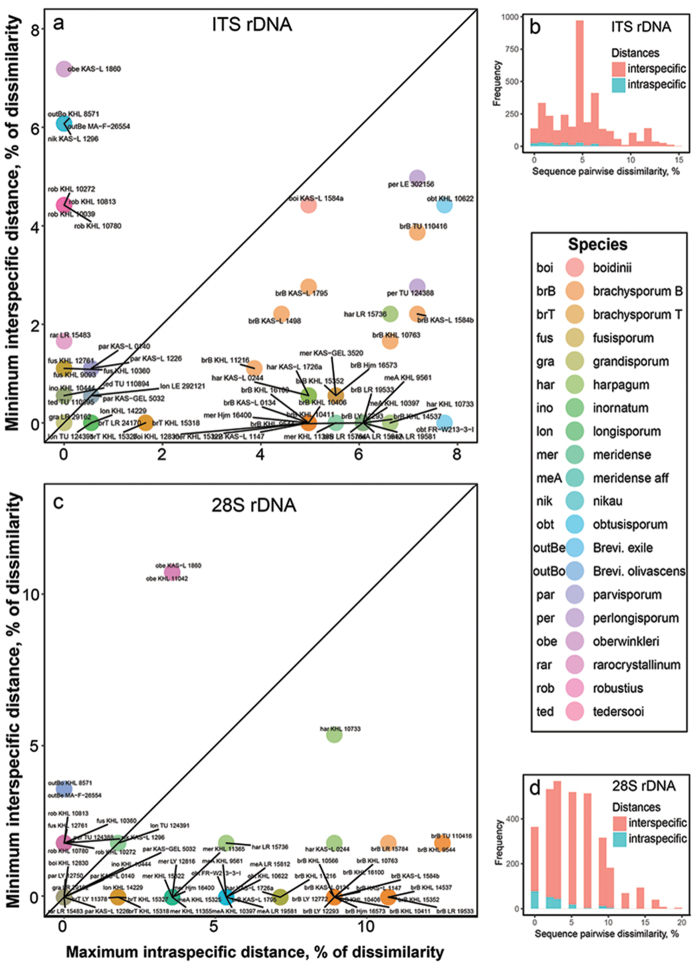
Figure 2.
Verifying the presence of the barcode gap in Subulicystidium rDNA sequences of ITS (a, b) and 28S (c, d) regions. a, c Maximal intraspecific divergence compared with minimal interspecific distances between the aligned rDNA sequences in ITS (a) and 28S (c) datasets. Specimens falling above 1:1 line indicate the presence of the barcoding gap (molecular distinctness of the species) b, d Frequency distributions of intra- and interspecific distances without referring to particular species in ITS (b) and 28S (d) datasets. In the legend, the capital “B” following epithet in S. brachysporum means morphological species concept following Boidin and Gilles (1988), while “T” means the species as described by Talbot (1958). Three-letter code before each specimen’s number corresponds to a species epithet as explained in the legend