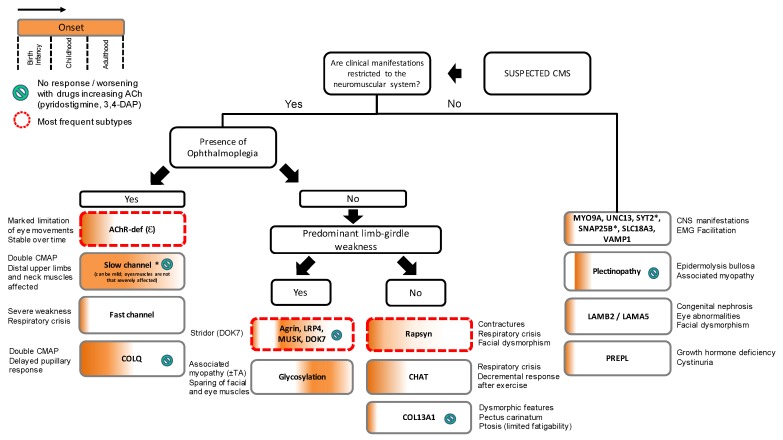
Figure 2.
Proposed algorithm for targeted genetic screening of suspected CMS cases. Clinical evaluation should start by exploring age at onset and presence of manifestations beyond the neuromuscular boundaries. Ophthalmoplegia and limb-girdle weakness are clinically useful to guide genetic screening. Key diagnostic features are provided outside the boxes. Most frequent subtypes of CMS include AChR-deficiency, DOK7 CMS, and rapsyn CMS which stand for approximately 70% of all cases in the UK. (*) Slow channel syndrome, SYT2 CMS, and SNAP25B CMS are dominantly inherited. CNS, central nervous system; TA, tubular aggregates.