Fig. 6.
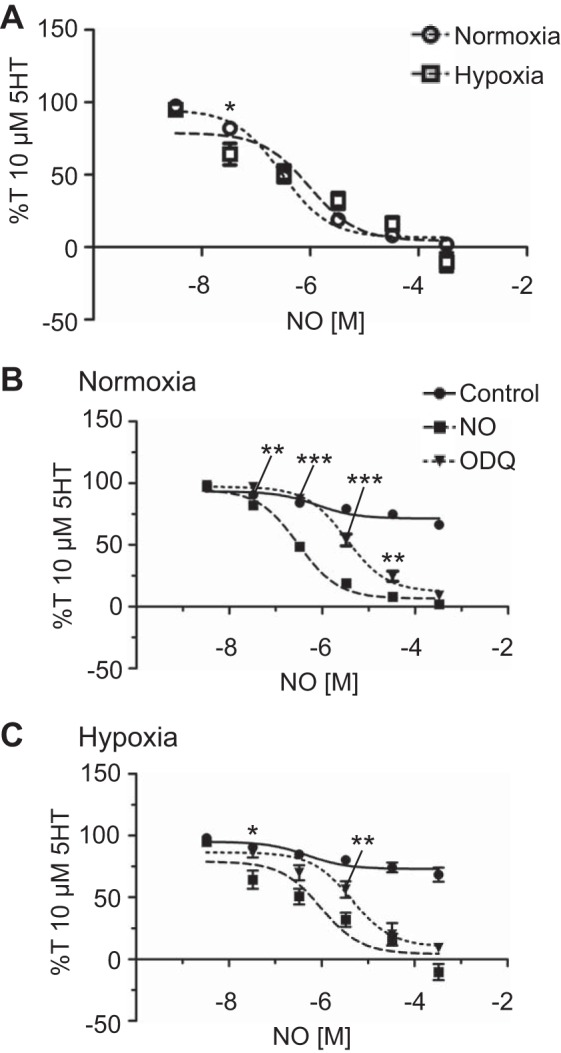
Nitric oxide (NO)-dependent vasorelaxation is preserved following long-term hypoxia (LTH). N-nitrosoproline (ProliNO)-induced isometric tension values normalized to 10 µM serotonin (5-HT)-precontracted tension (%T10 μM 5-HT) for normoxic (open circles, dotted line, n = 5/19) and LTH (open square, n = 7/18) sheep (A), normoxic (n = 5/19, B) and LTH (n = 7/18, C) sheep in the absence (squares) of 1H-[1,2,4]oxadia-zolo[4,3-a]quinoxalin-1-one (ODQ), in the presence of 10 μM ODQ (inverted triangles, dotted line; n = 7/26 normoxic and 4/12 LTH animals), and in the presence of NaOH (filled circles) as a vehicle- and time-matched control (n = 7/32 normoxic and 4/13 LTH animals). Lines show resultant fits with a Hill equation to the dose-response relationships, and markers show means ± SE. The data were analyzed by 2-way analysis of variance with a Bonferroni posttest analysis for each dose. Statistical significance is noted between groups (A) or relative to the presence of ProliNO (B and C). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001.
