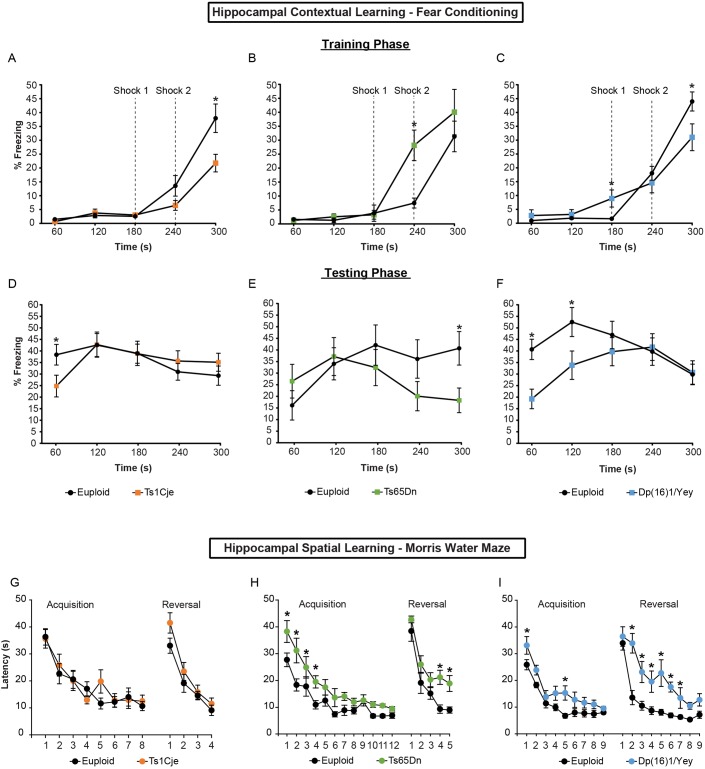
Fig. 6.
Hippocampal-based tasks in adult Ts1Cje, Ts65Dn and Dp(16)1/Yey males. Hippocampal-dependent spatial and contextual memory were investigated using the fear conditioning and Morris water maze (MWM) tests. (A-F) The contextual fear conditioning test has two phases: training and testing. During the training phase, mice are given two mild shocks 60 s apart. On the following day, mice are placed in the same chamber but no shocks are applied. Freezing behavior is documented. Animals used in A-F: Ts1Cje mice (n=13 trisomic mice, n=15 euploid mice); Ts65Dn (n=12 trisomic mice, n=12 euploid mice); and Dp(16)1/Yey mice (n=18 trisomic mice, n=17 euploid littermates). (G-I) The MWM test has two phases: acquisition and reversal. Both tests utilize a hidden platform to analyze learning (acquisition phase) and reversal learning (reversal phase). Mice are initially tested using a visible platform to exclude any confounds related to testing procedures or non-learning based deficits in the mice. Ts1Cje males show no deficits during either the acquisition phase or the reversal learning phase (G). Ts65Dn males show no deficits during the acquisition period after the 4 days needed to stop thigmotaxic behavior and acclimate to the task (previously published in Olmos-Serrano et al., 2016b). However, these mice show a deficit in reversal learning compared with their euploid controls (H). Dp(16)1/Yey males show impaired learning on days 1 and 5 of the acquisition phase. Additionally, these males also show a strong deficit in reversal learning compared with their euploid controls (I). Animals used in G-I: Ts1Cje mice (n=13 trisomic mice, n=11 euploid mice); Ts65Dn (n=14 trisomic mice, n=14 euploid mice); and Dp(16)1/Yey mice (n=13 trisomic mice, n=11 euploid littermates). Data are mean±s.d., *P<0.05.