Abstract
Background
Phytophthora nicotianae Breda de Haan (Phytophthora parasitica Dastur) causes severe damage to citrus crops worldwide. A population of citrandarins was created from the cross between the susceptible parent Citrus sunki Hort. Ex Tan. and the resistant parent Poncirus trifoliata (L.) Raf. cv. Rubidoux, both parents and two reference rootstocks (Rangpur lime and Swingle citrumelo) were grafted in a greenhouse on Rangpur lime. Inoculations were performed at 10 cm and 15 cm above the grafting region and the resulting lesions were evaluated by measuring the lesion length 60 days after inoculation. As control, non-inoculated plants of each genotype were used. In addition, we evaluated the expression of 19 candidate genes involved in citrus defense response 48 h after pathogen infection by quantitative Real-Time PCR (qPCR). We mapped genomic regions of Quantitative Trait Loci (QTLs) and Expression Quantitative Trait Loci (eQTLs) associated with resistance to P. parasitica in the linkage groups (LGs) of the previously constructed maps of C. sunki and P. trifoliata.
Results
We found disease severity differences among the generated hybrids, with lesion lengths varying from 1.15 to 11.13 mm. The heritability of the character was 65%. These results indicate that there is a great possibility of success in the selection of resistant hybrids within this experiment. The analysis of gene expression profile demonstrated a great variation of responses regarding the activation of plant defense pathways, indicating that citrandarins have several defense strategies to control oomycete infection. The information of the phenotypic and gene expression data made possible to detect genomic regions associated with resistance. Three QTLs and 84 eQTLs were detected in the linkage map of P. trifoliata, while one QTL and 110 eQTLs were detected in C. sunki.
Conclusions
This is the first study to use eQTLs mapping in the Phytophthora-citrus interaction. Our results from the QTLs and eQTLs mapping allow us to conclude that the resistance of some citrandarins to the infection by P. parasitica is due to a favorable combination of QTLs and eQTLs transmitted by both parents.
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (10.1186/s12864-018-4888-2) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Keywords: Citrus sunki, Defense genes, Hybrids, Expression quantitative trait loci, Poncirus trifoliata
Background
Hybrids of microtangerines, such as the ones obtained from the cross of Sunki mandarin (Citrus sunki Hort. Ex Tan.) with trifoliate [Poncirus trifoliata (L.) Raf.], are called citrandarins. They are part of a new generation of rootstocks for citrus and combine the advantageous characteristics of mandarins, such as tolerance to Citrus blight and Citrus sudden death, with the qualities of trifoliates, which correspond to high resistance to Phytophthora, immunity to Citrus tristeza virus and resistance to citrus nematode, besides the great ability to form compact, productive plants with good fruit quality [1]. In a study on the Phytophthora-Citrus pathosystem, a F1 population from the crossing between C. sunki (susceptible parent) and P. trifoliata cv. Rubidoux (resistant parent) was obtained and evaluated for Phytophthora gummosis. Differences in the level of symptoms in both parents and progeny were observed [2].
Root rot, caused by Phytophthora, and gummosis and its various synonyms (foot rot, neck rot and trunk gum disease) are among the diseases that damage citrus crops. Citrus nurseries and orchards worldwide have been severely damaged by Phytophthora nicotianae Breda de Haan (Phytophthora parasitica Dastur) and Phytophthora citrophthora (Smith & Smith). In Brazil, P. parasitica is the most predominant species associated with the disease [3]. These pathogens can infect the main branches of the plants, inducing the formation of cankers with gum exudation of the lesions [3, 4]. Infected plants usually lose their vigor and may die prematurely [5].
P. parasitica is an oomycete, which belongs to the kingdom Stramenopila, comprising a diversified group of organisms [6]. During infection, oomycetes establish intimate relationships with their hosts through the formation of haustoria, structures used to obtain nutrients from plants, reprogramming the host defense metabolism. Species from the genus Phytophthora are hemibiotrophic pathogens, which means they initiate the infection as biotrophic agents in the first 36–48 h and colonize the host as necrotrophic pathogens, alternating the way of obtaining nutrients in order to guarantee its dissemination from necrotic plant tissues [7]. Gummosis is considered the most serious disease caused by Phytophthora spp. The lesions caused by the Phytophthora grow around the tree trunk damaging the cambium and inner bark killing it [8].
It is known that more than one mechanism of resistance and/or tolerance are involved in the citrus defense response to Phytophthora due to the large differences in types of affected tissues, and consequently to different citrus species’ responses to the infection. In general, responses that are common to all plant species affected by phytopathogens can be activated, such as hypersensitivity reaction (HR), the development of structural barriers and the production of antimicrobial compounds called phytoalexins. In addition, induction of specific responses to a given population of Phytophthora may occur, which are controlled by host resistance genes [9].
The great volume of information generated by genome sequencing projects has allowed a large-scale approach to differential gene expression analysis using techniques such as microarray, RNA Sequencing and qPCR (Real Time Quantitative PCR). Some information has already been produced to elucidate the molecular basis of the host response to Phytophthora gummosis disease [10, 11]. These studies have reported on changes in global gene expression profile and have shown differentially expressed genes involved in processes such as cellular defense and metabolism of carbohydrates, lipids and proteins. Defense genes are activated in response to pathogen infection by signal transduction mechanisms, which are regulated by phytohormones pathways, with salicylic acid (SA), jasmonic acid (JA), ethylene (ET) and abscisic acid (ABA) being the most common ones [12].
According to Pieterse et al. [13], the crosstalk that occurs between the SA, JA and ET pathways confers a directed defense response against different plant pathogens. There is a synergy between the JA and ET pathways, while there is a mutual repression between these two pathways with the SA pathway. In addition, it has been shown that ABA, which is known as the abiotic stress hormone in plants and is considered a negative regulator of resistance to phytopathogens, may be involved in increasing plant resistance to disease through its positive effect on callose deposition. ABA may also contribute to plant defense by the convergence of signaling with the JA pathway, which synergistically triggers the expression of defense genes responsive to both hormones [13, 14].
Genomics emerges as a technique that encompasses quantitative loci mapping and gene expression analysis to identify the association between the allelic status of a genome region and the quantification of gene transcripts [15]. These genomic regions are referred to as Expression Quantitative Trait Loci (eQTLs). The study of QTLs and eQTLs is of great importance for understanding pathogen-host interaction and to understand mechanisms of resistance and response to diseases.
In this study, we mapped the genomic regions associated with resistance to P. parasitica by means of phenotypic (QTLs) and expression (eQTLs) analyses in the linkage groups (LGs) of previously constructed maps of C. sunki and P. trifoliata. We evaluated the resistance of C. sunki x P. trifoliata hybrids to P. parasitica, as well as the expression of candidate genes related to resistance to P. parasitica by qPCR in the parents and hybrids used in the experiment.
Methods
Plant material and inoculation of P. parasitica
A population of 110 hybrids of C. sunki (susceptible to Phytophthora) x P. trifoliata (resistant) and parents was established in a greenhouse. Rangpur lime (Citrus limonia Osbeck) and Swingle citrumelo [Citrus paradisi Macfad. cv. Duncan x Poncirus trifoliata (L.) Raf.], two reference rootstocks in citrus cultivation, were also evaluated. Plants were multiplied by bud grafting using Rangpur lime as rootstock, and were kept in a greenhouse until the stem reached a diameter of approximately 0.8 to 1.0 cm.
The isolate IAC-01/95 from the isolates’ collection of the Plant Pathology Clinic of Sylvio Moreira Citrus Center, which was obtained from infected soil, was used in this assay. Mycelial disks of the pathogen growing in carrot-agar culture medium [16], containing 1 ml of Rifampicin, 1 ml of Ampicillin and 2 ml of Benomyl per 1000 ml of the medium, were removed from the colonies and transferred to Petri dishes containing 15 ml of this medium.
To activate the pathogenicity of the isolate, a re-isolation was performed from the lesion sections of tissue infected with the pathogen’s mycelium (pre-inoculation). Small portions of the lesions were taken and inoculated in Sicilian lemon fruits. These fruits were incubated at 25 °C with a photoperiod of 16 h for nine days. Then, they were carefully opened under brief asepsis inside a flow cabinet. With the disease affecting a large area of the fruit, the contaminated seeds were removed and transferred to Petri dishes containing the selective culture medium with carrot-agar. They were subsequently kept at 25 °C in the dark for six days, until the formation of the pathogenic mycelium.
The experimental design was a completely randomized assay with two replicates of each genotype and one plant per plot. Each hybrid was conducted with a single stem and inoculation was performed at 10 cm and 15 cm above the grafting region, totalizing two inoculations per genotype, as described by Siviero et al. [2]. This method consists of: disinfestation with alcohol of the surface of the trunk region to be inoculated; incision in the bark using a cork borer and removing a 5 mm diameter disc, thus exposing the cambium zone; introduction of a disk of equal diameter of virulent P. parasitica mycelium maintained in culture medium; placing back the same disc of the bark and protection of the wound site caused by inoculation with cotton and tape. As a control, and to remove the effect of the stress caused by the wound, only the incision itself was made in the bark of plants with a cork borer, without inoculation of the pathogen, in each genotype of the experimental population.
Evaluation of lesions and statistical analysis of phenotypic data
To evaluate the lesions, plants were maintained in an artificial lighting environment with a photoperiod of 16 h, a temperature of 25 °C and a relative humidity of 85%, with daily irrigations. The resulting lesions were evaluated 60 days after inoculation by measuring the length of the injured area after bark removal of the trunk with the aid of a digital caliper, totally exposing the developed lesion.
For the normality’s hypothesis of the data and for the statistical analysis, were used the average lengths of the lesions from inoculated individuals (LLI - Lesion length by inoculation) minus the average lengths obtained from control individuals (LLC – Lesion length in control), which were around 5 mm, due to the cork borer’s diameter used to cause injury to the plant, resulting in the variable RLL (Real lesion length) [LLI - LLC = RLL]. A QQ-plot for the distribution of lesion means was obtained using the Minitab 18 software (http://www.minitab.com/), based on the Kolmogorov-Smirnov normality test, with log (base 10)-transformed phenotypic data.
Statistical analyses were performed using the SASM-AGRI software [17], applying the F-test for analysis of variance and using the appropriate statistical model in a completely randomized design. In addition, the Scott-Knott test for comparison of treatments means was also used.
The averages of the phenotypic data from the RLL evaluation of the progeny of the crossing between P. trifoliata and C. sunki were used to calculate the genetic parameters (heritability, variance, and coefficient of variation) for the variable measured using the model 83 of the SELEGEN-REML/BLUP software [18].
