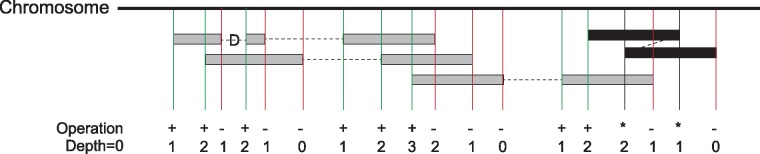
Fig. 1.
Mosdepth coverage calculation algorithm. An array the size of the current chromosome is allocated. As each alignment is read from a position-sorted BAM or CRAM file, the value at each start is incremented and the value at each stop is decremented. As illustrated by the alignment with a deletion (D) CIGAR operation, each alignment may have multiple starts and ends. If the leftmost read (the one seen first) of a paired-end alignment has an end that overlaps the position of its mate (which is given as a field in the BAM record) then it is stored in a hash-table until its mate is seen. At that time, the overlap between the mates is calculated, the regions of overlap are decremented and the item is removed from the hash. This prevents double counting coverage from two ends of the same paired-end DNA fragment (black alignment, ‘*’ operation means no coverage increment or decrement is made). Once all reads for a chromosome are consumed, the per-base coverage is simply the cumulative sum of the preceding positions