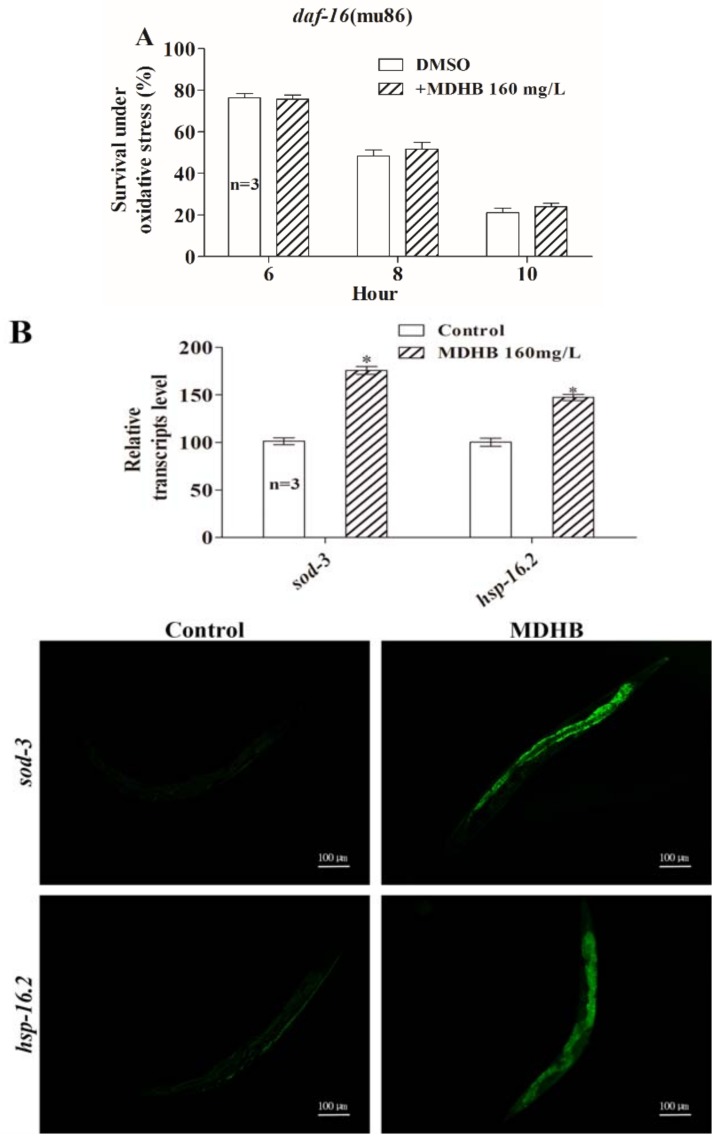
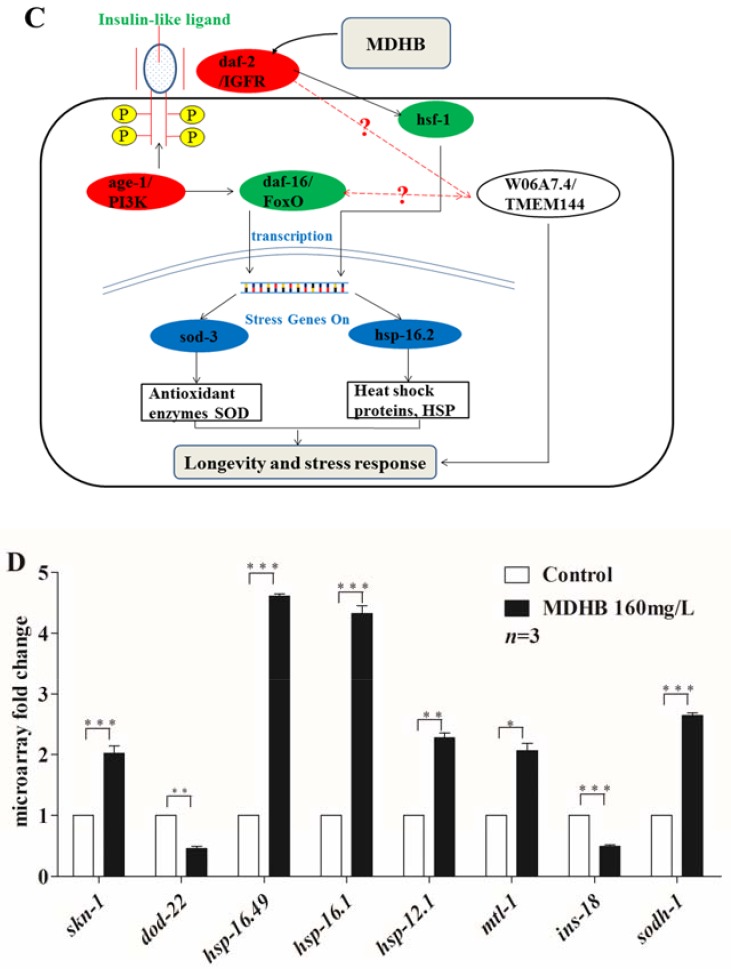
Figure 8.
Influence of MDHB on the expression of daf-2/daf-16 target genes. (A) Influence of MDHB on survival rates of daf-16 (mu86) mutants under oxidative stress conditions induced by H2O2. MDHB did not enhance stress resistance in daf-16 (mu86) mutants. (B) Influence of MDHB on the expression of hsp-16.2 and sod-3 genes under normal conditions. Green fluorescent protein (GFP) was tested and quantified using a fluorescence multi-reader, and analyzed by the standard Student t-test. (C) A drawing of daf-2/daf-16 signaling and its mammalian homologues shows the supposed mechanism of action of MDHB in C. elegans. Active IIS promotes the phosphorylation-dependent cytoplasmic sequestration of the transcription factors daf-16/FoxO and hsf-1. The insulin/IGF-1 receptor ortholog daf-2 and other pathway components that promote IIS are colored red, and molecules that either antagonize IIS or are antagonized by IIS are colored green. Genes that are promoted by daf-16/FoxO are colored blue. Molecular, which may either promote or antagonize the activity of its target genes, are marked with black arrows. Genes that either antagonize daf-2/daf-16 or are antagonized by daf-2/daf-16 are marked with red arrows. Abbreviations: IIS, insulin/insulin-like growth factor-1 signaling; IGFR, Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinase; FoxO, forxhead box protein O; P, the phosphate groups. (D) Influence of MDHB on the expression of partial daf-2/daf-16 pathway targets. The effects of MDHB on the expression of genes were detected through a microarray profiling analysis. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001; ns: not significant.