Leaf collection, RNA extraction and cDNA synthesis
Leaf collection was performed 48 h after inoculation of the pathogen in the plants. Leaves were placed in liquid nitrogen and stored in a − 80 °C freezer until the extraction of RNA. The choice of collection time was based on previous time course studies that evaluated the systemic response of plants using the expression of genes involved in the Phytophthora-citrus interaction [11, 19] and associated with the signaling pathways of phytohormones that activate several defense mechanisms in the plant.
Total RNA extraction from plant material was performed according to the lithium chloride (LiCl) method described by Chang et al. [20]. To avoid contamination with genomic DNA, samples were treated with DNase I, RNase-Free kit (Fermentas Life Sciences), following the manufacturer’s recommendations. 300 mg of leaves from the same genotype were ground with liquid nitrogen and three tubes of the resulting macerate (100 mg each) were collected, totaling three biological replicates per genotype. Total RNA was then quantified in NanoDrop ND-8000 spectrophotometer (Thermo Scientific), and its integrity was evaluated with 1.2% denaturing agarose gel electrophoresis.
The cDNA was synthesized according to instructions from the Revertaid H Minus First Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit (Fermentas), using oligo (dT) primers, and then treated with RNAse H (1 U) to remove any RNA contamination. Subsequently, the obtained cDNA was diluted in RNAse-free water at the ratio of 1:50, with the three biological replicates of cDNA (50 μL each) being mixed. This formed a pool of samples represented in a single tube containing 150 μL of diluted cDNA from each genotype to be analyzed in gene expression and eQTL mapping assays.
qPCR for validation of gene expression
The expression of 19 candidate genes by qPCR (Additional file 1: Table S1), selected in previous studies with microarray and gene expression [10, 11], was evaluated in 51 hybrids, the two parents (C. sunki and P. trifoliata), Rangpur lime and Swingle citrumelo. The selection of hybrids for the qPCR assays was performed based in the application of the Scott-Knott test on the phenotypic data, which were separated into three groups (susceptible [S]; moderately susceptible [MS]; and tolerant and/or resistant [T/R]). Six hybrids were selected and formed the S group together with the two susceptible rootstocks (C. sunki and Rangpur lime). Three hybrids formed the MS group, and 42 hybrids together with the two resistant rootstocks (P. trifoliata and Swingle citrumelo) formed the T/R group. In general, we screened for genes related to cellular defense processes, which involve the main pathways of phytohormones such as SA, JA, ET and ABA. Moreover, some genes, such as LEA5 and RPS4, found differentially expressed by microarray among P. trifoliata, C. sunki and in some hybrids, in order to be a strong candidate in Phytophthora resistance [10], and other genes, such as PR2, PR3 and PAL, which were induced within 48 h after infestation in previous time course studies evaluating target genes related to the pathosystem formed by Phytophthora with two citrus species phenotypically opposed to the invader, corresponding to P. trifoliata (resistant) and C. sunki (susceptible) [11], were also evaluated. As endogenous controls, the FBOX (F-box family protein), SAND (SAND protein family) and GAPC2 (Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrigenase C2) genes were analyzed.
The oligonucleotides primers flanking the gene regions were synthesized using the Primer Express 2.0 software (Applied Biosystems), and checked for specificity by Primer-BLAST tool in the NCBI (National Center for Biotechnology Information) database. Their sequences were found in the literature, in studies evaluating qPCR experiments with Arabidopsis, tobacco, rice and in the CitEST database for citrus plants.
The amplifications by qPCR for the gene expression assays were performed using 7.5 μL of GoTaq qPCR Master Mix (Promega), 3 μL of cDNA (1:50 dilution), which was taken from the pool formed by the three replicates (150 μL each), 200 nM of each primer and water to complete a final volume of 15 μL, and carried out in a 7500 Fast Real Time PCR System (Applied Biosystems) with cycles of: 50 °C for 2 min; 95 °C for 10 min; 40 cycles of 95 °C for 15 s and 60 °C for 1 min. For each reaction, a dissociation curve was performed to verify possible non-specific contaminations and reactions. In addition, the reactions for each pair of primers were made in duplicates, always using control without cDNA to detect possible contaminations.
Normalization of qPCR data and gene expression analyses
Expression stability for each housekeeping gene was evaluated using the GenEx v. 6 (http://www.multid.se/) software, which provides the GeNorm algorithm to make paired comparisons between the endogenous genes, determining the best combination (two or more genes) to be used and calculating the average value of the Expression stability, called the M value (m-value) for each gene. The data that served as input for the calculation of the M value by the GeNorm algorithm were the relative quantities of each sample together with the efficiency of the primer, according to Mafra et al. [21].
For the detection of relative quantities, expression levels, fold change values and stability of endogenous genes, two treatments were considered in the study of the Phytophthora-citrus complex: plants inoculated with P. parasitica (infected group) and non-inoculated plants (control group). Calculations were made based on the number of amplification cycles required to reach a fixed threshold (cut-off cycle - Ct) in the exponential phase of PCR. The amplification efficiency and Ct data were calculated for each qPCR reaction by the Real-time PCR Miner software [22], which implements a normalizing algorithm to the raw fluorescence data according to the function of the PCR cycles. For each gene, an average efficiency of all PCRs was calculated. The mean of the Ct values of the two technical replicates of each genotype analyzed was also estimated (Additional file 2: Table S2). With these data, the relative quantification was calculated. It was determined by the 2-ΔΔCT method between the conditions of qPCR [23], which serves as parameter for the calculation of the expression levels of each sample. Hence, a methodology derived from this procedure was established, which does not consider the efficiency value (E) of the gene equal to 100%. Instead, the actual value of E was used in the calculations of the relative quantities (Q) of each sample by the formula Q = EΔC T.
Expression levels of each genotype were calculated by a normalization factor, given by the geometric mean of the estimated relative quantities for the two reference genes that had a smaller M value in the two treatments evaluated by the GeNorm algorithm. The calculation of expression levels in each sample was done by the ratio between the value of the relative quantity found in the target gene and the normalization factor of that genotype under analysis.
At last, the Fold change values of each inoculated individual were calculated in relation to the non-inoculated ones, by the ratio of the expression levels of the infected group on the control group. For statistical analysis, Fold change data were transformed into logarithmic scale (base 2), to meet the data normality using the Minitab 18 software (http://www.minitab.com/). An F-test (ANOVA: a criterion) was made to compare log2Fold change results for each gene between the three groups (S, MS and T/R). If the obtained p-value was significant, a post-hoc paired Student’s t-test was applied to compare the differences between the sample means of the three groups.
Gene expression profile
To obtain the gene expression profile of the experiment, by comparing the 19 candidate genes among the 51 hybrids, the two parents, Rangpur lime and Swingle citrumelo, Log2Fold change values served as input to the MeV (MultiExperiment Viewer) program v. 4.9 (http://sourceforge.net/projects/mev-tm4/). It was possible to group both the genes and the samples by the Hierarchical clustering (HCL), using the Pearson correlation as metric distance, which resulted in the gathering of genes with closer expressions and the separation of the genotypes in clusters. These parameters were visualized in a graphical representation called heatmap.
In addition, to better understand the relationship between the candidate genes, a dissimilarity matrix was obtained from the Euclidean Distance, so that this comparative analysis could also be demonstrated with a heatmap.
QTLs and eQTLs mapping
In the present study, we used pre-built linkage maps of C. sunki and P. trifoliata [24], that were constructed using DArT-seq™ molecular markers and the OneMap software [25]. The analyses were performed using the FullsibQTL package of the programming language R [26]. For the QTLs mapping, the means of the RLL phenotypic data in logarithmic transformation (base 10) in the segregating population of 110 hybrids were considered. For the eQTLs mapping, the Log2Fold change values calculated by the relative expression in the segregating population composed of 51 selected hybrids were used to map the eQTLs on the two parental linkage maps, as well as the phenotypic trait, thus detecting polymorphisms associated with gene expression. The strategy of composite interval mapping (CIM) [27] was used. A maximum of 20 cofactors were stipulated to locate QTLs and eQTLs outside the mapping range. The calculation of the critical LOD score to determine the presence of true QTL and eQTL was done by the random permutation test (α = 0.05; n = 1000 replicates) [28], available in FullsibQTL. The percentages of phenotypic variation (R2) explained by QTLs and eQTLs were also estimated.
Results
Evaluation of lesions caused by P. parasitica and phenotypic analyses
The means of lesions by inoculation of the 110 hybrids, C. sunki, P. trifoliata, Rangpur lime and Swingle citrumelo with P. parasitica are shown in Fig. 1.
Fig. 1.
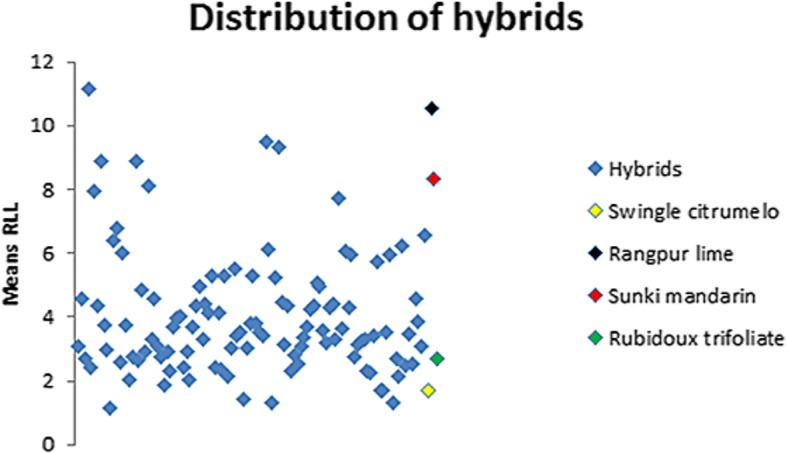
Means’ distribution of real lesion length (RLL) in the individuals of experiment
The RLL from the population composed by P. trifoliata, C. sunki, the 110 hybrids, Rangpur lime and Swingle citrumelo met the expectation of normal distribution data by the Kolmogorov-Smirnov (KS) normality test.
There were significant differences between the RLL means of the 114 genotypes (Additional file 3: Table S3). It can be stated that the genotypes Rangpur lime, Sunki mandarin, hybrids 8, 204, 209, 40, 13, 847, 11 and 244 are susceptible to P. parasitica, because they presented higher RLL values. Hybrids 30, 312, 27, 284, 205, 248, 33, 274, 250, 262 and 99 showed moderate susceptibility to the disease, with intermediate RLL values. On the other hand, the remaining 93 genotypes behaved as tolerant and/or resistant to Phytophthora, including P. trifoliata and Swingle citrumelo, because they presented smaller RLL values.
Broad-sense heritability coefficient was considered high (65%) for the RLL character (Table 1).
Table 1.
