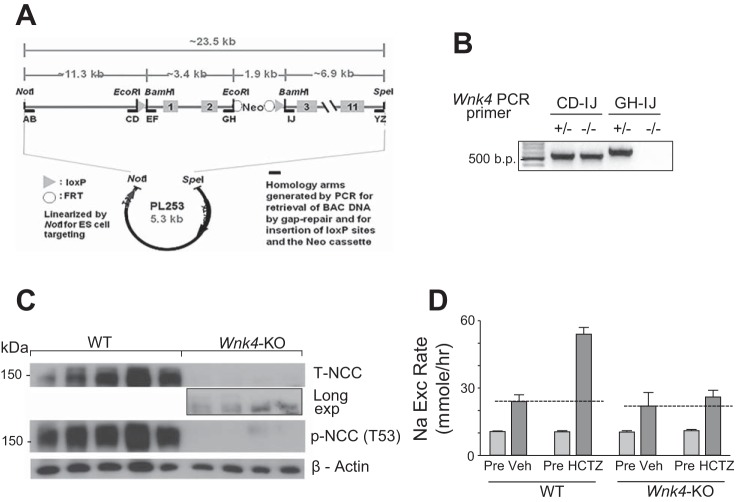
Fig. 3.
Blunting of HCTZ-induced Na+ excretion in Wnk4-KO mice. A: gene targeting strategy and primer position for genotyping. B: genotyping of Wnk4-KO mice. The “CD-IJ” primer set generates ~500 bp PCR product from the mutant allele, in which the large (>5 kb) DNA fragment flanked by the loxP sites is deleted. This primer set does not generate PCR product from WT allele due to its size. The “GH-IJ” primer set generates PCR product from WT, but not the mutant allele. C: Western blot analysis of total NCC (T-NCC) and phospho-NCC recognized by antibody specific to threonine-53 phosphorylated NCC peptide [p-NCC (T53)] in kidney extracts from WT and Wnk4-KO mice. β-Actin is for loading control. D: HCTZ-induced Na+ excretion during the acute phase (HCTZ) after the drug administration was detected in WT mice, but not in the Wnk4-KO mice. The level of HCTZ-induced Na+ excretion in Wnk4-KO mice was not significantly different from that in vehicle-treated Wnk4-KO or WT mice. n = 15–17 each.