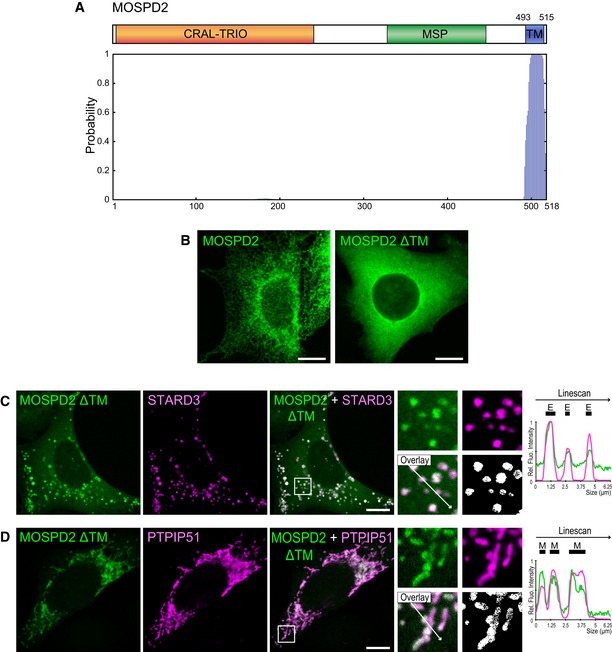
Figure EV1. MOSPD2 is a putative tail‐anchored protein.
-
ATop: Schematic representation of MOSPD2. Numbers indicate the positions of the first and the last residue of the putative transmembrane domain (blue box). Bottom: Determination of the number and position of transmembrane helices using TMHMM software 73. Vertical bars of the diagram represent the probability for a given amino acid to be included in a transmembrane helix. MOSPD2 is predicted to possess a single carboxyl‐terminus transmembrane helix.
-
BLocalization of GFP‐MOSPD2 (left, green) and GFP‐MOSPD2 ΔTM (right, green) expressed in HeLa cells. The GFP‐MOSPD2 ΔTM protein is lacking the last 26 amino acids of MOSPD2, which include the transmembrane domain. Scale bars: 10 μm.
-
C, DLocalization of GFP‐MOSPD2 ΔTM (green) and Flag‐STARD3 (C, magenta), or HA‐PTPIP51 (D, magenta), expressed in HeLa cells. The subpanels on the right are higher magnification (3.5×) images of the area outlined in white. The Overlay panel shows merged green and magenta images. The Coloc panel displays a colocalization mask on which pixels where the green and the magenta channels co‐localize are shown in white. Right: Linescan analyses with fluorescence intensities of the green and magenta channels along the white arrow shown on the subpanel Overlay. Black rectangles indicate the positions of late endosomes (E) and mitochondria (M). Scale bars: 10 μm.