Estimates of genetic parameters for Real lesion length (RLL) character
| Estimatesa | RLL (mm) |
|---|---|
| Vg | 2.8 |
| Vr | 1.48 |
| Vp | 4.28 |
| H2 | 0.65 ± 0.15 |
| CVg% | 41.76 |
| CVr% | 30.35 |
| Overall mean | 4.0065 |
agenotipic variance (Vg); residual variance (Vr); phenotypic variance (Vp); broad-sense heritability coefficient (H2); coefficient of variation for genotypic variance (CVg%); coefficient of variation for residual variance (CVr%) and overall character mean
Gene expression and genotypic analyses
Three endogenous normalizing genes were analyzed and all of them presented high expression stability (Table 2), with M values varying from 0.16 for the best candidates to Normalizers (FBOX and SAND) at 0.21 (GAPC2), which had the highest m-value recorded. Therefore, the FBOX and SAND genes were selected as normalizing genes for the analyses of candidate genes, related to resistance to P. parasitica.
Table 2.
Normalizing genes evaluated by the GeNorm algorithm, with the values of mean Ct, standard deviation (SD) of Ct values and stability M value (m-value)
| Gene | Mean Cta | SDa | m-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| FBOX | 28.06 | 1.88 | 0.16 |
| SAND | 31.29 | 1.78 | 0.16 |
| GAPC2 | 24.18 | 2.10 | 0.21 |
aMean of Ct data and standard deviation of Ct data by qPCR reactions using duplicates of 55 samples related to two experimental treatments (inoculation and control)
The results of the relative gene expression in the population composed of P. trifoliata, C. sunki, 51 hybrids, Rangpur lime and the Swingle citrumelo satisfied the expectation of normal distribution. The p-value obtained by the KS test was bigger than 0.150 for 17 analyzed genes, which made the log2Fold change values highly significant (p ≥ 0.01 and p ≥ 0.05) and allowed the development of the following comparative analyses. Only the PR2 and PR4 genes had a smaller p-value (0.038 and 0.077, respectively).
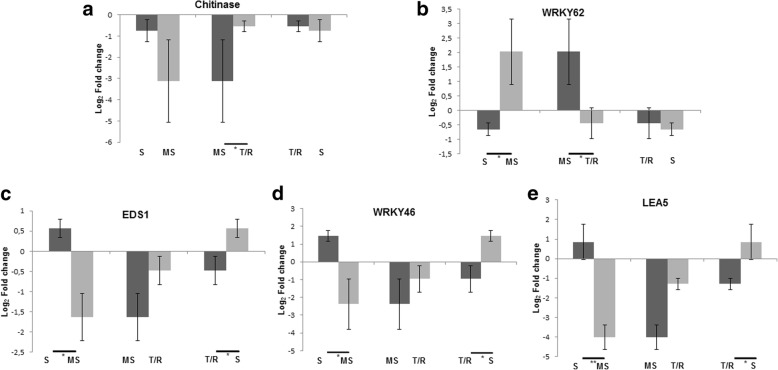
The F-test (ANOVA: a criterion) results for variance analysis using log2Fold change values from 19 target genes evaluated in the P. trifoliata, C. sunki, 51 hybrids, Rangpur lime and Swingle citrumelo revealed that only five genes (EDS1, WRKY46, WRKY62, Chitinase and LEA5) had significant different expression among the three groups (S, MS and T/R). The EDS1, WRKY46 and LEA5 genes had a smaller p-value (0.0079, 0.0073 and 0.0022, respectively), and were highly significant at 1% (p-value ≤0.01) compared to WRKY62 and Chitinase (0.0254 and 0.0495, respectively), with significant difference at 5% (p-value ≤0.05).
After the F-test, a paired Student’s t-test was applied to the five genes with statistically significant difference, comparing the sample means of the three groups in pairs (Fig. 2).
Fig. 2.
Paired Student’s t-test, showing the expression pattern per grouping in which there was a significant difference by F-test. S = susceptible; MS = moderately susceptible; T/R = tolerant and/or resistant. Five genes are shown: a = Chitinase, b = WRKY62, c = EDS1, d = WRKY46 and E = LEA5. The log2Fold change values are represented in relation to the non-inoculated control (log2Fold change = 0). *Difference (α = 0.05) between groups in pairs. **Difference (α = 0.01) between groups in pairs
The heatmap (Fig. 3), based on the comparative analysis performed by the Hierarchical clustering (HCL) of 19 target genes and the 55 selected genotypes (51 hybrids, their two parents, Rangpur lime and Swingle citrumelo), allowed the grouping of genes and related genotypes, using the Pearson correlation as metric distance to obtain the best intra and intervariable grouping possible. The genotypes were separated into five secondary clusters distributed in two main clusters, while the genes in three secondary clusters arranged in two main clusters. The color scale representing the log2Fold change values showed that the gene expression data ranged from − 8.29 to 5.53.
Fig. 3.
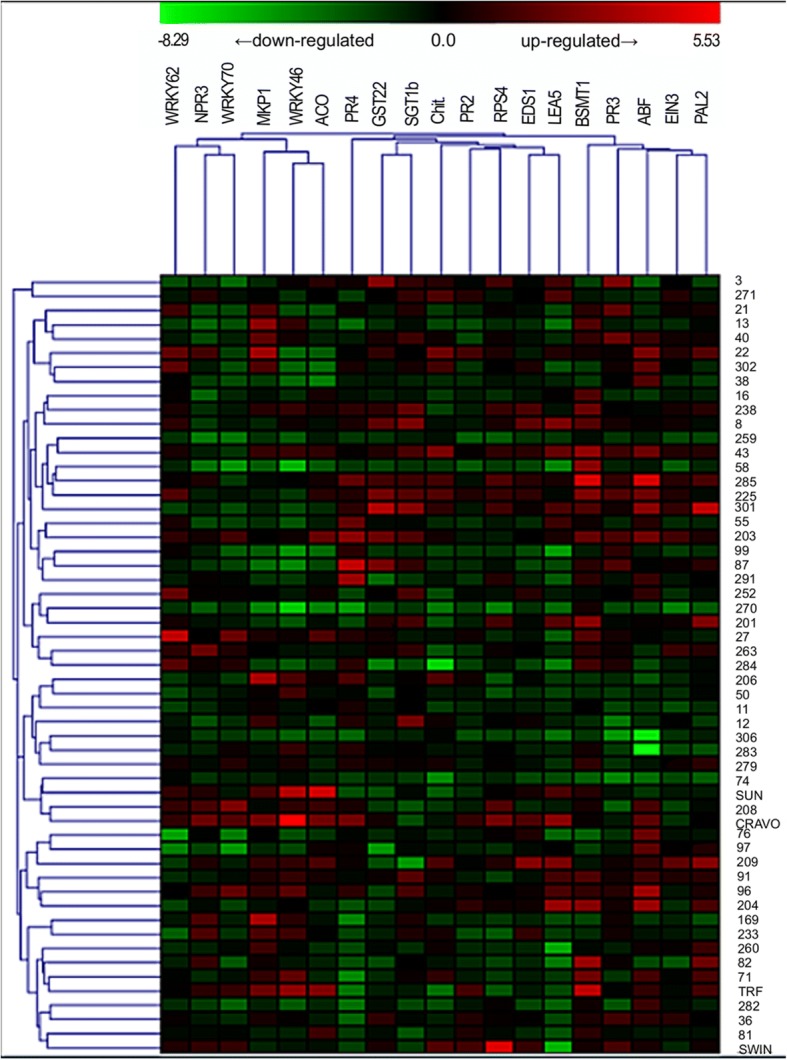
Heatmap of the gene expression profile by clustering analyses between 19 evaluated target genes with 55 selected genotypes (51 hybrids, Rubidoux trifoliate [TRF], Sunki mandarin [SUN], Rangpur lime [CRAVO] and Swingle citrumelo [SWIN]). The heatmap was made using Log2Fold change normalized data as input to the MeV (MultiExperiment Viewer) program v. 4.9 (http://sourceforge.net/projects/mev-tm4/). Names of genes and gene hierarchical cluster are shown in the top of the figure. Log2Fold change expression values representation ranges from red (highest expression) to green (lowest expression). Sample names (55 selected genotypes) are shown on the right side of the figure, while sample hierarchical cluster is shown on the left side
Another heatmap (Fig. 4) was constructed for a more accurate analysis of the relationship among the candidate genes, from a dissimilarity matrix, which uses as a metric distance the measure called Euclidean Distance, allowing to observe the difference degree among genes in a range of 0 to 1.
Fig. 4.
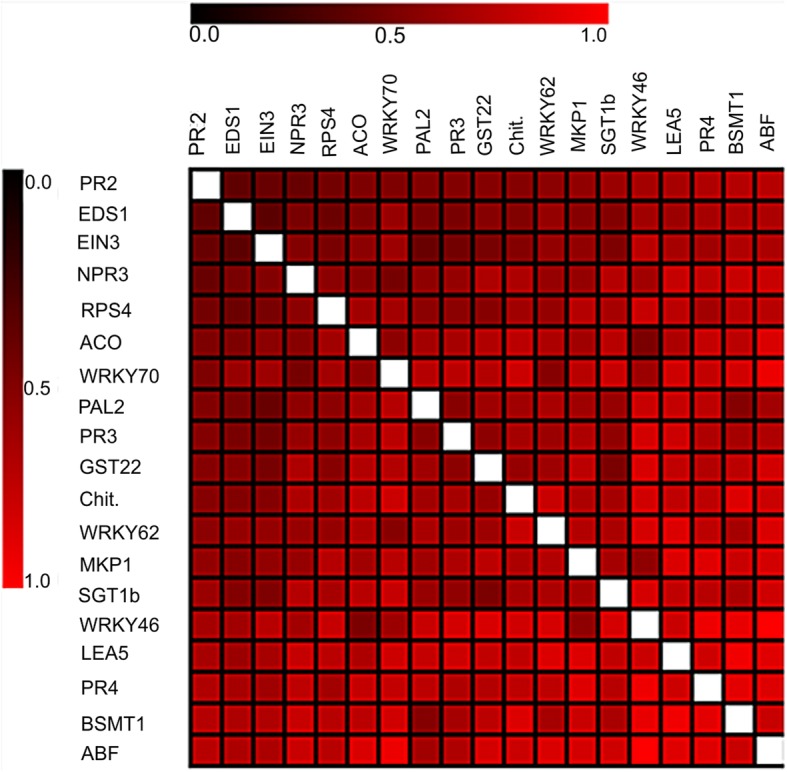
Heatmap representing the global dissimilarity matrix between 19 evaluated target genes from the paired comparison of genes using the Euclidean Distance. The heatmap was made using Log2Fold change normalized data as input to the MeV (MultiExperiment Viewer) program v. 4.9 (http://sourceforge.net/projects/mev-tm4/). Color shades in the dissimilarity matrix represent degree of similarity: dark red indicates high similarity, light red high dissimilarity
QTLs analysis and mapping
Using the two genetic maps previously constructed for each parent of the hybrids progeny [22] and according to RLL phenotypic data, it was possible to detect QTLs associated with the lesion length character caused by Phytophthora in citrus.
