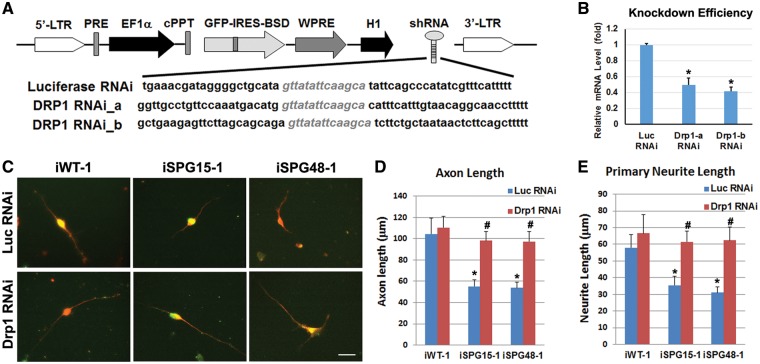
Figure 8.
Effect of Drp1 knockdown in rescuing axonal defects in SPG15 and SPG48 iPSC-derived telencephalic neurons. (A) Schematic map of pLVTHM containing shRNAs that target Drp1. (B) To assess knockdown efficiency, HEK293 cells were transiently transfected with vectors expressing luciferase shRNA or Drp1 shRNAs. qRT-PCR analysis showed a significant reduction of Drp1 mRNA by both Drp1 shRNAs. (C) After Infection of Drp1 or Luciferase (Luc) RNAi viruses (GFP+, green), Tau+ (red) axons in telencephalic neurons from control, SPG15 and SPG48 groups were visualized. Scale bar: 20 μm. (D, E) There was a significant decrease in axonal length (D) and primary neurite length (E) in SPG15 and SPG48 neurons as compared with control neurons, which could be rescued by knocking down Drp1. Data are presented as means ± SEM from at least 15 axon segments in three independent experiments. *P < 0.05 versus Luc RNAi or iWT-1 control, #P < 0.05 versus iSPG15-1 or iSPG48-1 Luc RNAi.