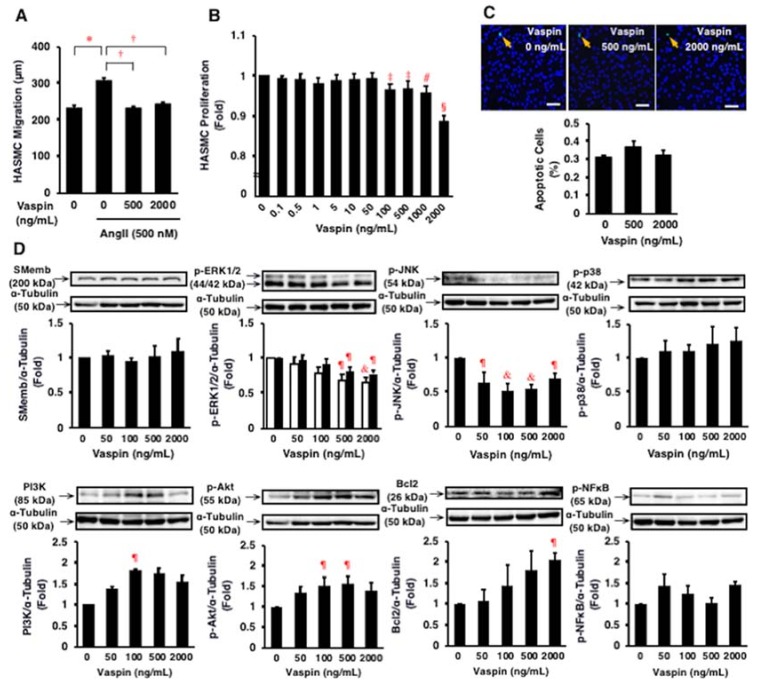
Figure 4.
Effects of vaspin on migration, proliferation, apoptosis, and intracellular signal transductions in HASMCs. (A) Effect of vaspin on angiotensin II (Ang II)-induced migration was determined in 10 cells per well using a BIOREVO BZ-9000 microscope. The experiments were repeated independently 4 times. * p < 0.005, † p < 0.0001. (B) Effect of vaspin on proliferation was determined by WST-8 assay (n = 4). ‡ p < 0.05, # p < 0.001, § p < 0.0001 vs. 0 ng/mL of vapin. (C) Effect of vaspin on apoptosis was evaluated by detecting apoptotic cells (green) using the TUNEL method. Nuclei were co-stained with 6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (blue). The graph indicates the percentage of apoptotic cells in 3 independent experiments. Bar = 100 μm. (D) Relevant intracellular signals in response to vaspin were assessed by immunoblotting. The blotted membranes were cut for reacting with different antibodies, and the blots were stripped and reprobed in the same membrane. Top: Representative results of protein expression/phosphorylation of SMemb, ERK1/2, JNK, p38, PI3K, Akt, Bcl2, and NFκB. Bottom: Densitometric data of each molecule after normalization relative to α-tubulin (n = 4–5). ¶ p < 0.05, & p < 0.01 vs. 0 ng/mL of vapin (corresponding control).