Based on the methodology of composite interval mapping (CIM), four QTLs were detected with LOD score higher than or equal to 3.0, three for the P. trifoliata (resistant parent) map and one for the C. sunki (susceptible parent) map (Figs. 5 and 6). In this model, only the additive effect was estimated, and the signal indicates the linkage phase between the marker and the QTL.
Fig. 5.
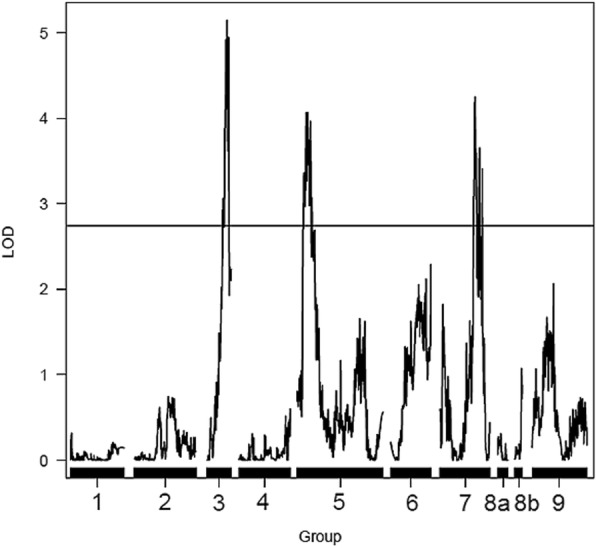
Detection of QTLs related with the resistance to Phytophthora parasitica in the Poncirus trifoliata linkage map. Y-axis: LOD; X-axis: distance in centiMorgans; LOD score = 2.74
Fig. 6.
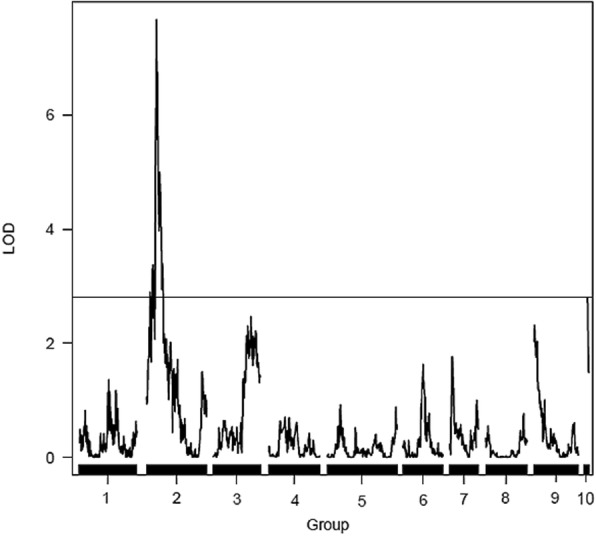
Detection of one QTL related with the resistance to Phytophthora parasitica in the Citrus sunki linkage map. Y-axis: LOD; X-axis: distance in centiMorgans; LOD score = 2.81
QTLs were found in LGs 3, 5 and 7 of the P. trifoliata map with 1:1 segregation due to the significant additive effect for this parent (Fig. 5). Regarding the QTLs analysis in the C. sunki linkage map, there was only one QTL located in LG 2 that showed 1:1 segregation ratio, also with significant additive effect for this parent (Fig. 6).
Table 3 shows the results of the QTLs mapping. “LOD scores” of the detected QTLs ranged from 4.06 to 7.67 while R2 values presented small to moderate effects, ranging from 1.77 to 16.8%.
Table 3.
Map, linkage group (LG), flanking markers, position of the QTL in centiMorgans (cM position), LOD score, proportion of phenotypic variation (R2) explained by QTL in % and additive effect by the QTLs mapping
| Map | LG | Flanking markers | cM position | LOD score | R2 (%) | Additive effect |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P. trifoliata | 3 | 100,025,033|F|0 | 109.81 | 5.14 | 1.77 | −0.03 |
| P. trifoliata | 5 | 100,029,470|F|0 | 58.51 | 4.06 | 6.3 | −0.05 |
| P. trifoliata | 7 | 100,087,520|F|0 | 190.66 | 4.25 | 7.41 | 0.05 |
| C. sunki | 2 | 100,088,096|F|0 | 61.74 | 7.67 | 16.8 | −0.08 |
eQTLs analysis and mapping
Using the two genetic maps previously constructed for the progeny of the citrandarins [22] and according to gene expression profile from relative expression values (log2Fold change) of 19 target genes evaluated with the 51 selected hybrids, it was possible to detect eQTLs in response to infection caused by P. parasitica. Only those with LOD score higher than or equal to 3.0, calculated by the random permutation test for each analyzed gene, with a confidence interval of 95%, were considered as consistent eQTLs. In this model, there is only one effect’s type (additive effect) and the signal indicates the linkage phase between the marker and the eQTL.
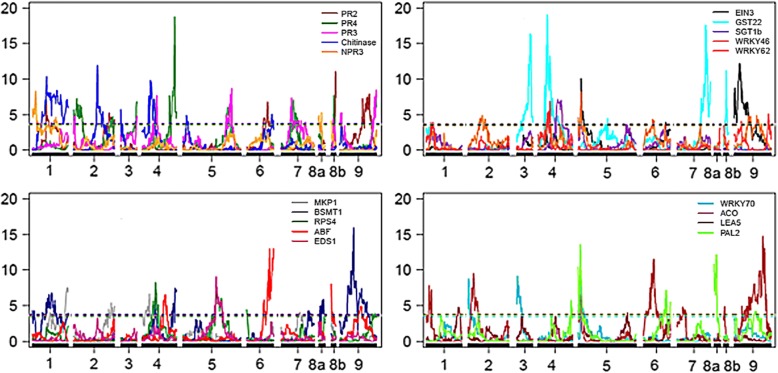
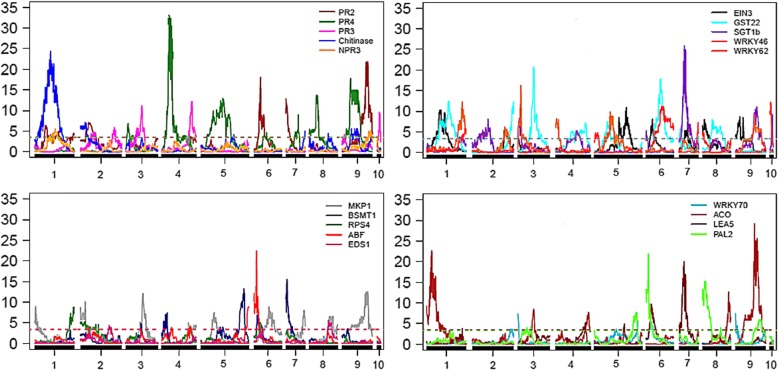
According to the methodology of composite interval mapping (CIM), 164 eQTLs with LOD ≥ 3.0 were detected for 19 evaluated genes: 84 of them for the P. trifoliata map, with mean of approximately four eQTLs per gene and 1:1 segregation due to the significant additive effect for this parent; and 110 for the C. sunki map, with mean of approximately six eQTLs per gene that showed 1:1 segregation, with significant additive effect for this parent. All target genes possessed at least one eQTL associated with their expression on both the Rubidoux trifoliate map and the Sunki mandarin map (Figs. 7, 8 and 9).
Fig. 7.
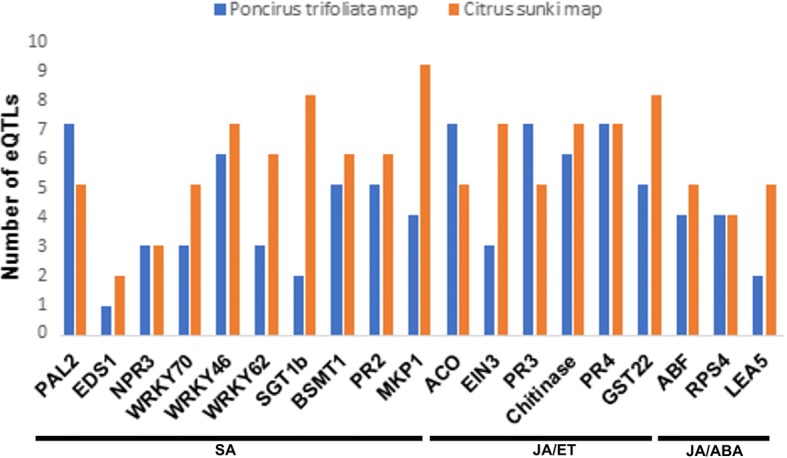
Distribution of the number of eQTLs detected for each candidate gene in relation to the Poncirus trifoliata and Citrus sunki maps
Fig. 8.
Detection of eQTLs in the Poncirus trifoliata map related to expression of 19 target genes. Y-axis: LOD; X-axis: distance in centiMorgans; LOD score = 3.0
Fig. 9.
Detection of eQTLs in the Citrus sunki map related to expression of 19 target genes. Y-axis: LOD; X-axis: distance in centiMorgans; LOD score = 3.0
In general, the calculated LOD scores were close to 3.0 for all evaluated genes in the two maps. The LOD scores of the eQTLs were consistent and ranged from 3.58 to 19.02 for the P. trifoliata map (Additional file 4: Table S4), while ranging from 3.39 to 33.13 for the C. sunki map (Additional file 5: Table S5).
Twenty three hotspots were identified on the Rubidoux trifoliate map, with mean of approximately two hotspots per LG, as well as 31 hotspots on the Sunki mandarin map, with approximately three hotspots per LG. Genes that had overlapping eQTLs localized in hotspots ranged from two to eight on genetic maps (Table 4). In addition, the interposition between an eQTL from the WRKY46 gene and a QTL in the same genomic position was found exactly on the marker 100,087,520|F|0 in the LG7 of the P. trifoliata map at 190.66 cM, indicating a complex network that regulates both gene expression and phenotype.
Table 4.
