Figure 6. Aβ1–42‐dependent axonal Atf4 translation requires immediate axonal Vim translation.
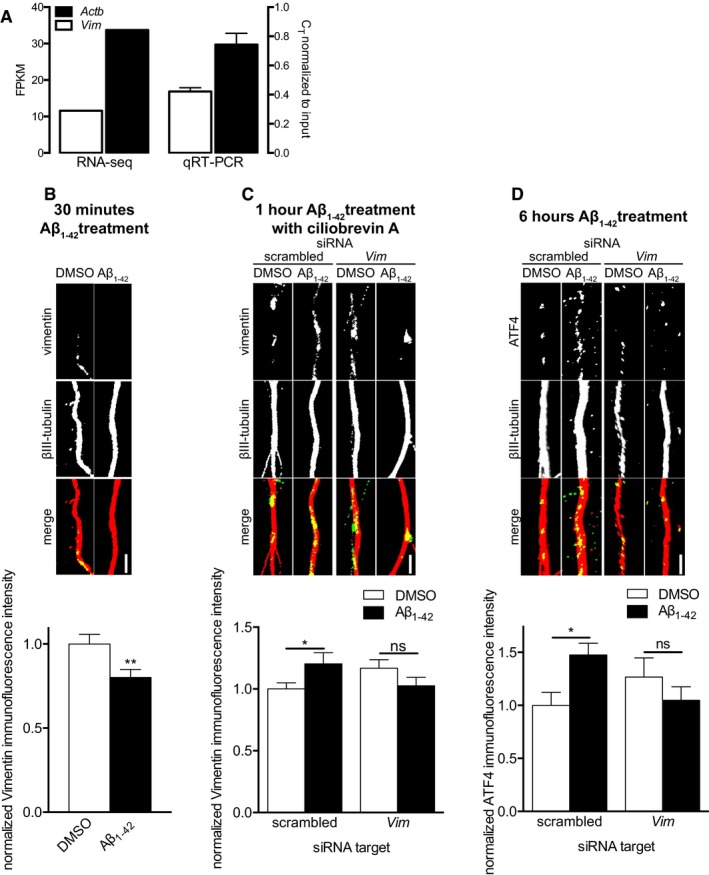
- Hippocampal neurons were grown in microfluidic chambers for 10–11 DIV, the RNA from the axonal compartment was harvested and mRNA levels for β‐actin (Actb) and vimentin (Vim) were determined by RNA‐Seq (left, data from Baleriola et al 7) and qRT–PCR (right). By both methods, vimentin transcripts are readily detectable at lower but comparable levels to β‐actin transcripts, one of the most abundant transcripts in axons. Mean ± SEM of three independently performed experiments (n = 3) each with triplicate qRT–PCR measurements.
- Hippocampal neurons were cultured in microfluidic chambers for 11–12 DIV, and axons were treated with vehicle or Aβ1–42 for 30 min. Axons were immunostained for vimentin and βIII‐tubulin. Mean ± SEM of 30 optical fields per condition (n = 6 independently performed experiments per group). **P < 0.01; unpaired t‐test.
- Hippocampal neurons were cultured in microfluidic chambers for 10–11 DIV, and axons were transfected with scrambled or Vim‐targeting siRNA. 24 h after transfection, axons were treated with ciliobrevin A for 45 min followed by vehicle or Aβ1–42 for 1 h. Axons were immunostained for vimentin and βIII‐tubulin. Mean ± SEM of 43–45 optical fields per condition (n = 9 independently performed experiments per group). *P < 0.05; ns, not significant; Holm–Sidak multiple t‐tests.
- Hippocampal neurons were cultured in microfluidic chambers for 10–11 DIV, and axons were transfected with scrambled or Vim‐targeting siRNA. 24 h after transfection, axons were treated with vehicle or Aβ1–42 for 6 h. Axons were immunostained for ATF4 and βIII‐tubulin. Mean ± SEM of 30–35 optical fields per condition (n = 6–7 independently performed experiments per group). *P < 0.05; ns, not significant; Holm–Sidak multiple t‐tests.
