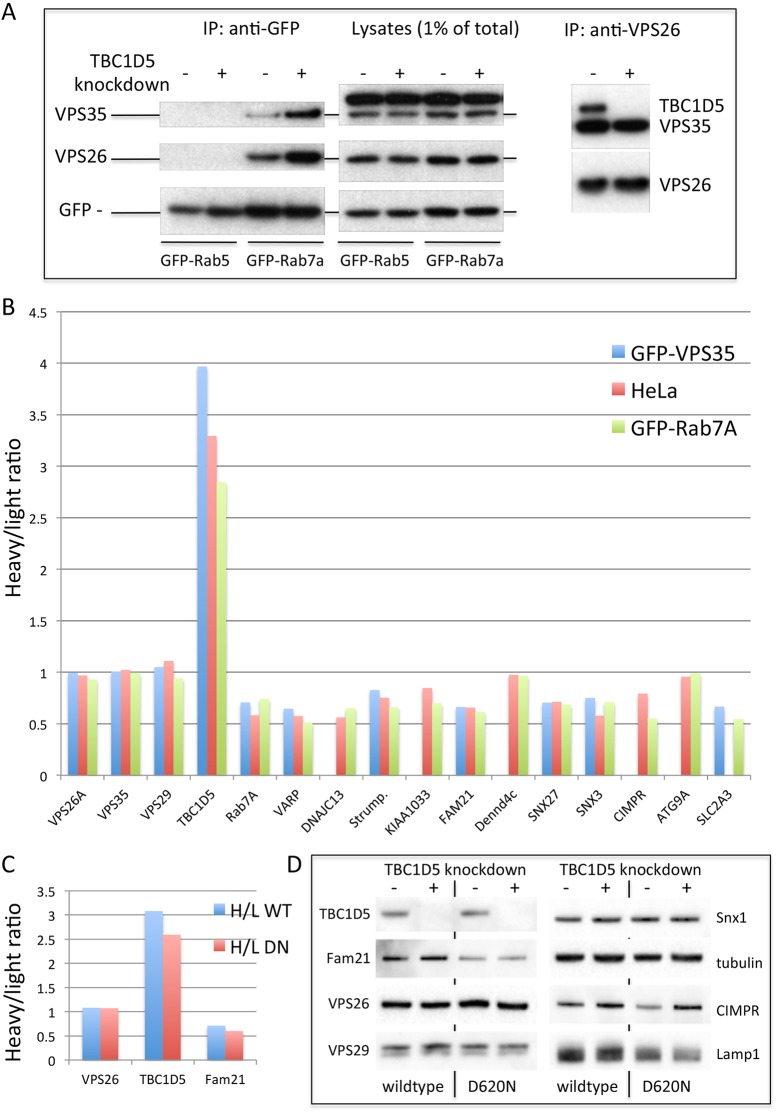
Fig. 3.
TBC1D5 knockdown enhances the associations of the retromer CSC. (A) Cells expressing either GFP-Rab5 or GFP-Rab7a were treated with siRNA to silence TBC1D5 expression. After lysis under native conditions, the GFP-tagged proteins were recovered by immunoprecipitation (IP) using anti-GFP. The immunoprecipitated proteins were analysed by western blotting. Retromer CSC proteins were detected in the GFP-Rab7a IP but not GFP-Rab5 IP. The knockdown of TBC1D5 increased the levels of retromer CSC proteins associated with GFP-Rab7a but no changes in protein levels were observed after TBC1D5 knockdown when lysates were analysed. IP of VPS26 confirmed that TBC1D5 expression was abolished and that loss of TBC1D5 does not alter the interaction between VPS26 and VPS35. (B) Following a protocol for SILAC labelling, three HeLa cell lines were labelled over several passages with heavy or light amino acids before being subjected to TBC1D5 knockdown (in the light amino acid-labelled cells) and treated with the DSP crosslinking reagent. After lysis, VPS26 was recovered by IP and the resulting IPs analysed by mass spectrometry. Levels of the proteins in the IPs are shown as a ratio of heavy:light normalised to VPS26. The retromer CSC proteins all give values close to 1, indicating that TBC1D5 knockdown does not affect retromer CSC assembly. The TBC1D5 protein has a ratio ∼3-3.5 consistent with a knockdown of the protein. Other proteins detected generally gave ratios <1, showing that more peptides labelled with light amino acids were detected, indicating an increased level of the protein after TBC1D5 knockdown. (C) Cells expressing either GFP-VPS35 WT or GFP-VPS35 D620N (DN) were treated as in B and the lysates were treated with anti-GFP antisera. The knockdown of TBC1D5 can enhance the interaction of the VPS35 D620N mutant with Fam21. (D) Lysates from cells in C analysed by western blotting to confirm TBC1D5 knockdown.