. The axis labels denote elements of the matrix D in equation (2.7). The points in each panel correspond to the intrinsic perturbations calculated by the linear noise approximation equation (2.9). The red line segments are drawn vertically from these points to the nearest boundary of the low-error region. The points in the panels for the infecteds fall within the low-error region. Parameters were as in table 1, with β set to 1.66, 8.31 and 14.9. (Online version in colour.)