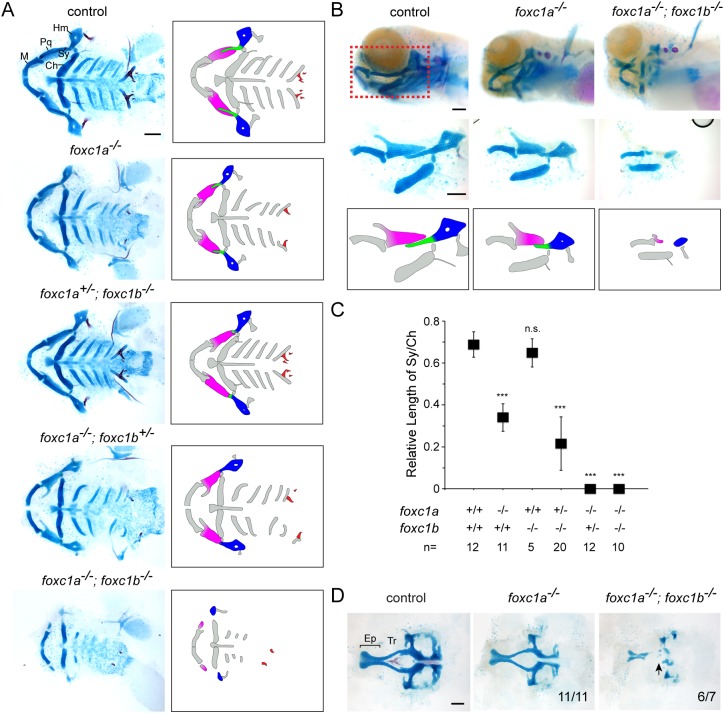
Fig. 2.
Loss of upper facial cartilage in Fox-C mutants. (A) Ventral views of dissected facial skeletons, with cartilage in blue and bones and teeth in red. Schematics show affected elements in color. Ch, ceratohyal; Hm, hyomandibular; M, Meckel's; Pq, palatoquadrate; Sy, symplectic. (B) Lateral views of intact heads stained with Alcian Blue (cartilage) and Alizarin Red (bones and teeth). Shown below are unilateral dissections of skeletal elements of the first and second arches (red boxed region). Accompanying schematics show dose-dependent reductions of the Pq (magenta), Sy (green) and Hm (blue) cartilages. foxc1a−/− and foxc1a−/−; foxc1b−/− mutants also display cardiac edema and an overall smaller head. (C) Quantification of the relative length of Sy compared with Ch. ***P<0.001 versus wild-type sibling control using Student's t-test. n.s., not significant versus control (P=0.35). Error bars represent s.e.m. (D) Dissections of neurocranial cartilages show loss of the trabecular cartilages (Tr, arrow) in foxc1a−/−; foxc1b−/− mutants. Numbers denote proportions of embryos with displayed phenotypes. Ep, ethmoid plate. Scale bars: 25 μm.