Figure 9. Ens is involved in proper Dsh localization in epithelial cells.
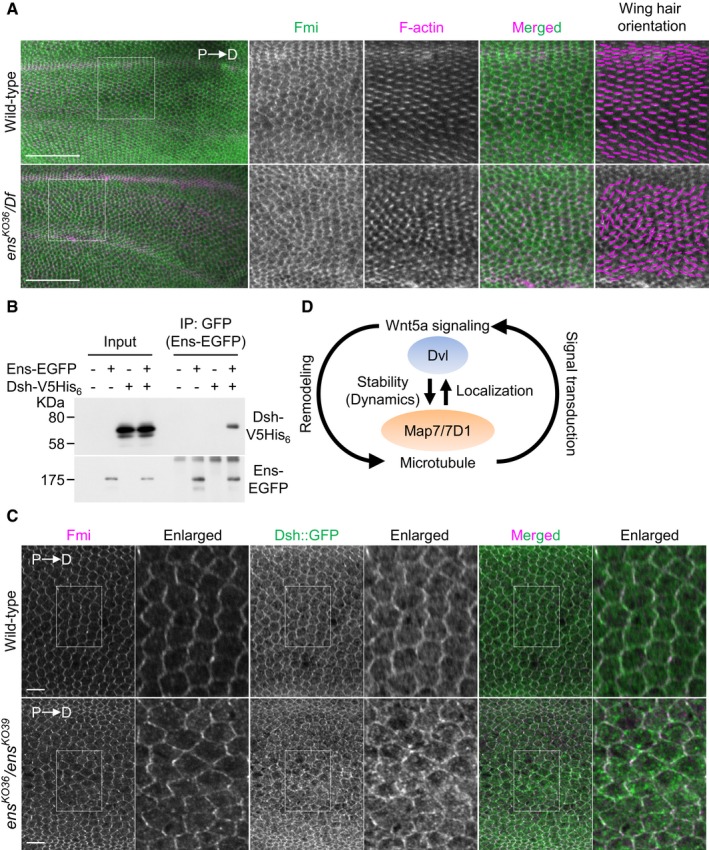
- Pupal wings of wild‐type or ens KO36 /Df(3L)BSC735 (ens KO36 /Df) mutants at 32–34 h APF (after puparium formation) were stained with an anti‐Fmi antibody and Phalloidin. P, proximal side; D, distal side. High magnification views of boxed area (intervein region between L3 and L4 veins) are shown at right. Magenta lines in right side panels indicate wing hair orientation. Because ens KO36 /Df mutants died before eclosion, we obtained their pupae by selecting third instar larvae, which were identified by the loss of GFP fluorescence from the balancer chromosome. Oregon‐R was used as wild type.
- Lysates from HeLa cells expressing Ens‐EGFP and Dsh‐V5His6 were immunoprecipitated with an anti‐V5 antibody, and the immunoprecipitates were probed with anti‐V5 and anti‐GFP antibodies.
- Localization of Dsh::GFP in 30 h APF pupal wing stained for Fmi, and GFP and F‐actin (shown in Fig EV2). The Dsh::GFP localization was analyzed in intervein region between L3 and L4 veins. We obtained ens KO36 /ens KO39 pupae by selecting third instar larvae, which were identified by the loss of mCherry fluorescence from the balancer chromosome. w; dsh::EGFP was used as wild type.
- Proposed model for a feedback loop between MT remodeling and Wnt5a signaling mediated by the Map7/7D1‐Dvl axis. See Discussion for details.
