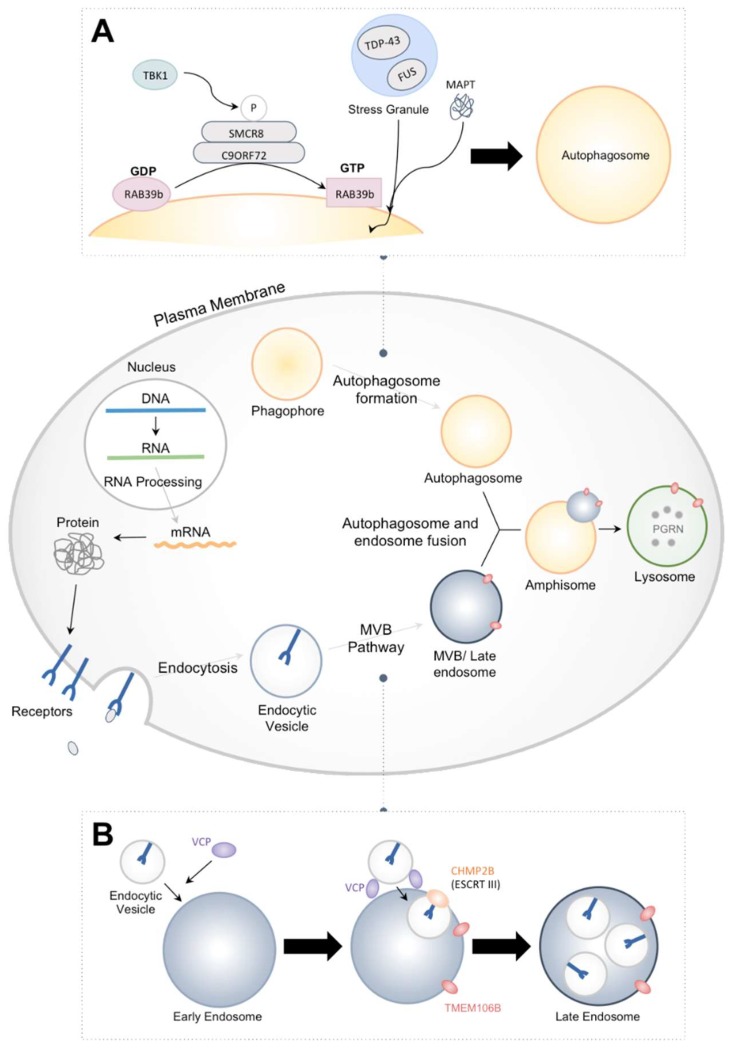
Figure 1.
Role of proteins associated with frontotemporal dementia (FTD) in endosomal–lysosomal and autophagy pathway. FTD associated proteins, highlighted in yellow, are involved in both autophagy and endosomal–lysosomal pathways. (A) Phagophores in the cytoplasm undergo autophagosome formation with the assistance of C9ORF72, TANK binding kinase 1 (TBK1), microtubule-associated protein tau (MAPT), transactive DNA-binding protein (TDP-43), and fused in sarcoma (FUS) proteins, as well as various other protein complexes not included in the figure above. (B) Endocytic vesicles bearing receptor cargo transition through maturation stages to form MVBs and eventually fuse with the lysosomes. ESCRT complexes and additional proteins, including valosin containing protein (VCP) and transmembrane protein 106B (TMEM106B), contribute in the development of the endosome and MVB pathway in the endosomal–lysosomal pathway.