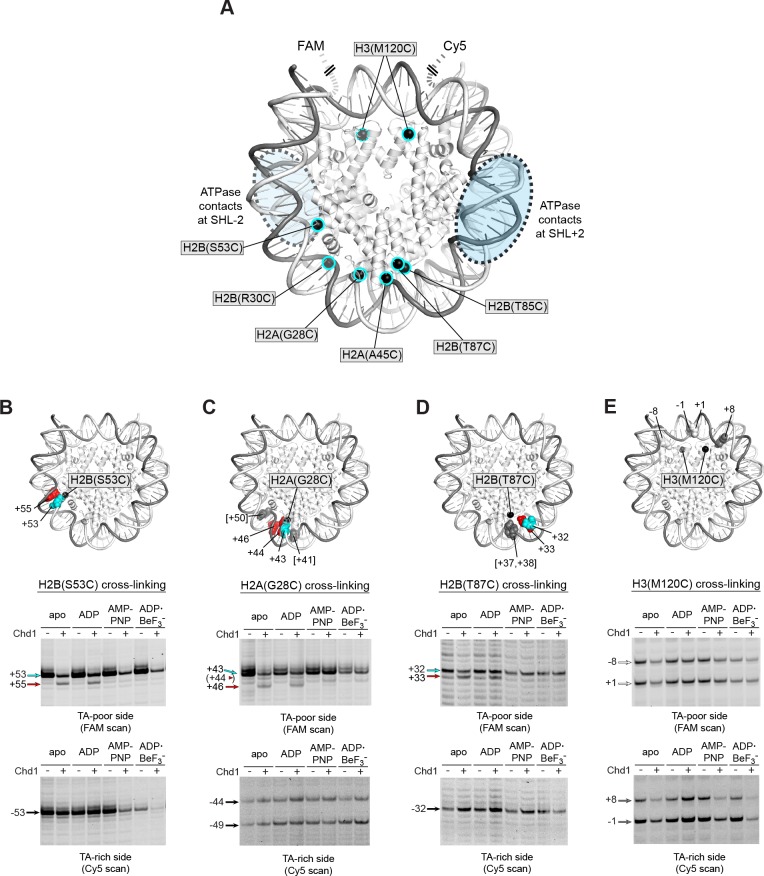
Figure 2. Chd1 binding in apo and ADP conditions shifts nucleosomal DNA on the TA-poor side of the 601 sequence.
(A) Molecular representation of a 601 nucleosome (Makde et al., 2010), indicating sites of cysteine substitution for site-specific cross-linking. Blue dotted ovals indicate the regions bound by the Chd1 ATPase motor at each SHL2 site (Farnung et al., 2017; Nodelman et al., 2017; Sundaramoorthy et al., 2018). (B) Histone H2B(S53C) cross-linking reactions in the presence and absence of Chd1. PyMOL representation shows cross-links on the TA-poor side of the nucleosome that occur for the nucleosome alone (cyan) and in the presence of Chd1 (red). Cross-linking was performed using 150 nM canonical 601 nucleosomes with 40 bp flanking DNA on each side (40N40), in the presence or absence of 600 nM Chd1. Cross-linked products were separated on urea denaturing gels and visualized by FAM or Cy5 fluorescence. Numbering refers to the distances of cross-linked sites from the 601 dyad (bp). (C) Histone H2A(G28C) cross-linking reactions, performed as described in B. In the PyMOL representation, sites of cross-linking that occur on the complementary strand are indicated by gray spheres with numbering in square brackets (see Figure 2—figure supplement 2B for +41 and +50 cross-linking sites). (D) Histone H2B(T87C) cross-linking reactions, performed as described in B. As for (C), cross-links that occur on the complementary strand [+37/+38] are shown as gray spheres in the PyMOL representation (Figure 2—figure supplement 2C). (E) Histone H3(M120C) cross-linking reactions, performed as described in B. All cross-linking experiments are representative of 3 or more experiments. Extended gel images are shown in Figure 2—figure supplement 2D.
Figure 2—figure supplement 1. Titration of Chd1 for H2B(S53C) cross-linking reaction.
