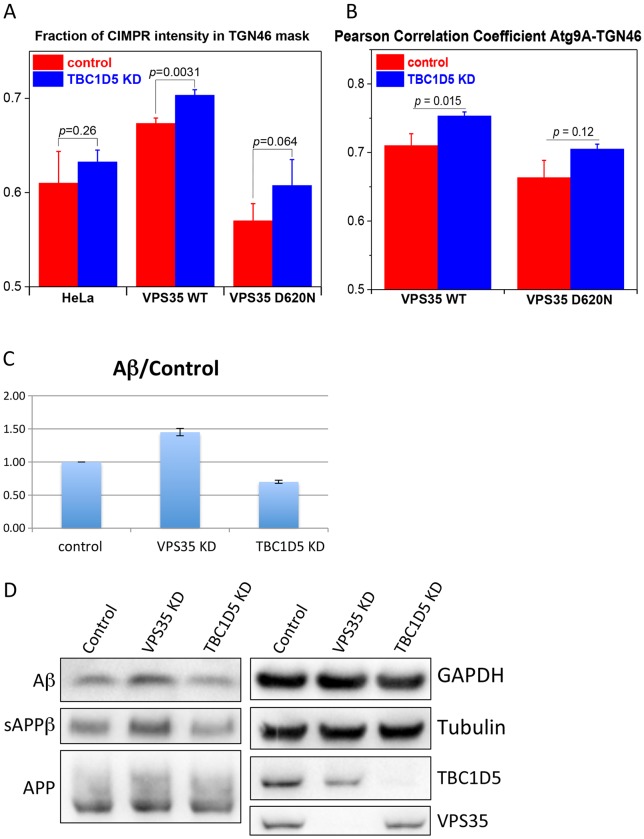
Fig. 6.
Knockdown of TBC1D5 can enhance retromer function. (A) Three different cell lines were treated with siRNA to knockdown TBC1D5 expression. Following fixation, cells were labelled with antibodies against CIMPR and TGN46 and then imaged using an automated microscope. The fraction of CIMPR present in a TGN46 mask is shown graphically. For each of the cell lines, knockdown on TBC1D5 enhances the colocalisation of CIMPR with TGN46 but only the GFP-VPS35 cells demonstrate statistical significance. Values are mean±s.d. and P-values for knockdown versus control are shown for each cell line. (B) TBC1D5 expression was silenced in cells expressing GFP-VPS35 wild type or the D620N mutant. Following fixation, the cells were labelled with antibodies against Atg9A and TGN46 and then imaged using an automated microscope. The Pearson correlation coefficient for Atg9A-TGN46 mask is shown graphically. For each of the cell lines, knockdown of TBC1D5 enhances the colocalisation of Atg9A with TGN46 but only the GFP-VPS35 wild-type cells demonstrate statistical significance. Values are mean±s.d. and P-values for knockdown versus control are shown for each cell line. (C) HEK293 cells stably expressing APPswedish were treated with siRNA to silence VPS35 or TBC1D5. Cell culture medium was collected and analysed for the Aβ peptide by western blotting. Knockdown of VPS35 increases APP processing to Aβ but loss of TBC1D5 expression has the opposite effect. The data shown are from two independent experiments that were highly reproducible. Values are mean±s.d. For both the VPS35- and TBC1D5-knockdown conditions, P<0.01 using Student's t-test compared with control. (D) Representative blots of media (for Aβ and sAPPβ) and lysates (for APP, VPS35, TBC1D5 and the loading controls, GAPDH and tubulin) from C showing the reduction in Aβ detected when TBC1D5 is silenced. There is also a reduction in sAPPβ.