Fig. 1.
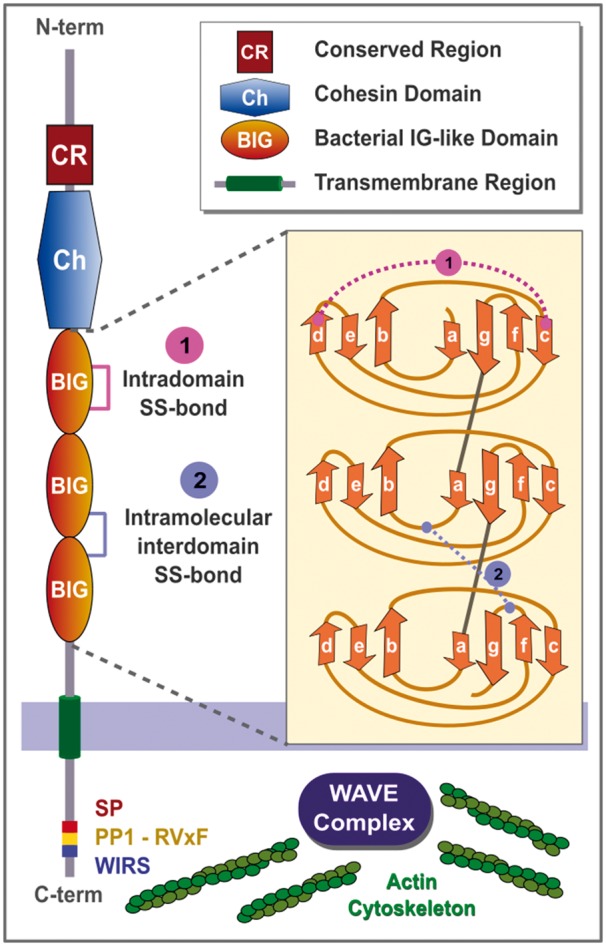
Domain architecture and common features in the TMEM132 family. Schematic representation of conserved domains present in TMEM132 family members: a conserved region (CR; shown in red; see Supplementary Fig. S6) precedes a cohesin domain (blue; see Supplementary Fig. S5), and three adjacent BIG domains (orange; Supplementary Figs S3 and S4). The predicted intradomain and interdomain disulphide bridges of these BIG domains are indicated in the right panel (magenta and violet lines, respectively). The seven beta-strands, forming part of the immunoglobulin-like core of BIG domains, are labelled a-g following an established convention (Bork et al., 1994) (Supplementary Fig. S7). Evolutionarily conserved TMEM132 intracellular motifs putatively related with the control of actin cytoskeletal dynamics are: a putative serine phosphorylation motif (SP), a phosphatase-1 (PP1) interaction motif (RVxF) (Hendrickx et al., 2009; Heroes et al., 2013), and a WIRS (WAVE regulatory complex interacting receptor sequence) cytoplasmic motif (Chen et al., 2014)