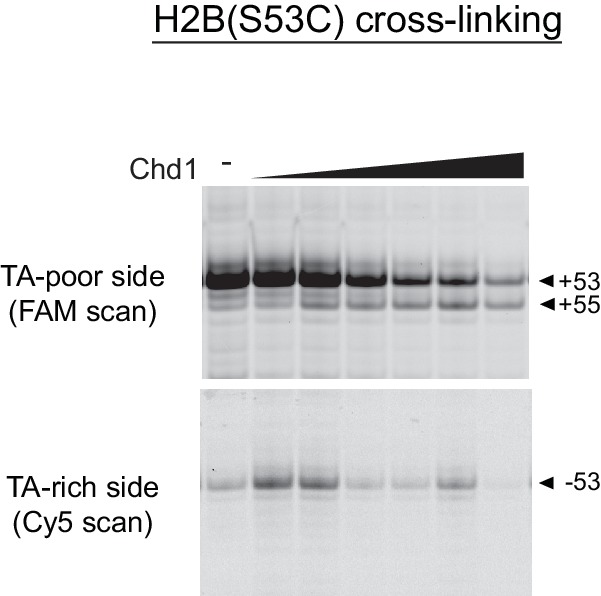
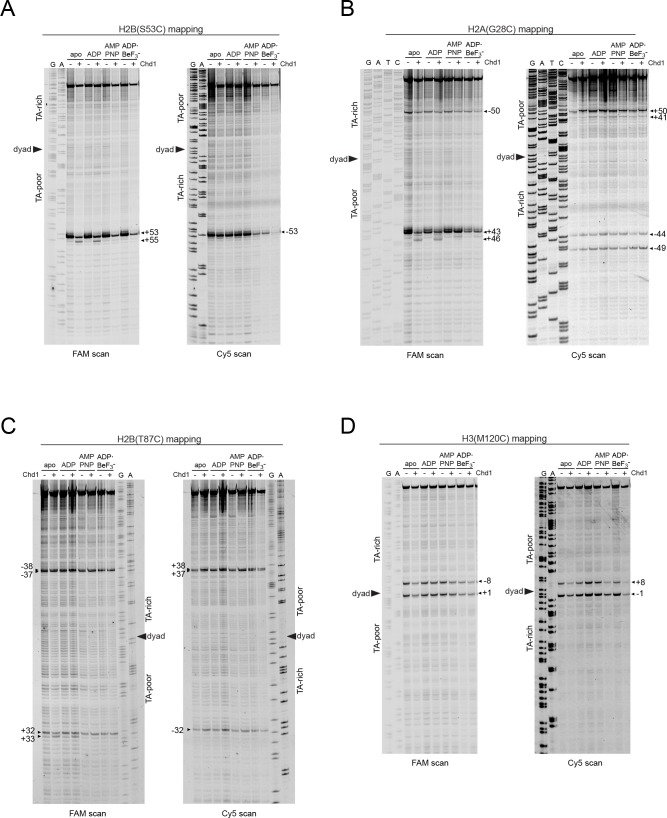
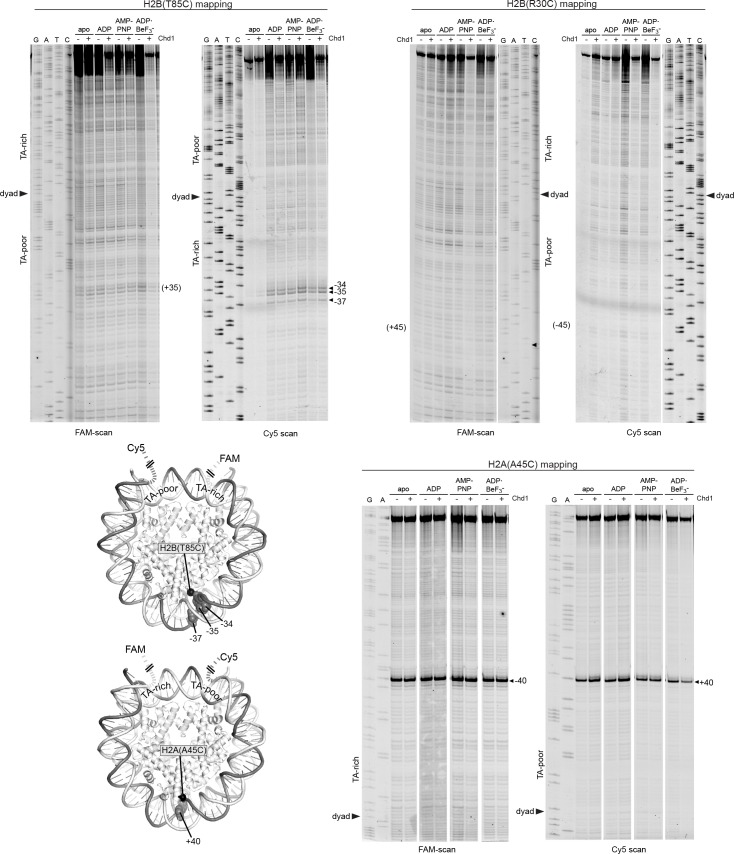
Figure 2—figure supplement 2. Extended gel images for histone mapping of Widom 601 nucleosomes.
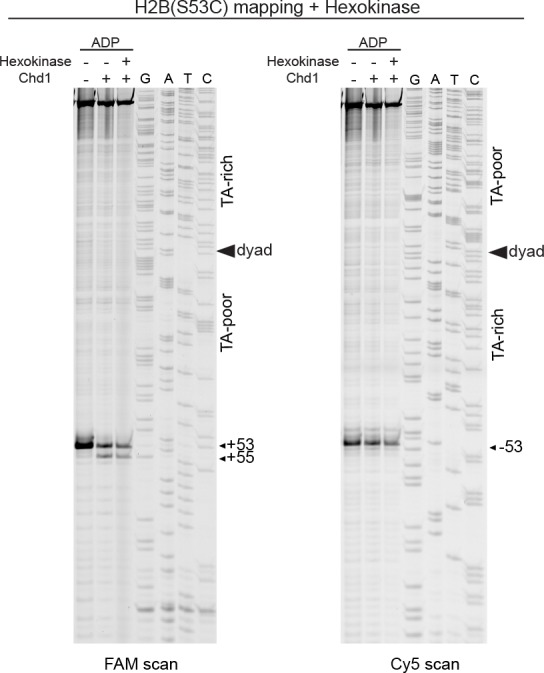
Figure 2—figure supplement 3. Treatment with hexokinase confirms that ADP is sufficient for supporting a Chd1-dependent shift in H2B(S53C) cross-linking.