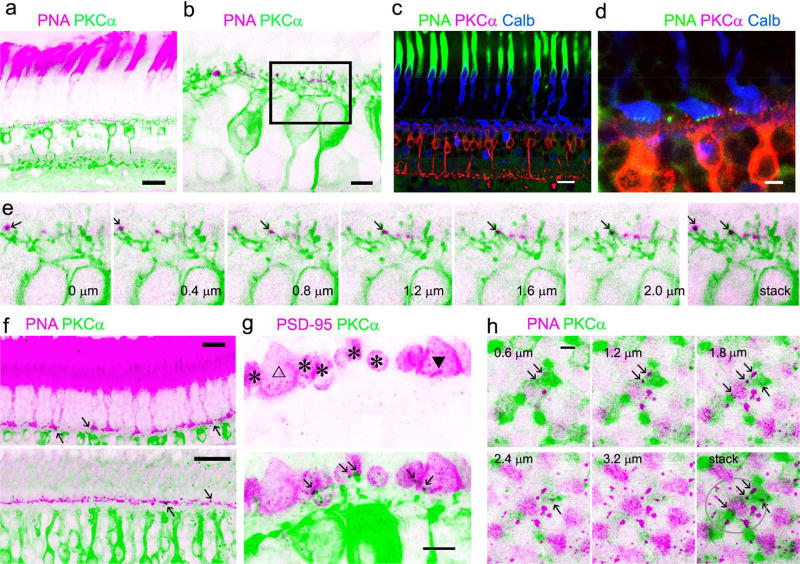
Fig. 6.
Baboon cone-RBC synapses. Retina preparations are triple- (a to d) or double-labeled. Cone somas and pedicles are brightly labeled for calbindin D-28k (Calb) (c, d). PNA intensively labels cone inner segments (a, c, e) and reveals clusters of puncta in the basal membrane of cone pedicles (d). Each cluster of PNA-positive puncta belongs to a cone pedicle (d). Consecutive confocal optical sections of a rectangular region in b show that some PKCα-labeled RBC dendrites colocalize with PNA (e). Some RBC dendrites coincide with PNA in cone pedicles (see arrows) in retinal slices (f, upper-peripheral retina, lower-para-central retina) and cone telodendrites in the flat-mount retina (h). h displays overexposed images of consecutive horizontal confocal optical sections of a cone pedicle and its telodendrites (in the circle). In retinal slices (g) large triangular cone pedicles are positively labeled for PSD95 (triangle) and distinguishable from small oval-shaped rod spherules (asterisks). RBC dendrites contact rod spherules and one cone pedicle (closed triangle) but do not contact the other cone pedicle (open triangle). Scale bars are 20 µm in a, c and f and 5 µm in the rest images.