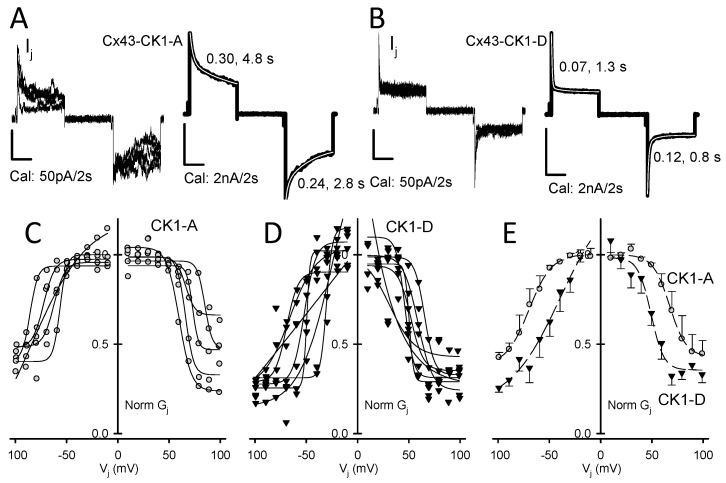
Figure 1.
Cx43-CK1-D displays stronger Vj-sensitivity than Cx43-CK1-A. (A) Five individual Ij responses to Vj = ±80 mV pulses (left) and sum (right) of 38 similar traces from Cx43-CK1-A cell pairs; (B) Five individual Ij responses to Vj = ±80 mV pulses (left) and sum (right) of 30 similar traces from Cx43-CK1-D cell pairs. For (A,B), tau values of Ij inactivation (2nd order exponential decays) are shown and the fits (white) displayed over the corresponding sum traces; (C) Vj-dependence of Gj from individual experiments in Cx43-CK1-A (gj = 2.8 ± 1.0; n = 5) cell pairs; (D) Vj-dependence of Gj from individual experiments in Cx43-CK1-D (gj = 1.7 ± 1.1; n = 7) cell pairs. For (C,D), gj from each experiment was normalized as described in the Methods and the Boltzmann fits are shown in solid black lines; (E) Average Vj-dependence for CK1-A (gray circles) and CK1-D (black triangles) and their corresponding Boltzmann fits (dashed lines). Fast inactivation and V0 values were different between Cx43-CK1-D and Cx43-CK1-A. For fitting parameters, see Table 1, Tables S1 and S2.