Figure 4. Transcription is partially required for Aβ1–42‐dependent axonal ATF4 synthesis.
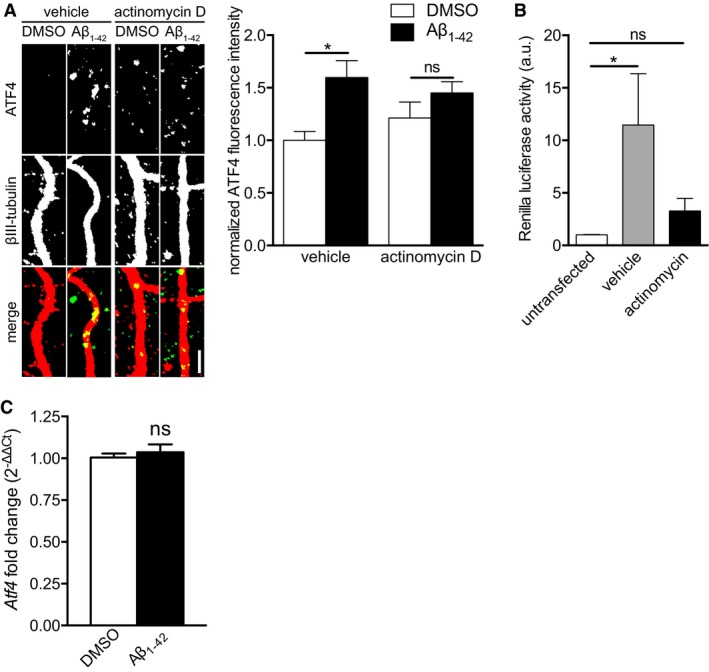
- Hippocampal neurons were cultured in microfluidic chambers for 11–12 DIV, cell bodies were treated with actinomycin D (40 μM), and axons were subsequently treated with vehicle and Aβ1–42 for 6 h. Axons were immunostained for ATF4 and βIII‐tubulin. Mean ± SEM of 39–40 optical fields per condition (n = 8 independently performed experiments per group). *P < 0.05; ns, not significant; Holm–Sidak multiple t‐tests. Scale bar, 5 μm.
- Hippocampal neurons were cultured in microfluidic chambers for 10–11 DIV. Cell bodies were transfected with Renilla luciferase plasmid. 24 h after transfection cell bodies were treated with actinomycin D (40 μM) for 6 h. Cell bodies were lysed, and luciferase activity was measured using a luciferase assay. Mean ± SEM of nine independently performed experiments (n = 9) each with duplicate luciferase measurement. *P < 0.05; ns, not significant; one‐way ANOVA with Bonferroni's multiple comparisons test.
- Hippocampal neurons were cultured in microfluidic chambers for 11–12 DIV, and axons were treated with Aβ1–42 for 1 h. Cell bodies were lysed, and RNA was purified. Atf4 transcript levels were measured by qRT–PCR. Levels were normalized to the RNA input. Mean ± SEM of six independently performed experiments (n = 6) each with triplicate qRT–PCR measurements. ns, not significant; unpaired t‐test.
