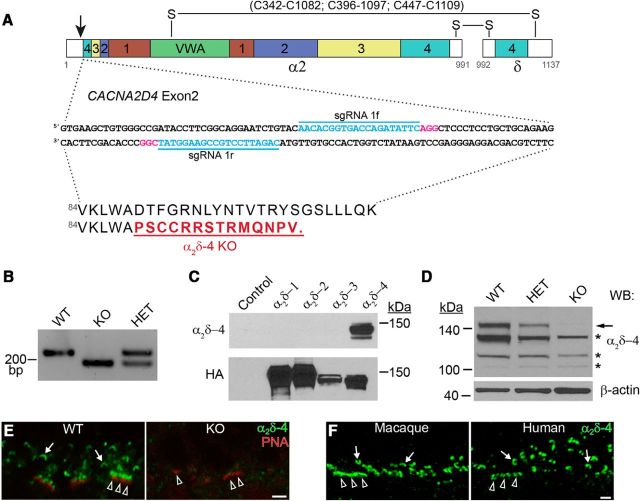
Figure 1.
Generation of α2δ-4 KO mice. A, Schematic illustrating domain structure of α2δ-4 and strategy for interrupting exon 2 using the indicated guide RNA sequences (sgRNA 1f and 1r). The four chemosensory domains (1–4) are indicated in colored boxes. VWA, von Willebrand A domain. Numbers beneath diagram indicate amino acids. Putative disulfide bonds (S-S) between α2 and δ are shown above the diagram. The resulting amino sequence change (underlined) and premature truncation are shown below. B, PCR with primers flanking the deleted region in exon 2 using retinal genomic DNA from WT, KO, and HET mice. C, D, Western blots probed with α2δ-4 or HA antibodies of lysates from HEK293T cells untransfected (control) or transfected with HA-tagged α2δ variants (C) or retina from WT, HET, or KO mice (D). Arrow and asterisks indicate specific and nonspecific protein detection, respectively. E, F, Confocal micrographs showing labeling with α2δ-4 antibodies in WT and α2δ-4 KO mouse retina at P21 (E) and macaque and human retina (F). E, Mouse retina was double-labeled with fluorescent PNA to mark cone terminals. α2δ-4 labeling is present at ribbons of rods (arrows) and cones (arrowheads). Scale bars, 2 μm.