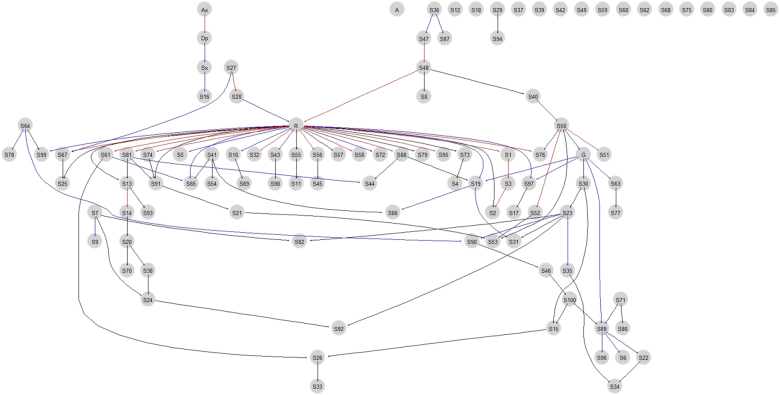
Fig. 1. Bayesian network inferred.
A Bayesian network learned from the data of childhood asthmatics with a Hill-Climbing algorithm. Edges represent conditional dependencies, and connected nodes represent variables that are conditionally dependent on each other. Red edges represent edges with an arc strength >0.5, blue edges represent edges with an arc strength between 0.2 and 0.5, and black edges represent edges with an arc strength between 0.1 and 0.2. Edges with an arc strength <0.1 were removed from the network. For a certain node, nodes connected above (parent nodes), nodes connected below (children nodes), and the other parent nodes of these children nodes form a Markov blanket, which is required to predict the behavior of that node. Thus, we evaluated the interactive effects of depression severity (parent of the Sx node) and rs4672619 (S16) genotypes (children of the Sx node) on asthma symptom severity (Sx node). A age quartile, Ax anxiety quartile, Dp depression quartile, G gender (male/female), Sx symptom severity quartile, R ethnicity (non-Hispanic white/African American/Hispanic/Asian), and S1-100 top-ranked 100 SNPs (S16, rs4672619)