Relationship of genes that presented overlapping eQTLs located in hotspots for each linkage group (LG) in the two genetic maps built for each parent of the F1 progeny of citrandarins
| Poncirus trifoliata map | Citrus sunki map | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| LG | Genes | LG | Genes |
| 1 | PR2, Chitinase and PAL2 NPR3, WRKY62 and ACO MKP1 and LEA5 |
1 | PR4, SGT1b, WRKY46 and WRKY70 PR3-Chitinase-GST22-ACOa, MKP1, BSMT1-ABFa and PAL2 |
| 2 | PR2 and ABF | ||
| PR3, EIN3 and WRKY46 | |||
| Chitinase-MKP1-RPS4a GST22 and WRKY70 | |||
| 2 | PR4 and PR3 Chitinase, EIN3-SGT1b-WRKY46-WRKY70a, ACO-PAL2a and LEA5 RPS4-EDS1a and GST22 |
||
| 3 | Chitinase, EIN3 and LEA5 | ||
| MKP1-GST22a BSMT1, WRKY70 and PAL2 | |||
| 3 | PR2 and MKP1 PR4, PR3 and WRKY70 |
||
| 4 | PR2 and BSMT1-GST22a | ||
| Chitinase, MKP1 and WRKY62 SGT1b, WRKY46 and LEA5 | |||
| 4 | PR2 e ACO PR4-PR3a, RPS4 and WRKY62 ABF, WRKY46 and PAL2 |
||
| 5 | PR2, EIN3 and PAL2 | 5 | PR2-MKP1a and PAL2 |
| Chitinase and ABF | PR4 and BSMT1 PR3 and EIN3 SGT1b and WRKY46-ACOa |
||
| WRKY46 and ACO | |||
| 6 | NPR3, BSMT1 and PAL2 | ||
| 7 | PR4 and PR3 BSMT1 and GST22a |
||
| 6 | PR2 and EIN3 | ||
| NPR3 and GST22 RPS4 and WRKY62 SGT1b, WRKY46-LEA5a and ACO | |||
| 8a | PR4 and BSMT1-PAL2a | ||
| PR3, RPS4 and WRKY62 | |||
| Chitinase, MKP1 and GST22 | |||
| 7 | PR2-RPS4-EIN3a | ||
| PR4, MKP1 and GST22 BSMT1, ABF-PAL2a and SGT1b WRKY70 and LEA5 | |||
| 8b | PR2, PR4-GST22a, PR3, NPR3, ABF and ACO | ||
| 9 | PR4, PR3 and GST22 Chitinase and ACO |
8 | PR4 and GST22 |
| Chitinase-EDS1a | |||
| MKP1 and ACO | |||
| EIN3, WRKY62 and PAL2 | |||
| 9 | PR2, MKP1, RPS4, ABF and GST22-LEA5a PR4 and BSMT1 |
||
| 10 | PR3, NPR3, SGT1b and WRKY62 | ||
aGenes that presented located eQTLs exactly in the same position in centiMorgans
Discussion
The RLL means of the hybrids ranged from 1.15 to 11.13 mm, which is in accordance with previous study carried out by Siviero et al. [2], that worked with the same population, using as inoculum a 3 mm disc (cork borer) of oomycete mycelium. The parents represented the extreme points in lesion lengths, with about 15.10 mm for C. sunki, and 2.30 mm for P. trifoliata. The lesion length values for the F1 individuals ranged from 5.8 to 12.2 mm (discounting 3 mm from the mean values obtained) [2]. In our study, the parents had very contrasting results for the lesion developed by the infection with P. parasitica, with P. trifoliata (Rubidoux trifoliate) reaching 2.71 mm and C. sunki (Sunki mandarin), 8.36 mm (Fig. 1). According to the literature, Sunki mandarin is susceptible to Phytophthora, while trifoliate behaves as resistant rootstock [29, 30]. The lesion in the Rangpur lime reached 10.52 mm, surpassing the Sunki mandarin, in order to be classified as susceptible; and in the Swingle citrumelo, the RLL mean was 1.72 mm, reaching values smaller than P. trifoliata. Swingle citrumelo rootstock is known as being tolerant for trunk and root infections [31].
The results also indicated that hybrids from the crosses between Sunki mandarin and Rubidoux trifoliate present great genetic variability, being few (17%) susceptible or moderately susceptible to Phytophthora (Additional file 3: Table S3).
The value of broad-sense heritability coefficient in Table 1 indicates that 65% of the phenotypic variation is due to the action of genes, demonstrating good genetic control and great chance of success in the selection of individuals within the experiment. This result disagrees with Siviero [32], which found a low value of heritability (18.7%) when evaluating the lesion caused by inoculation of P. parasitica.
Considering gene expression results, the M values of endogenous normalizing genes are in accordance with the literature [33] and with the GeNorm manual, because they are below the limit of 1.5 (Table 2). Thus, FBOX and SAND genes were classified as the most uniform by both the SD and the GeNorm algorithm, surpassing the GAPC2 housekeeping gene, which is commonly used for the normalization of gene expression assays by qPCR in plants [34, 35].
Three expression patterns were found after the F-test and paired Student’s t-test (Fig. 2). In the first one, there was a significant difference within the MS and T/R groups for the Chitinase gene (Fig. 2a). The expression of Chitinase was down-regulated in these two groups, but there was a higher repression in the MS group. According to Punja & Zhang [36], there are different classes of plant chitinases from molecular, biochemical and physicochemical criteria, that are constitutively expressed at high levels in the plant in response to several abiotic and biotic factors. In addition, the same author stated that the level of protection is variable in transgenic plants that express cloned genes of chitinases in response to a fungal pathogen.
In the second pattern, significant differences for the WRKY62 gene were found when comparing log2Fold change means between S and MS, as well as MS and T/R (Fig. 2b). In relation to the combination S and MS, this gene was found induced in most genotypes belonging to the MS group, predominantly evidencing the existence of S hybrids that repressed the WRKY62 gene. This may show a small participation of this gene in the defense response to P. parasitica, considering that genotypes with intermediate lesion lengths express it more than others with larger lesion length. On the other hand, the results with the combination MS and T/R indicate that tolerant and/or resistant hybrids of C. sunki x P. trifoliata don’t response to P. parasitica infection with WRKY62 gene, since the mean is down-regulated for this group and consequently smaller than the mean of the MS group, which was up-regulated. Previous studies state that the transcription factor WRKY62 has a different performance in comparison to other members of the WRKY family, negatively regulating the SA-mediated response and positively regulating a typical PTI (PAMP-triggered immunity) response, by interacting with an also negative regulator of the SA downstream pathway called HDA19 (histone deacetylase 19) [37, 38].
In addition to the second pattern of expression, a third one was detected, in which there were significant differences for three genes (EDS1, WRKY46 and LEA5) when comparing the log2Fold change means between S and MS, as well as T/R and S (Figs. 2c, d and e). The genes were induced in most genotypes belonging to the S group, evidencing the predominant existence of MS and T/R hybrids that repressed the EDS1, WRKY46 and LEA5 genes.
Perhaps resistant citrandarins activate other defense mechanisms, such as the production of ROS (Reactive Oxygen Species) and phytoalexins that are enough to contain the advance of P. parasitica. In the literature, it is described that resistance to pathogenic fungi belonging to the genus Verticillium, which attack the tomato crop, involves a more basal and nonspecific response, with resistant plants producing depositions (callose, among others) on cell walls and synthesizing antimicrobial agents, including phytoalexins [39]. In addition, previous studies using the microarray technique and qPCR to evaluate differential gene expression in susceptible and resistant tomato varieties to the isolates of Verticillium dahliae, identified genes induced to this pathosystem, such as those coding for PR proteins; and found a larger induction, as well as a larger number of genes differentially expressed in susceptible plants to the pathogen. Thus, these results indicate that the increase of systemic gene expression in susceptible plants does not protect them, and that this exaggerated and inductive reaction may trigger the symptoms of the disease [40–42]. In fact, according to Dalio et al. [43], in the susceptible plant (C. sunki), P. parasitica deploys effectors, such as elicitins, NPP1 (Necrosis-inducing Phytophthora protein 1), CBEL (Cellulose-binding elicitor and lectin activity), RxLR and CRN (Crinkler), whereas the host responds by activating the main defense signaling pathways, resulting in hypersensitive response and necrosis. Despite its strength, this defense response fails to withstand P. parasitica invasion, confirming its hemibiotrophic life style. In P. trifoliata, the effectors were strongly expressed, nevertheless failing to induce any immunity manipulation and disease development, suggesting a non-host resistance type, in which the plant relies on preformed biochemical and anatomical barriers. The LEA5 gene, in addition to play an important role in resistance to abiotic stresses, may also be related in defense responses to pathogen infection, being responsive to increased levels of JA and ABA [44]. The transcription factor WRKY46, as well as WRKY70, acts as a positive regulator of the SA signaling pathway [45]. At last, the EDS1 gene acts on the SA upstream pathway, and consequently in its biosynthesis from an ETI (effector-triggered immunity) [46, 47].
In the cluster analysis of the first heatmap (Fig. 3), there was a higher variation in log2Fold change values within the sampled individuals than in the genes. The BSMT1 and SGT1b genes were predominantly up regulated. These genes are part of the SA metabolism [47] and may therefore have a greater participation in the resistance of this population to P. parasitica. On the other hand, most hybrids and four analyzed rootstocks were down-regulated for the EIN3 gene (Fig. 3), an important regulator of the ET downstream pathway [48], indicating that it may not interfere in the defense response of the different phenotypes to P. parasitica.
In relation to the genotypes, it was found that the Sunki mandarin and Rangpur lime rootstocks, described in the literature as susceptible to Phytophthora, were close (same cluster), showing a similar gene expression profile. A similar event occurred for the Rubidoux trifoliate and the Swingle citrumelo, which are resistant to the oomycete. In addition, hybrids 43, 203, 225 and 285, belonging to the T/R group and to the same cluster in the heatmap, had the highest expression of the 19 evaluated target genes, strongly inducing genes like BSMT1 and ABF. Thus, they are promising materials for understanding the resistance to P. parasitica and can be selected for future research related to citrus gummosis disease (Fig. 3). On the other hand, tolerant and/or resistant hybrids, such as 270, 283 and 306 (the last two are in the same cluster) predominantly repressed the candidate genes, suggesting that they probably develop other defense mechanisms against infection caused by P. parasitica. For hybrids belonging to the S and MS groups, inferences can also be made for the genotypes 11 and 99, for example, since they presented most of the genes down-regulated, evidencing that they have low resistance to P. parasitica. At the same time, many susceptible hybrids (8, 204, 209, 40, 13, 27 and 284) sometimes suppressed some genes, or induced other genes, being grouped in different clusters, what contributes to the idea that different defense mechanisms associated with plant resistance can be established against infestation of P. parasitica.
