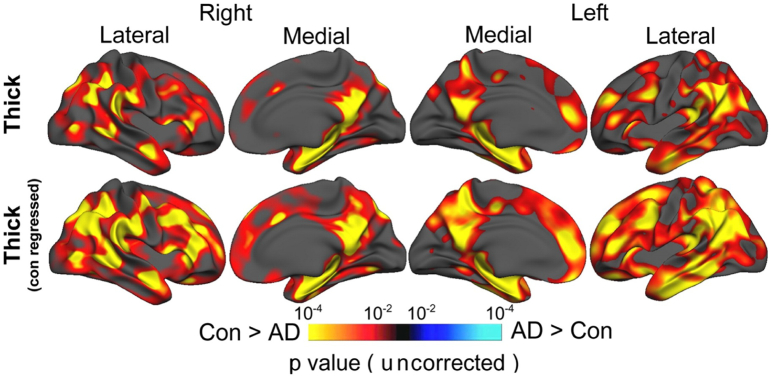
Fig. 3.
The effect of grey/white contrast on cortical thickness measurement using FreeSurfer. Statistical p maps thresholded at p < 10−2 superimposed on a template brain's semi-inflated surface showing the results from GLMs testing the difference between Alzheimer's disease (AD) and controls (Con). Warm colors denote areas with significantly thinner cortex in AD compared to controls. Adjusting for grey/white tissue contrast (bottom row) increases sensitivity to the AD-control differences in cortical thickness over large portions of the brain compared to results obtained when not adjusting for this contrast (top row).
Adopted with permission from Westlye et al. (2009).