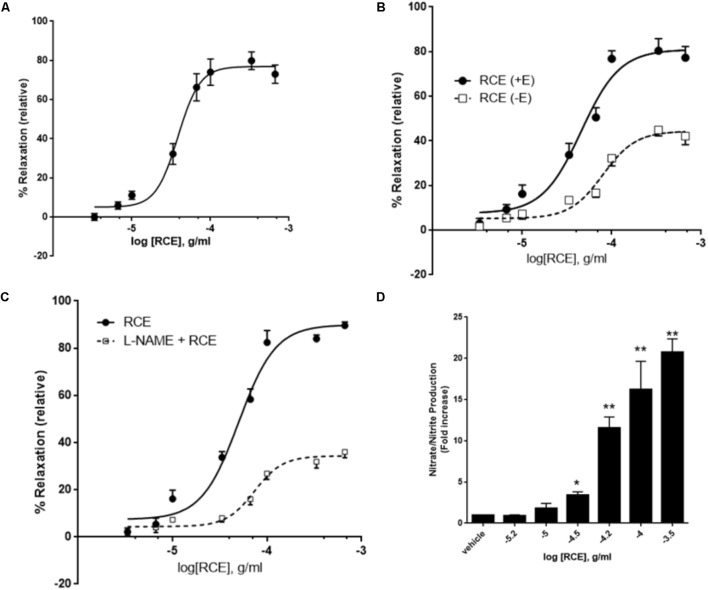
FIGURE 1.
Role of endothelium and NO on RCE-induced relaxation. (A) Cumulative dose-dependent relaxation responses to Rhus coriaria extract (RCE) on rat isolated aortic rings. Segments of aorta were precontracted with norepinephrine (3 μM). The data expressed are mean ± SEM (n = 7). (B) Cumulative dose-dependent relaxation curves were generated to sumac (RCE) on norepinephrine-precontracted rat isolated aortic rings, either intact (+E; circles) or devoid of endothelium (–E; squares). The data expressed are mean ± SEM (n = 7; p < 0.01 for +E versus –E). (C) Endothelium-intact aortic rings were subjected to cumulative doses of sumac in the absence (circles) or pre-presence of L-NAME (100 μM; squares). Data represent mean ± SEM (n = 7; p < 0.01 for RCE versus L-Name plus RCE). (D) Endothelium-intact rings were incubated with increasing doses of RCE and levels of NO determined. Each bar displays mean ± SEM, ∗p < 0.05 and ∗∗p < 0.01.