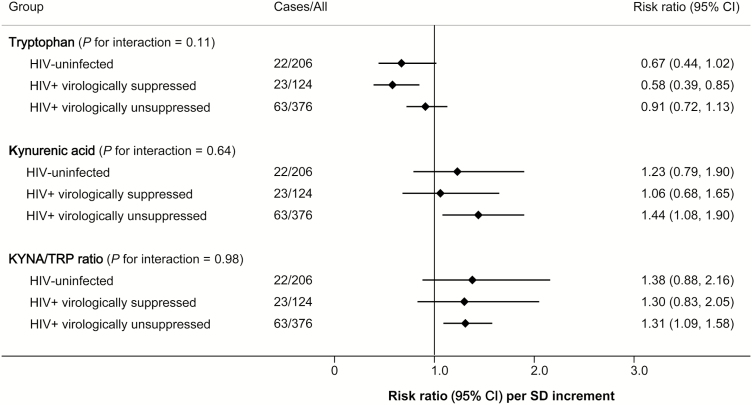
Figure 2.
Associations of plasma tryptophan, kynurenic acid, and kynurenic acid-to-tryptophan ratio with risk of carotid artery plaque in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)–uninfected, HIV+ persistently virologically suppressed, and HIV+ virologically unsuppressed participants. Data are risk ratio (95% confidence interval) on risk of carotid artery plaque per standard deviation increment in log-transformed metabolite variables, adjusted for age, sex, race/ethnicity, education, study site, current smoking, history of hepatitis C virus, systolic blood pressure, total cholesterol, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, antihypertensive medication use, lipid lowering medication use, and body mass index. HIV+ persistently virologically suppressed participants were defined as participants who had consistent plasma HIV RNA levels <80 copies/mL simultaneous with continuous antiretroviral therapy use over the study period. Abbreviations: CI, confidence interval; HIV, human immunodeficiency virus; KYNA/TRP, kynurenic acid-to-tryptophan; SD, standard deviation.