The comparison of the congruence pattern of the gene expression is presented in Fig. 4. The Euclidean Distance is widely used as a parameter to investigate how much an object differs from the other, being efficient to evaluate the intravariable divergence [49]. The darker the color, the more intense the interaction between two genes, demonstrating a larger congruence between expressions. Therefore, smaller distance was observed between the PR2 and EDS1 genes, which are part of SA signaling pathway. EDS1 acts on the biosynthesis of this phytohormone and PR2 consists of a responsive defense gene to SA accumulation. PR2 encodes the β-1,3-glucanase protein with anti-oomycetes properties, because it constitutes an enzyme that degrades the cell wall of these organisms that is composed of β-glucans [37]. However, the less intense the color, the more distant the genes will be, which denotes a smaller congruence of the expressions between genes. It was found that three genes (BSMT1, PR4 and ABF) in comparison with WRKY46 obtained the largest distances. It is known that WRKY46 is a transcription factor belonging to the large WRKY family, and acts as a positive regulator of the SA downstream pathway. The BSMT1 gene is known to be part of SA metabolism, converting this phytohormone into MeSA (Methyl Salicylate), and has functions as a defense signal for the expression of JA-dependent defense genes. The PR4 gene encodes a chitinase (PR protein) that is activated by the JA pathway in the ERF branch, contributing to the synergy between the JA/ET pathways. The ABF gene is essential in downstream regulation of the ABA pathway, inducing the expression of many responsive defense genes to this gaseous hormone [45, 50, 51]. Hence, there is a smaller relationship between their expressions when evaluating the specific resistance response to Phytophthora.
Regarding the QTL mapping in both linkage maps (Figs. 5 and 6), Siviero et al. [2] in their study of QTLs mapping for evaluation of resistance to Phytophthora in hybrids of C. sunki x P. trifoliata, using maps previously constructed by Cristofani-Yaly et al. [52], also found three QTLs for the Rubidoux trifoliate parent. In addition, Siviero et al. [2] also detected only one QTL for Sunki mandarin.
According to Anderson et al. [53], many studies with mapping reveal QTLs in a few loci with moderate R2 values (10 to 20%), while there are several other loci with small effects (R2 smaller than 10%), which is similar to those found in the present study. QTLs identified in LGs 3, 5 and 7 on the P. trifoliata map explain 1.77; 6.3 and 7.41% of the phenotypic variation, respectively. The QTL for C. sunki parent, located in LG 2, was responsible for most of the phenotypic variation of the RLL values, explaining 16.8% of it (Table 3). Thus, this suggests that Sunki mandarin has greater contribution in transmitting alleles for gummosis response to the progeny. Some studies with QTLs mapping in other plants reported about resistance alleles located in the susceptible parent, as well as susceptibility alleles in the resistant one [54, 55]. In addition, Siviero et al. [2] also detected a QTL with moderate effect, which explained 18% of the phenotypic variation.
The high value found for heritability (65%) shows that the genetic nature presents a predominant role in the phenotype manifestation, a fact that was not shown in previous studies, in which heritability values found for the character were low, reaching less than 20%, as in the study of Siviero et al. [2].
The detection of several QTLs associated with resistance to Phytophthora and the variation of RLL phenotypic data of the hybrids in response to inoculation with P. parasitica are indicative that the lesion length character is complex, being controlled by polygenes, as mentioned in the literature [30, 31]. This study of Phytophthora-citrus pathosystem demonstrates a great possibility of success in the selection of resistant hybrids within the experiment, an important scenario in a breeding program. The QTLs location and the understanding of their genetic effects contribute to the detection and selection of possible candidate genes responsible for the variation of the studied phenotype [56].
According to Shi et al. [57], a high detection power of eQTLs can be found even in small populations (population size below or close to 50). In addition, as the methodology established by the software for QTLs mapping is similar to eQTLs mapping, a population size larger than 50 is sufficient to provide high resolution to the activity of mapping and detecting QTLs/eQTLs of small effect. The larger the population size, the saturation of the genetic map and the heritability of the phenotypic character, the larger the genomic information related to the mapping [58–60]. As a high heritability (65%) for the RLL character was found in the present study, a high saturation of the two maps of each parent and the population of selected hybrids for the eQTLs mapping being equal to 51, a large volume of eQTLs from the differential gene expression profiles for each candidate gene analyzed via RT-qPCR was found.
PR4, PR3, ACO and PAL2 genes presented the highest number of eQTLs on the P. trifoliata map, each one with six of them, while on the C. sunki map there was a larger number for the MKP1 gene, totalizing nine eQTLs (Fig. 7). The PR4, Chitinase and PR3 genes, which are responsive to the JA/ET pathways, encode a class of enzymes called chitinases, which degrade cell wall [61]. They detained a larger number of chromosomal regions that affect their transcription levels in response to infection caused by P. parasitica on both the Rubidoux trifoliate map and the Sunki mandarin map. On the other hand, a smaller number (only one eQTL) for the EDS1 gene was found, which is below the mean of eQTLs per gene in both maps. One of the main regulators of the SA upstream pathway, EDS1 acts to promote SA biosynthesis due to effector-triggered immunity (ETI) [47]. This gene may not have much participation in the defense response of the interaction Phytophthora-citrus, a fact explained by its expression pattern and by smaller quantity of genomic regions in the two contrasting parents, responsible for the variation of its gene expression in the segregating progeny.
Regarding the phenotypic variation (R2) values explained by the eQTLs, both on the maps of the Rubidoux trifoliate and the Sunki mandarin (Additional file 4: Table S4 and Additional file 5: Table S5), R2 values reached up to 11.54% for the P. trifoliata map; and up to 24.97% for the C. sunki map. Equivalent to the phenotypic variation values explained by QTLs in mapping studies [53], many eQTLs in the present study are composed of loci with small effects (R2 less than 10%), while few are formed by chromosome regions with moderate effects (10 to 20%).
Studies with eQTLs allow the identification of chromosomal regions that affect the expression of multiple genes (hotspots). Such phenomenon can be seen by a series of overlapping eQTLs on the LGs of genetic maps, and its consequence can be attributed to genome regions rich in closely linked genes, by identifying nearby eQTLs; or to a single genomic region regulating the transcription levels of many genes, from the detection of distant eQTLs. Nonetheless, it is reported in the literature that many hotspots control the expression of enzyme-coding genes involved in various metabolic pathways, and some hotspots may even regulate the pathway as a whole [62–65].
It could be verified that there was an intense overlap of eQTLs from the quantification of the 19 gene transcripts (Table 4), independent of the signaling pathway involved, as observed in Figs. 8 and 9. Thus, the interposition between eQTLs does not seem to follow the relationship between the genes, including eQTLs from the transcripts associated with different signaling pathways of phytohormone, which were overlapping exactly at the same position or in the proximal regions of hotspots, both on the P. trifoliata map and on the C. sunk map.
Co-regulated genes in plants have been extensively identified in genetic analyses by eQTLs mapping, with the concept that different transcription levels from distinct genes may be under control of the same loci regulators. In addition, this type of methodology allows the detection of other regulatory networks, from the co-location between QTLs and eQTLs, identifying associations between the allelic state of a genomic region with the quantification of gene transcripts within QTLs involved in the variation of complex agronomic traits. The overlap of QTLs and eQTLs may corroborate to a strong association between gene transcript levels and phenotypic data [66–68]. The WRKY46 gene is a transcription factor of the WRKY family and its activation is involved in plant responses against phytopathogen infection [37, 45]. It has a gene expression pattern and co-location of QTL and eQTL in P. trifoliata map that suggest a larger participation in the interaction of P. parasitica with hybrids of C. sunki x P. trifoliata.
Kirst et al. [69], using the pseudo-testcross strategy to map eQTLs on two parental genetic maps in hybrids of eucalyptus, suggested that different genotypes of the progeny have distinct regulatory loci in the parents, which may explain the genetic differences in the gene expression. In the present study, the susceptible parent Sunki mandarin seemed to have a greater contribution in the transmission of alleles to the progeny, since it was detected in comparison with the map of the trifoliate Rubidoux: a single QTL of moderate effect; higher number of eQTLs; and greater number of hotspots and consequently greater overlap. However, it is worth mentioning that there was an expressive identification of QTLs, eQTLs and hotspots in the Rubidoux trifoliate map, suggesting that there is an interaction between the two parents to confer a favorable combination of QTLs/eQTLs to be transmitted to citrandarins in response to infection of the causal agent of citrus gummosis disease.
According to Dalio et al. [43], that studied the contrasting interactions of Sunki mandarin (susceptible) and trifoliata Rubidoux (resistant) in Phytophthora, they noticed that SA, JA and ET pathways seem to be activated in susceptible rootstock upon infection. The plant responds by strongly activating several genes related to all three main defense signaling pathways (SA, JA and ET). This major transcriptional shift results in HR. Nonetheless, this is not efficient to kill or stop pathogen colonization. Since P. parasitica has a hemibiotrophic life style, it might benefit from cell death and release of nutrients. On the other hand, trifoliata Rubidoux, even in contact with several P. parasitica effectors, does not activate SA, JA or ET pathways.
In our work, in relation to inoculation, the bark was removed as according to Boava et al. [11]. These authors reported the induction of defense-related genes in P. trifoliata plants and smaller lesion induced by the pathogen, when compared to C. sunki. We also observe this fact, but we observed in general that the eQTLs for C. sunki had higher values of phenotypic variations (R2) than those observed for P. trifoliata.
As argued by Dalio et al. [43], inoculation method by wounding used in our work might favor a first establishment of the pathogen and a concomitant defense response of the plant in P. trifoliata, which impairs further development of the pathogen. But we also observed defense response in Sunki and it was not enough to contain the infection. So it seems to us that the genes studied here are not the main ones involved in resistance. It appears that P. trifoliata and citrandarins presents other defense mechanisms that may be related to structural and chemical barriers as well as hypothesized by Dalio et al. [43].
Conclusions
We have identified citrandarins that are promising genotypes for future research related to gummosis disease. The heritability for the lesion length character caused by P. parasitica is considered high, demonstrating that genetics exerts larger influence than the environment. From our genetic maps constructed for both parents of the segregating progeny, QTLs that act in the process of expression of the lesion length character related to the inheritance of the citrus gummosis have been identified. The performance of both parents is of extreme importance for the transmission of a favorable combination of QTLs to their hybrids.
This is the first study of functional genomics involving eQTLs mapping in the Phytophthora-citrus interaction. Genomic regions in the maps of both parents that act on the gene expression process for the lesion length character associated with citrus gummosis disease were mapped, identifying a series of overlapping eQTLs and consistent hotspots related to the 19 target genes. In addition, our results indicated the formation of a complex regulatory network of both gene expression and phenotype, by the co-location of a QTL with an eQTL in the same marker on the P. trifoliata map. As for our QTL mapping, the eQTLs mapping revealed that the susceptible parent Sunki mandarin seemed to have a greater contribution in transmitting alleles to the progeny. The mutual action of both parents is indispensable for the transmission of a favorable combination of eQTLs to citrandarins, which confer defense against P. parasitica.
