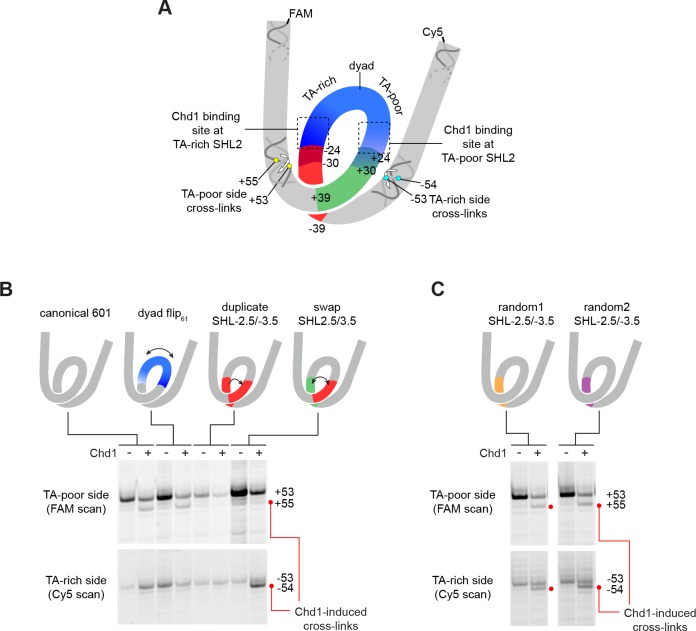
Figure 4. The sequence of DNA 24–39 bp from the dyad can restrict or permit shifts in H2B(S53C) cross-linking upon Chd1 binding.
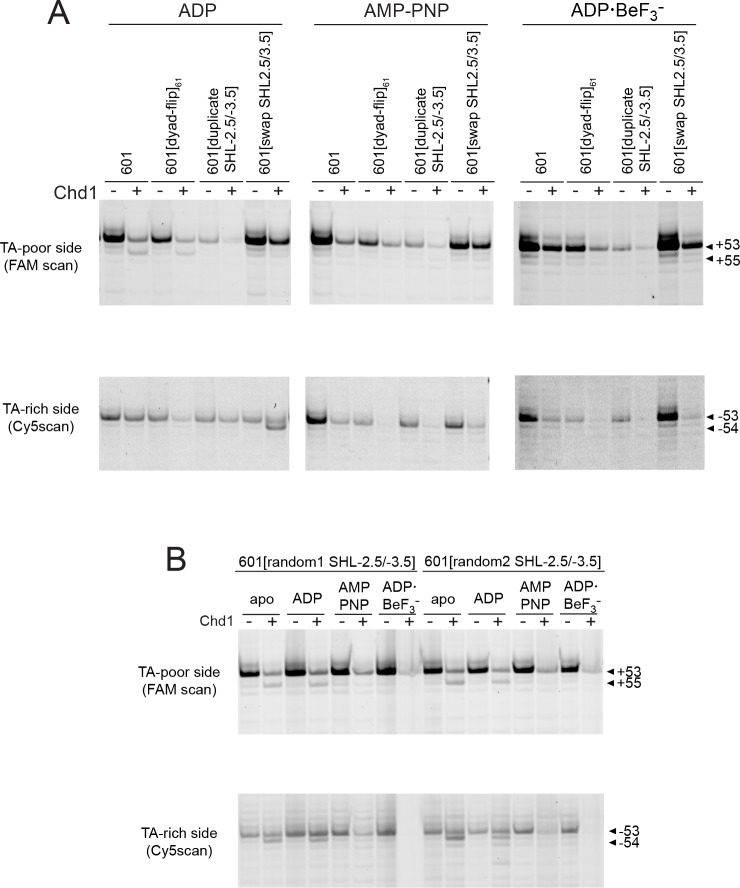
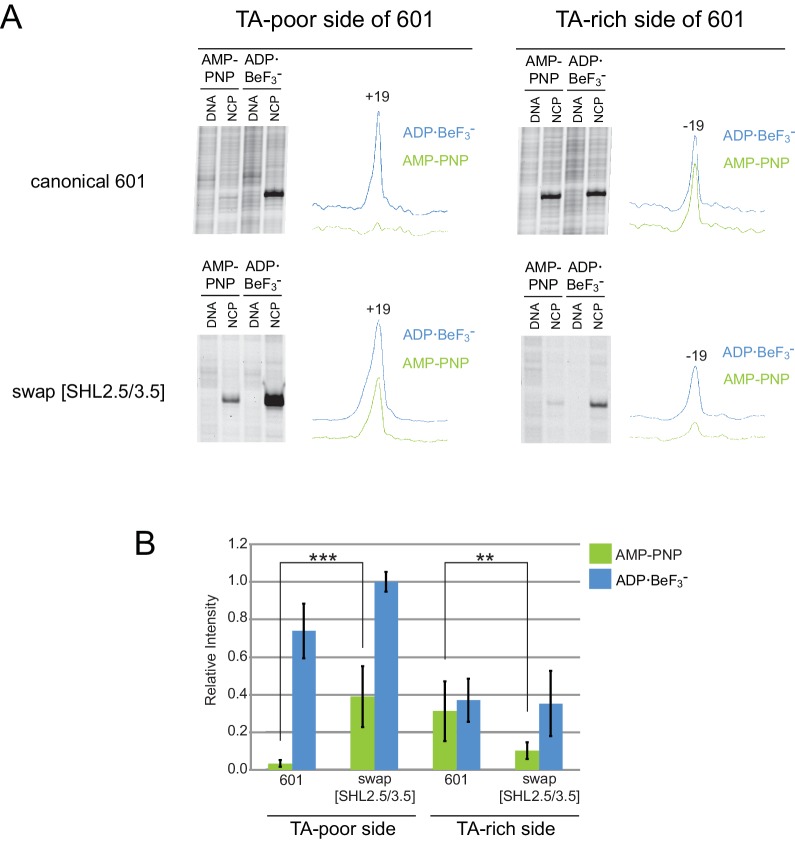
(A) Schematic representation of the nucleosome, highlighting sequence elements of the canonical Widom 601 sequence that are altered in 601 variants. (B) The 24–39 bp segment of the canonical 601 is responsible for allowing or blocking Chd1-dependent shifts in H2B(S53C) cross-linking. Shown are cross-linking experiments for the canonical Widom 601 and three 601 variants, carried out with 150 nM 40N40 nucleosomes and 600 nM Chd1 under apo conditions. Schematic cartoons indicate the region of 601 altered for each nucleosome variant. (C) Replacing the 24–39 bp segment on the TA-rich side of the 601 with random DNA sequences allows Chd1 binding (apo condition) to stimulate a shift in H2B(S53C) cross-linking on the TA-rich side. Each gel in B and C is representative of 4 or more experiments. The DNA sequences for all 601 variants are given in Figure 1—figure supplement 2. Similar experiments to those carried out in B and C but in other nucleotide conditions, are shown in Figure 4—figure supplement 1.