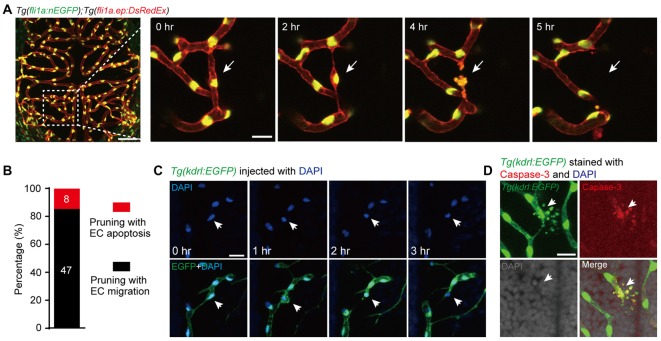
Figure 1.
Vessel pruning is accompanied with endothelial cell (EC) apoptosis in the brain of larval zebrafish. (A) In vivo time-lapse confocal images showing that an EC (arrows) underwent apoptosis on a pruned brain vessel in a Tg(fli1a:nEGFP);Tg(fli1a.ep:DsRedEx) larva at 3–3.5 days post-fertilization (dpf), in which EC nuclei were labeled by both enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP) and DsRed (yellow). Left, projected confocal image of the whole brain vasculature; Right, time-lapse confocal images of the dashed outlined area in the left. (B) Summary of the percentages of EC apoptosis- and migration-accompanied brain vessel pruning (n = 17 larvae). (C) In vivo time-lapse confocal images showing that an EC (arrows) underwent apoptosis on a brain pruned vessel in a DAPI-injected Tg(kdrl:EGFP) larva at 3–3.5 dpf, in which EC nuclei were labeled by DAPI (blue). (D) Immunofluorescence images showing that, on a pruned vessel, an EC with typical apoptotic morphology (arrows) expressed Caspase-3. The numbers on the bars (B) represent the number of pruned vessels examined. Scales: 50 μm (left in (A), 15 μm (right in (A), 50 μm (C) and 15 μm (D).