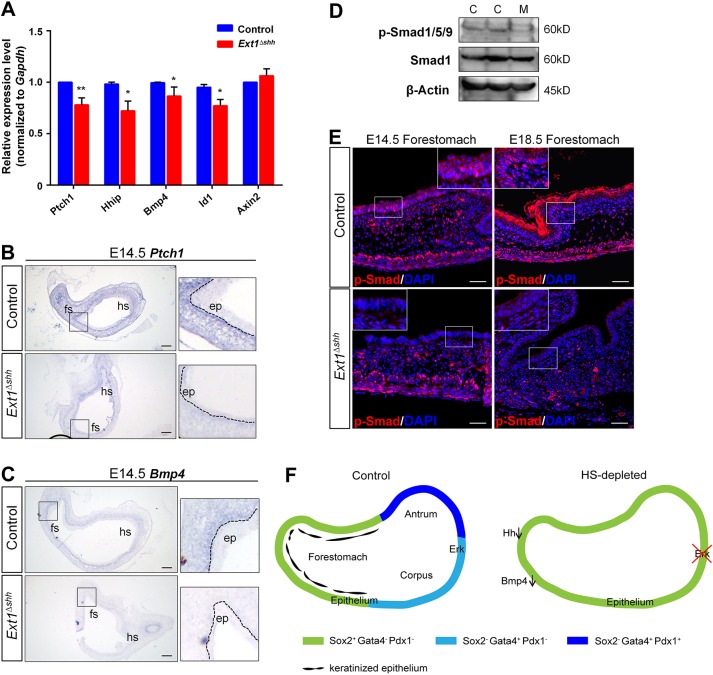
Fig. 7.
Epithelial HS depletion attenuates Hh-Bmp signaling activity in the stomach. (A) Expression of Hh, Bmp and Wnt signaling targets. Both Hh targets (Ptch1, Hhip1, Bmp4) and Bmp target (Id1) are downregulated after HS ablation at E14.5. **P<0.05, *P<0.01. Error bars indicate s.e.m. (n=4 per group). (B) ISH for Ptch1 transcripts. Mutant displays decreased Ptch1 signal strength in the mesenchyme, compared with the control. (C) ISH for Bmp4 confirms its decreased expression in mutant mesenchyme. (D,E) Phosphorylation of Smad1/5/9 is reduced in mutant revealed by western blotting and immunostaining. C, control; M, mutant (n=3). White dashed lines outline the epithelium. Magnified views of the boxed areas are presented in the insets (B,C,E). Scale bars: 100 μm (B,C), 50 μm (E). (F) Model for the functions of epithelial HS on stomach patterning and specification. In wild-type glandular stomach, epithelial HS promotes Fgf-Erk signaling activation in the overlying epithelium to regulate proper patterning and glandular cytodifferention. In the forestomach, epithelial HS is required for epithelial stratification and modulation of Hh-Bmp signaling. In HS-deficient mice, gastric epithelium is disorganized in both forestomach and hindstomach.