FIGURE 4.
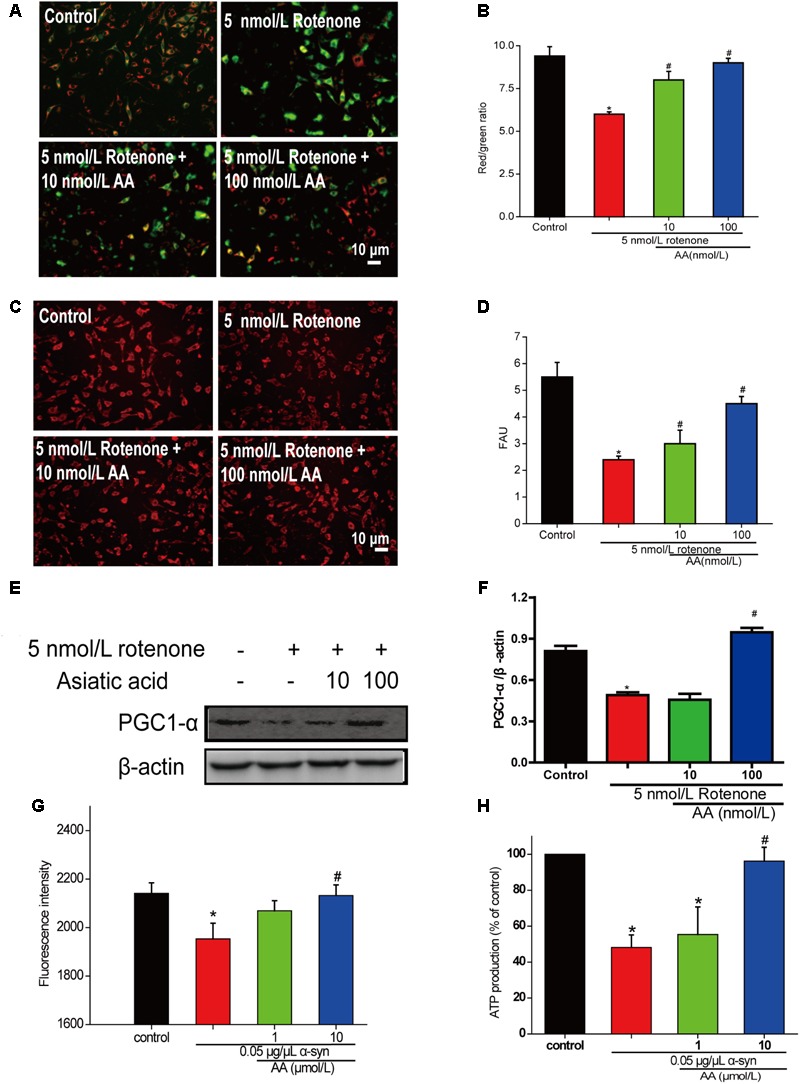
AA protects against mitochondrial dysfunction induced by PD-like injury. (A,B) SH-SY5Y cells were treated with 5 nM rotenone exposure for 4 weeks and then various concentrations of AA after 24 h. Intracellular red and green fluorescence of JC-1 was determined under an inverted fluorescence microscope (A) and on a spectrofluorometer (B). Mitochondria number was determined with an inverted fluorescence microscope (C) and spectrofluorometer (D) and based on expression of PGC1-α (E,H). (F) Effects of AA on mitochondrial membrane potential (JC-1 fluorescence intensity). Isolated mitochondria were treated with vehicle or AA for 60 min at 37°C and exposed to 0 or 0.05 μg/μL α-syn at the same time. Data are expressed as means ± SD, n = 3. ∗p < 0.01 vs. control group, #p < 0.01 vs. rotenone group. (G) Effects of AA on mitochondrial ATP synthesis. Isolated mitochondria were treated with vehicle or AA for 60 min at 37°C and exposed to 0 or 0.05 μg/μL α-syn at the same time. The values are expressed as percentage of control, which is set to 100%. Data are expressed as means ± SD, n = 3. ∗p < 0.01 vs. control group, #p < 0.01 vs. α-syn group. Bar: 10 μm.