Future prospects can be made as to the exact location of the 19 target genes among the genetic markers distributed on both parental maps, which allows the distinction of the various eQTLs detected in the present study. These can be categorized as cis-eQTLs (eQTLs close to the gene), explaining the variation of gene expression in the chromosomal region in which the gene is found; or trans-eQTLs (eQTLs distant from the gene), representing an effect of genetic polymorphisms that are located in other regions of the genome. This procedure brings larger genomic information to eQTLs mapping, and may contribute to advances in the area, since studies with eQTLs using the qPCR technique in plants are scarce in the literature.
Additional files
Selected genes for RT-qPCR assays. (XLSX 11 kb)
Gene expression data with mean Ct and SD for 19 candidate genes. (XLS 2436 kb)
Real lesion length (RLL) caused from the inoculation with P. parasitica in the individuals of the experiment. (XLSX 12 kb)
Gene, linkage group (LG), flanking markers, position of the eQTL in centiMorgans (cM position), LOD score, proportion of phenotypic variation (R2) explained by eQTL in % and additive effect by the eQTLs mapping in the Poncirus trifoliata map. (XLSX 16 kb)
Gene, linkage group (LG), flanking markers, position of the eQTL in centiMorgans (cM position), LOD score, proportion of phenotypic variation (R2) explained by eQTL in % and additive effect by the eQTLs mapping in the Citrus sunki map. (XLSX 18 kb)
Acknowledgments
MAM and MCY are recipients of research fellowships from the Conselho Nacional de Pesquisa de Desenvolvimento (CNPq) and also provided a scholarship to RPML.
Funding
The present study was conducted with the financial support of the Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (FAPESP) (Process n° 2011/18605–0) and the Instituto Nacional de Ciência e Tecnologia (INCT) de Genômica para Melhoramento de Citros (Processes: CNPq 465440/2014–2 and Fapesp 2014/50880–0). The funds provided by the research funding agencies were used to conduct all the molecular and phenotypical analysis performed and in writing the manuscript. RPML received a scholarship from the Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq) (Process n° 830834/1999–0).
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article [and its supplementary information files].
Abbreviations
- ABA
Abscisic acid
- CitEST
Citrus Expressed Sequence Tags
- eQTL
Expression Quantitative Trait Loci
- ET
Ethylene
- HR
Hypersensitivity reaction
- JA
Jasmonic acid
- JA/ABA
Jasmonic acid and/or Abscisic acid
- JA/ET
Jasmonic acid and/or Ethylene
- LG
linkage group
- LLC
Lesion length in control
- LLI
Lesion length by inoculation
- MS
Moderately susceptible
- QTL
Quantitative Trait Loci
- RLL
Real lesion length
- RNA-Seq
RNA Sequencing
- ROS
Reactive Oxygen Species
- RT-qPCR
Real Time quantitative PCR
- S
Susceptible
- S/MS
Susceptible and/or Moderately susceptible
- SA
Salicylic acid
- T/R
Tolerant and/or Resistant
Authors’ contributions
MCY and MAM planned and supervised the study. RPML and MCY contributed to the design and execution of the project. RPML and MCY carried out plant growth and inoculation. RPML, MC and MCY performed out the evaluation of the lesions and QTL mapping analysis. RPML participated in extraction of plant RNA, in cDNA synthesis and validation of genes by RT-qPCR. RPML performed gene expression analysis. RPML and MC performed eQTL mapping analysis. RPML, MCY and MVM drafted the manuscript. MVM and MAM revised the manuscript critically and provided intellectual input. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The hybrid plants of Sunki Mandarin (female parent) and Poncirus trifoliata (pollen donor) belong to the Citrus Germplasm Bank of Centro de Citricultura Sylvio Moreira of Instituto Agronômico (CCSM–IAC), Cordeirópolis, SP, Brazil.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Footnotes
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (10.1186/s12864-018-4888-2) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Contributor Information
Rômulo P. M. Lima, Email: rpm_lima@hotmail.com
Maiara Curtolo, Email: maiaramc@hotmail.com.
Marcus V. Merfa, Email: mvm0010@tigermail.auburn.edu
Mariângela Cristofani-Yaly, Email: mariangela@ccsm.br.
Marcos A. Machado, Email: marcos@ccsm.br
References
- 1.Blumer S, Pompeu Junior J. Avaliação de citrandarins e outros híbridos de trifoliata como porta-enxertos para citros em São Paulo. Rev Bras Frutic. 2005;27:264–267. doi: 10.1590/S0100-29452005000200019. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Siviero A, Cristofani-Yaly M, Furtado EL, Garcia AAF, Coelho ASG, Machado MA. Identification of QTLs associated with citrus resistance to Phytophthora gummosis. J Appl Genet. 2006;47:23–38. doi: 10.1007/BF03194595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Medina Filho HP, Bordignon R, Siqueira WJ, Feichtenberger E, Carvalho MRT, Sobrinho JT. Resistência de híbridos e de clones de porta-enxertos de citros à infecção de raízes por Phytophthora nicotianae. Fitopatol Bras. 2004;29:169–178. doi: 10.1590/S0100-41582004000200008. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Alvarez LA, Gramaje D, Abad-Campos P, García-Jiménez J. Seasonal susceptibility of citrus scions to Phytophthora citrophthora and P. nicotianae and the influence of environmental and host-linked factors on infection development. Eur J Plant Pathol. 2009;124:621-635
- 5.Queiroz BPV, Melo JS. Antagonism of Serratia marcescens towards Phytophthora parasitica and its effects in promoting the growth of citrus. Braz J Microbiol. 2006;37:448–450. doi: 10.1590/S1517-83822006000400008. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Alexopoulos CJ, Mims CW, Blackwell M. Phylum Oomycota: in introductory mycology. 4. New York: John Wiley & Sons; 1996. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Glazebrook J. Contrasting mechanisms of defense against biotrophic and necrotrophic pathogens. Annu Rev Phytopathol. 2005;43:205–227. doi: 10.1146/annurev.phyto.43.040204.135923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Graham JH, Feichtenberger E. Citrus Phytophthora diseases: management challenges and successes. Journal of Citrus Pathology. 2015;2:1–11. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Hammerschmidt R. Phytoalexins: what have we learned after 60 years? Annu Rev Phytopathol. 1999;37:285–306. doi: 10.1146/annurev.phyto.37.1.285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Boava LP, Cristofani-Yaly M, Mafra VS, Kubo K, Kishi LT, Takita MA, Ribeiro-Alves M, Machado MA. Global gene expression of Poncirus trifoliata, Citrus sunki and their hybrids under infection of Phytophthora parasitica. BMC Genomics. 2011;12:39. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-12-39. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Boava LP, Cristofani-Yaly M, Stuart RM, Machado MA. Expression of defense-related genes in response to mechanical wounding and Phytophthora parasitica infection in Poncirus trifoliata and Citrus sunki. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol. 2011;76:119–125. doi: 10.1016/j.pmpp.2011.07.004. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Fernandes CF, Vieira Júnior JR, Silva DSG, Reis ND, Antúnes Júnior H. Mecanismos de defesa de plantas contra o ataque de agentes fitopatogênicos. 1. Porto Velho: Embrapa Rondônia; 2009. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Pieterse CM, Leon-Reyes A, Van Der Ent S, Van Wees SC. Networking by small-molecules hormones in plant immunity. Nat Chem Biol. 2009;5:308–316. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Mauch-Mani B, Mauch F. The role of abscisic acid in plant-pathogen interactions. Current Opinion Plant Biology. 2005;8:409–414. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2005.05.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Jansen RC, NAP JP. Genetical genomics: the added value from segregation. Trends Genet. 2001;17:388–391. doi: 10.1016/S0168-9525(01)02310-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Kaosiri T, Zentmyer GA, Erwin DC. Stalk length as a taxonomic criterion for Phytophthora palmivora isolates from cacao. Can J Bot. 1978;56:1730–1738. doi: 10.1139/b78-205. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Canteri MG, Althaus RA, Virgens Filho JS, Giglioti EA, Godoy CV. SASM-AGRI: Sistema para análise e separação de médias em experimentos agrícolas pelos métodos Scott-Knott, Tukey e Duncan. Revista Brasileira de Agrocomputação. 2001;1:18–24. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Resende MDV. Software SELEGEN–REML/BLUP. 1. Curitiba: Embrapa Florestas; 2002. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Teixeira JEC. PHD Thesis Universidade federal de Lavras. 2005. Genes de defesa de Citrus sunki e Poncirus trifoliata: expressão constitutiva e induzida por Phytophthora parasítica. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Chang S, Puryear J, Cairney J. A simple and efficient method for isolating RNA from pine trees. Plant Mol Biol Report. 1993;11:113–116. doi: 10.1007/BF02670468. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Mafra V, Kubo KS, Alves-Ferreira M, Ribeiro-Alves M, Stuart RM, Boava LP, Rodrigues CM, Machado MA. Reference genes for accurate transcript normalization in citrus genotypes under different experimental conditions. PLoS One. 2012;7:1–11. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0031263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Zhao S, Fernald RD. Comprehensive algorithm for quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction. J Comput Biol. 2005;12:1047–1064. doi: 10.1089/cmb.2005.12.1047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-∆∆Ct method. Methods. 2001;25:402–408. doi: 10.1006/meth.2001.1262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Curtolo M, Soratto T, Gazaffi R, Takita M, Machado MA, Cristofani-Yaly M. High-density linkage maps for Citrus sunki and Poncirus trifoliata using DArTseq markers. Tree Genet Genomes. 2018;14:5–10. doi: 10.1007/s11295-017-1218-9. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Margarido GRA, Souza AP, Garcia AAF. Onemap: software for genetic mapping in outcrossing species. Hereditas. 2007;144:78–79. doi: 10.1111/j.2007.0018-0661.02000.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Gazaffi R, Margarido GRA, Pastina MM, Mollinari M, Garcia AAF. A model for quantitative trait loci mapping linkage phase and segregation pattern estimation for a full-sib progeny. Tree Genetics & Genomics. 2014;10:791–801. doi: 10.1007/s11295-013-0664-2. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Zeng ZB. Precision mapping of quantitative trait loci. Genetics. 1994;136:1457–1468. doi: 10.1093/genetics/136.4.1457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Churchill GA, Dodge RW. Empirical threshold values for quantitative values for quantitative trait mapping. Genetics. 1994;138:963–971. doi: 10.1093/genetics/138.3.963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Boava LP, Cristofani-Yaly M, Furtado EL, Siviero A, Machado MA. XXXVII Congresso Brasileiro de Fitopatologia Maringá: Fitopatologia Brasileira. 2004. Mapeamento e estabilidade de QTLs ligados à resistência dos citros a gomose causada por Phytophthora parasitica; p. 279. [Google Scholar]
