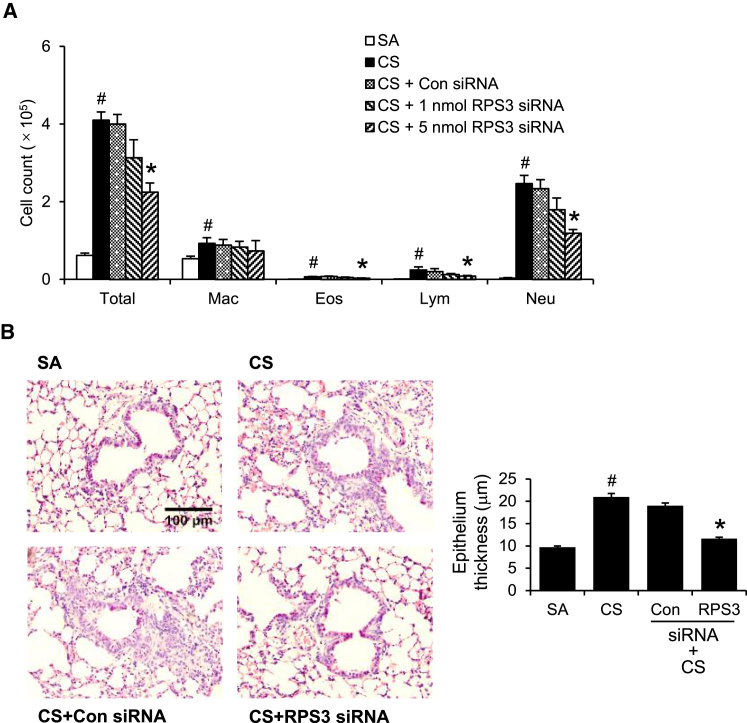
Figure 4.
Anti-inflammatory Effects of RPS3 siRNA in CS-Induced Acute Lung Injury In Vivo
(A) BAL fluid total and differential cell counts from CS-exposed (CS) mice with RPS3 siRNA (1 nmol and 5 nmol) or control siRNA (5 nmol) treatment (n = 9 mice per treatment group). SA, sham air exposed; Eos, eosinophil; Mac, macrophage; Neu, neutrophil; Lym, lymphocyte. (B) Representative H&E-stained lung sections at 200× magnification. Quantitative analysis of epithelium thickness was performed blinded (n = 4 mice per treatment group). Values are shown as means ± SEMs. *Significant difference from control siRNA, p < 0.05; #significant difference from the SA group, p < 0.05.