Figure EV2. Aβ1–42 oligomers increase Ca2+ levels in distal neurites in an NMDA‐dependent manner.
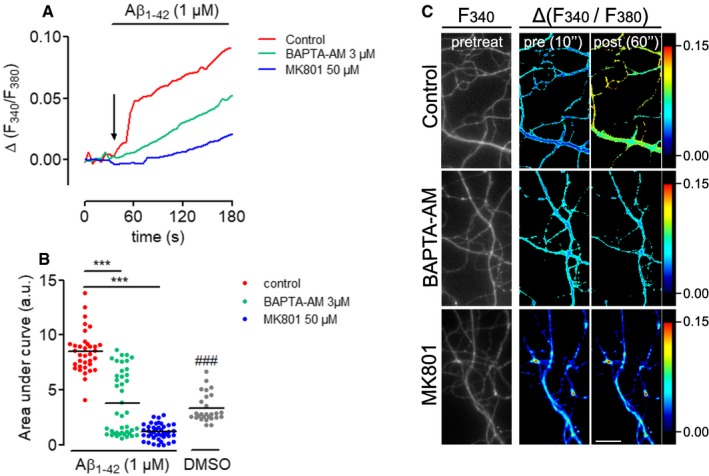
- Hippocampal neurons were grown at low density (5,000 cells cm−2) for > 10 DIV and loaded with Fura2‐AM. Ca2+ levels were measured before and during perfusion with Aβ1–42 oligomers in the presence or absence of the NMDA receptor antagonist MK801 and the Ca2+‐chelator BAPTA‐AM. Relative changes in Fura2‐AM fluorescence intensity were plotted as means of 35–42 neurites imaged in two independent experiments.
- Cumulative Ca2+ levels represented by the area under the curves in (A). Mean of 27–42 neurites imaged in two independent experiments. ***P < 0.001; one‐way ANOVA with Bonferroni's multiple comparisons test. ### P < 0.001, t‐test control Aβ1–42 vs. DMSO.
- Micrographs of representative axonal segments quantified in (A and B). Fura2‐AM levels before (two most left panels, grayscale and pseudocolor image) and after (right panel, pseudocolor image) Aβ1–42 perfusion at the indicated experimental conditions are shown. Scale bar, 25 μm.