- 30.Siviero A, Furtado EL, Boava LP, Barbasso DV, Machado MA. Avaliação de métodos de inoculação de Phytophthora parasitica em plântulas e plantas jovens de citros. Fitopatol Bras. 2002;27:1–7. doi: 10.1590/S0100-41582002000600003. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Medina Filho HP, Bordignon R, Siqueira WJ, Feichtenberger E, Carvalho MRT, Sobrinho JT. Resistência de clones e híbridos de porta-enxertos de citros à gomose de tronco causada por Phytophthora parasitica. Fitopatol Bras. 2003;28:534–540. doi: 10.1590/S0100-41582003000500011. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Siviero A. PHD Thesis Universidade Estadual “Júlio de Mesquita Filho”. 2001. Avaliação de métodos de inoculação de Phytophthora parasitica e mapeamento de QTLs de resistência em híbridos de Citrus sunki x Poncirus trifoliata à gomose. [Google Scholar]
- 33.Lilly ST, Drummond RS, Pearson MN, MacDiarmid RM. Identification and validation of reference genes for normalization of transcripts from virus-infected Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact. 2011;24:294–304. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-10-10-0236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Lobo AMBO, RNB L. Considerações estatísticas na análise de expressão gênica gerados pela técnica de RT-qPCR. 1. Sobral: Embrapa Caprinos e Ovinos; 2014. [Google Scholar]
- 35.He Y, Yan H, Hua W, Huang Y, Wang Z. Selection and validation of reference genes for quantitative real time PCR in Gentiana macrophylla. Front Plant Sci. 2016;7:1–13. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2016.00945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Punja ZK, Zhang YY. Plant chitinases and their roles in resistance to fungal diseases. J Nematol. 1993;25:526–540. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Vlot AC, Dempsey DA, Klessiq DF. Salicylic acid a multifaceted hormone to combat disease. Annu Rev Phytopathol. 2009;47:177–206. doi: 10.1146/annurev.phyto.050908.135202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Kim KC, Lai Z, Fan B, Chen Z. Arabidopsis WRKY38 and WRKY62 transcription factors interact with histone deacetylase 19 in basal defense. Plant Cell. 2008;20:2357–2371. doi: 10.1105/tpc.107.055566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Fradin EF, Thomma B. Physiology and molecular aspects of Verticillium wilt diseases caused by V-dahliae and V-albo-atrum. Mol Plant Pathol. 2006;7:71–86. doi: 10.1111/j.1364-3703.2006.00323.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Robb J, Lee B, Nazar RN. Gene suppression in a tolerant tomato-vascular pathogen interaction. Planta. 2007;226:299–309. doi: 10.1007/s00425-007-0482-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Van Esse HP, Fradin EF, de Groot PJ, de Wit PJ, Thomma BP. Tomato transcriptional responses to a foliar and a vascular fungal pathogen are distinct. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact. 2009;22:245–258. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-22-3-0245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Robb J, Shittu H, Soman KV, Kurosky A, Nazar RN. Arsenal of elevated defense proteins fails to protect tomato against Verticillium dahliae. Planta. 2012;236:623–633. doi: 10.1007/s00425-012-1637-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Dalio RJD, Maximo HJ, Oliveira TS, Azevedo TM, Felizatti HL, Campos MA, Machado MA. Molecular basis of Citrus sunki susceptibility and Poncirus trifoliata resistance upon Phytophthora parasitica attack. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact. 2018;31:386–398. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-05-17-0112-FI. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Amara I, Zaidi I, Masmoudi K, Ludevid MD, Pages M, Goday A, Brini F. Insights into late embryogenesis abundant (LEA) proteins in plants: from structure to the functions. Am J Plant Sci. 2014;5:3440–3445. doi: 10.4236/ajps.2014.522360. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Hu Y, Dong Q, Yu D. Arabidopsis WRKY46 coordinates with WRKY70 and WRKY53 in basal resistance against pathogen Pseudomonas syringae. Plant Sci. 2012;186:288–297. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2011.12.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Glazebrook J. Genes controlling expression of defense responses in Arabidopsis. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2001;4:301–308. doi: 10.1016/S1369-5266(00)00177-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Dempsey DMA, Vlot AC, Wildermuth MC, Klessig DF. Salicylic acid biosynthesis and metabolism. The Arabidopsis Book. 2011;9:1–24. doi: 10.1199/tab.0156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Konishi M, Yanagisawa S. Two different mechanisms control ethylene sensitivity in Arabidopsis via the regulation of EBF2 expression. Plant Signal Behav. 2008;(9):749–51. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 49.Mingoti SA. Análise de dados através de métodos de estatística multivariada. 1. Belo Horizonte: UFMG; 2005. [Google Scholar]
- 50.Choi H, Hong J, Ha J, Kang J, Kim SY. ABFs, a family of ABA-responsive element binding factors. The J of Biol Chemistry. 2000;275:1723–1730. doi: 10.1074/jbc.275.3.1723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Lorenzo O, Chico JM, Sánchez-Serrano JJ, Solano R. JASMONATE-INSENSITIVE1 encodes a MYC transcription factor essential to discriminate between different jasmonate-regulated defense responses in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 2004;16:1938–1950. doi: 10.1105/tpc.022319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Cristofani-Yaly M, Machado MA, Grattapaglia D. Genetic linkage maps of Citrus sunki Hort. Ex tan. And Poncirus trifoliata (L.) Raf. And mapping of citrus tristeza virus resistance gene. Euphytica. 1999;109:25–32. doi: 10.1023/A:1003637116745. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Anderson JA, Chao S, Liu S. Molecular breeding using a major QTL for Fusarium head blight resistance in wheat. Crop Sci. 2007;47:112–119. doi: 10.2135/cropsci2006.05.0359. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Iqbal MJ, Meksem K, Njiti VN, Kassem MA, Lightfoot DA. Microsatellite markers identify three additional quantitative trait loci for resistance to soybean sudden-death-syndrome (SDS) in ESSEX x Forrest RILs. Theor Appl Genet. 2001;102:187–192. doi: 10.1007/s001220051634. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Matiello RR. PHD Thesis Universidade de São Paulo. 2004. Patossistema milho x Colletotrichum graminicola: estudo de herança, mapeamento de genes de resistência e estimativas de danos de produção. [Google Scholar]
- 56.Grattapaglia D. Integrating genomics into Eucalyptus breeding. Genet Mol Res. 2004;3:369–379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Shi C, Uzarowska A, Ouzunova M, Landbeck M, Wenzel G, Lubberstedt T. Identification of candidate genes associated with cell wall digestibility and eQTL (expression quantitative trait loci) analysis in a Flint x Flint maize recombinant inbred line population. BMC Genomics. 2007;8:1–16. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-8-22. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Young ND. Construction a plant genetic linkage map with DNA markers. In: Philips PL, Vasil IK, editors. DNA-based markers in plants. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publisher; 1994. pp. 39–57. [Google Scholar]
- 59.Cruz EM. PHD Thesis Universidade Federal de Viçosa. 2006. Efeito da saturação e do tamanho da população F2 e de retrocruzamento sobre a acurácia de mapeamento genético. [Google Scholar]
- 60.Yan AO, Zhi-qui HU, Zai-xiang TANG, Xue-feng WANG, Chen-wu XU. A general method for QTL mapping in multiple related populations derived from multiple parents. Rice Sci. 2009;16:45–50. doi: 10.1016/S1672-6308(08)60055-4. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Van Loon IC, Van Strien EA. The families of pathogenesis-related proteins, their activities and comparative analysis of PR-1 type proteins. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol. 1999;55:85–97. doi: 10.1006/pmpp.1999.0213. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Kirst M, Myburg AA, de Léon JPG, Kirst ME, Scott J, Sederoff R. Coordinated genetic regulation of growth and lignin revealed by quantitative trait locus analysis of cDNA microarray data in an interspecific backcross of Eucalyptus. Plant Physiol. 2004;135:2368–2378. doi: 10.1104/pp.103.037960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Hubner N, Wallace CA, Zimbahl H, et al. Integrated transcriptional profiling and linkage analysis for identification of genes underlying disease. Nat Genet. 2005;37:243–253. doi: 10.1038/ng1522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Rosa GJM. Delineamento de experimentos em genética genômica. Rev Bras Zootec. 2007;36:211–218. doi: 10.1590/S1516-35982007001000019. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 65.West MAL, Kim K, Kliebenstein DJ, Van Leeuwen H, Michelmore RW, Doerge RW, Clair DAS. Global eQTL mapping reveals the complex genetic architecture of transcript-level variation in Arabidopsis. Genetics. 2007;175:1441–1450. doi: 10.1534/genetics.106.064972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Gion JM, Rech P, Grima-Pettenati J, Verhaegen D, Plomion C. Mapping candidate genes in Eucalyptus with emphasis on lignification genes. Mol Breed. 2000;6:441–449. doi: 10.1023/A:1026552515218. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Brown GR, Bassoni DL, Gill GP, Fontana JR, Wheeler NC, Megraw RA, Davis MF, Sewell MM, Tuskan GA, Neale DB. Identification of quantitative trait loci influencing wood property traits in loblolly pine (Pinus taeda L.). III. QTL verification and candidate gene mapping. Genetics. 2003;164:1537–1546. doi: 10.1093/genetics/164.4.1537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Cubillos FA, Coustham V, Loudet O. Lessons from eQTL mapping studies: non-coding regions and their role behind natural phenotypic variation in plants. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2012;15:192–198. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2012.01.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Kirst M, Basten CJ, Myburg AA, Zeng ZB, Sederoff R. Genetic architecture of transcript-level variation in differentiating xylem of a eucalyptus hybrid. Genetics. 2005;169:2295–2303. doi: 10.1534/genetics.104.039198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Selected genes for RT-qPCR assays. (XLSX 11 kb)
Gene expression data with mean Ct and SD for 19 candidate genes. (XLS 2436 kb)
Real lesion length (RLL) caused from the inoculation with P. parasitica in the individuals of the experiment. (XLSX 12 kb)
Gene, linkage group (LG), flanking markers, position of the eQTL in centiMorgans (cM position), LOD score, proportion of phenotypic variation (R2) explained by eQTL in % and additive effect by the eQTLs mapping in the Poncirus trifoliata map. (XLSX 16 kb)
Gene, linkage group (LG), flanking markers, position of the eQTL in centiMorgans (cM position), LOD score, proportion of phenotypic variation (R2) explained by eQTL in % and additive effect by the eQTLs mapping in the Citrus sunki map. (XLSX 18 kb)
Data Availability Statement
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article [and its supplementary information files].