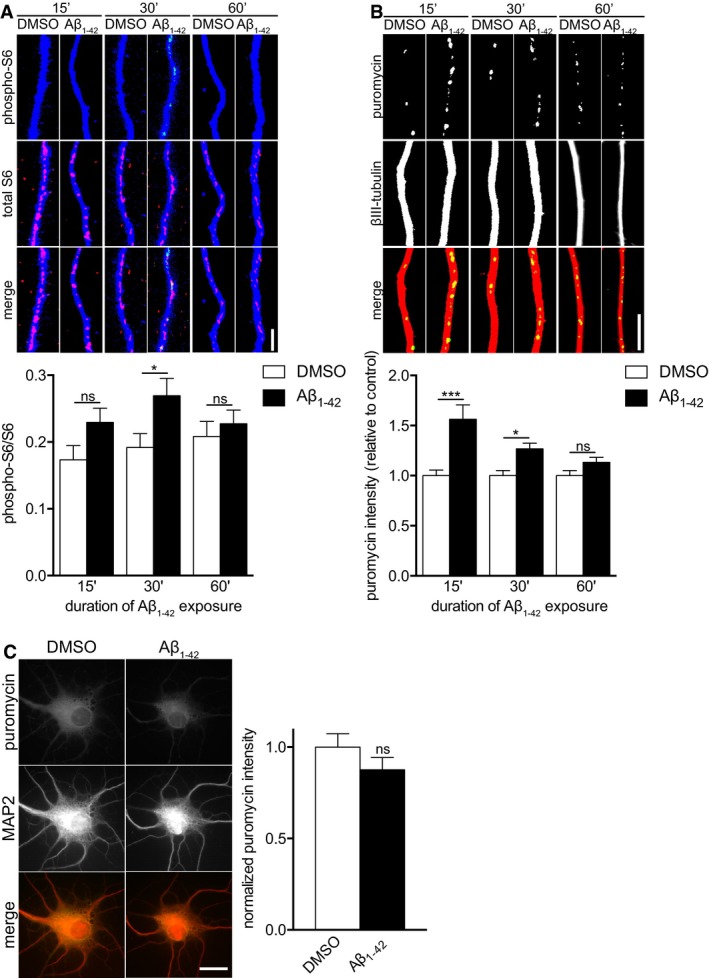
Hippocampal neurons were cultured in microfluidic chambers for 11–12 DIV, and axons were treated with vehicle or Aβ1–42 for 15, 30, or 60 min. Axons were immunostained for phospho‐S6, S6, and βIII‐tubulin. Mean ± SEM of 27–40 optical fields per condition (n = 6–8 independently performed experiments per group). *P < 0.05; ns, not significant; two‐way ANOVA with Bonferroni's multiple comparisons test.
Hippocampal neurons were cultured as in (A), and axons were treated vehicle or Aβ1–42 for 15, 30, or 60 min. During the 15‐min incubation or during the last 10 min prior to fixation for the 30 and 60 min time points, axons were treated with puromycin and then immunostained for puromycin and βIII‐tubulin. Mean ± SEM of 29–30 optical fields per condition (n = 6 independently performed experiments for 15 and 30 min, n = 3 independently performed experiments for 60 min). Aβ1–42 bars are normalized to their respective vehicle treatments. ***P < 0.001; *P < 0.05; ns, not significant; two‐way ANOVA with Bonferroni's multiple comparisons test.
Dissociated hippocampal neurons were cultured at a low density for 11–12 DIV and treated with vehicle or Aβ1–42 for 30 min. Ten minutes prior to fixation, puromycin was added. The neurons were immunostained for puromycin and MAP2. Mean ± SEM of 28–30 optical fields per condition (n = 6 independently performed experiments). ns, not significant; unpaired t‐test.
Data information: Scale bars, 5 μm.