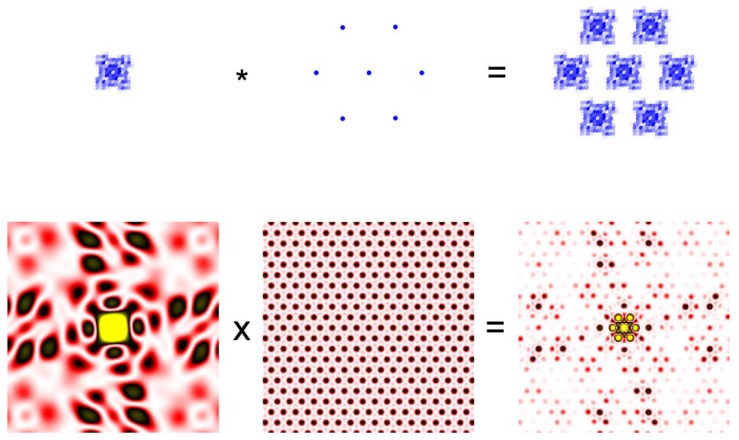
Figure 2.
Convolution theorem. A small crystal of protein molecules in which the molecules are arranged in a hexagonal lattice (Top right) is the convolution of two functions. The function defining the electron density of each molecule (Top left) and the function defining the hexagonal lattice (Top middle). The asterisk represents the operation of convolution. The bottom row represents the diffraction pattern (Fourier transform) of the functions in the top row. The diffraction pattern from the protein crystal is the product of the pattern from a single molecule from the lattice. The protein is meant to be a ryanodine receptor.