Figure 10.
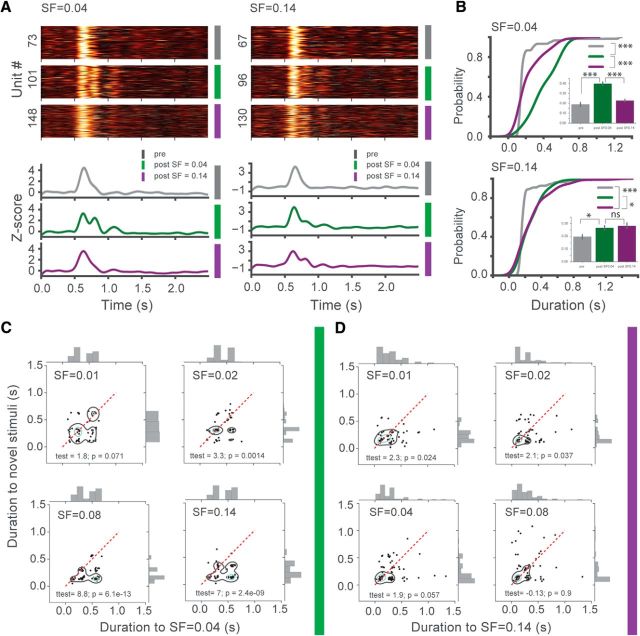
SF filtered noise stimuli dynamically modulate the duration of single-unit oscillatory activity in a SF-dependent manner. A, Oscillatory activity emerges in single units after experiencing SF filtered noise visual stimuli and specific to the trained stimulus as shown in heat maps of z scored PSTHs: pre (gray); post SF = 0.04 (green); post SF = 0.14 (purple). Top left, Response to SF = 0.04 across three different conditions. Top right, Same as left but for SF = 0.14. Bottom left, z score time course of population average of the units depicted in heat maps. The emergence of oscillatory activity to SF = 0.04 after experiencing that stimuli is seen, but not before or after SF = 0.14 training. Bottom right, Same as bottom left but for SF = 0.14, oscillations only observed after SF = 0.14 training but not before/after SF = 0.04 training. B, Cumulative distribution plots of the duration of oscillations in single units show significantly longer duration to the experienced stimulus compared with the novel or pretraining conditions; SF = 0.04 (top): two-sample Kolmogorov–Smirnov test post SF = 0.04 training versus pre (D = 0.71, p = 4.54E-16), versus SF = 0.14 training (D = 0.52, p = 3.02E-12). Inset, t(139) = 7.16, p = 4.21E-14, t(203) = 7.14, p = 1.61E-11, n = 81, 60, 124 units, respectively; SF = 0.14 (bottom): two-sample Kolmogorov–Smirnov test post SF = 0.14 training versus pre (D = 0.41, p = 9.25E-6), versus SF = 0.04 training (D = 0.21, p = 0.03). Inset, t test: (t(145) = 2.57, p = 0.01) and (t(171) = −0.53, p = 0.59 (not significant), n = 92, 55, 81, respectively. C, Duration of oscillatory activity in single units was significantly modulated by SF of the stimulus as evident from scatter plots (red dashed line indicates perfect correlation between conditions). Each dot indicates duration of single neuron's oscillatory activity to the familiar (x-axis) versus novel (y-axis) stimuli, so that clustering of dots below red line shows preference to the familiar stimulus. Green and black contours outline KDE of dots. Paired t test: SF = 0.04 versus SF = 0.01 (t(59) = 1.8, p = 0.071), versus SF = 0.02 (t(68) = 3.3, p = 0.0014), versus SF = 0.08 (t(69) = 8.8, p = 6.1E-13), versus SF = 0.14 (t(59) = 7, p = 2.4E-9), n = 60, 69, 70, 60, respectively. D, Same as D but for animals trained to SF = 0.14. SF = 0.14 versus SF = 0.01 (t(54) = 2.3, p = 0.024), versus SF = 0.02 (t(68) = 2.1, p = 0.037), versus SF = 0.04 (t(79) = 1.9, p = 0.057), versus SF = 0.08 (t(79) = −0.13, p = 0.9 (not significant), n = 55, 69, 80, 80, respectively. Error bars indicate SEM. *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001.