Table 4.
Hybrid drug conjugates targeting breast cancer
| Drug conjugate/Drug class | Status/model | Potency/efficacy |
|---|---|---|
Ribociclib‐vorinostat/cyclic‐dependent kinase CDK‐4–HDAC inhibitor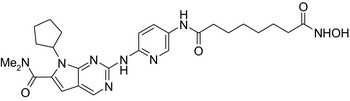
|
In vitro MDA‐MB‐231 cellsIn vivo 4T1 cells of rat breast cancer | Conjugate showed higher cytotoxicity on MDA‐MB‐231 cells (IC50 = 1.86 μmol/L) than vorinostat (IC50 = 2.59 μmol/L) and ribociclib (IC50 > 10 μmol/L) and stronger tumor growth inhibition in 4T1 cells (79%) than vorinostat (75.6%) and ribociclib (38.9%)65 |
Fibroblast growth factor 1 inhibitor‐nexturastat/FGFR 1‐HDAC‐6 inhibitor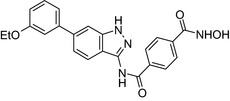
|
In vitro MCF‐7 cells | Conjugate showed cytotoxic activity on MCF‐7 cells (IC50 = 9 μmol/L)67 |
Raloxifen‐dimethyl fumarate/SERM–anti‐NF‐κB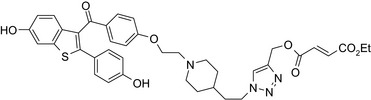
|
In vitro MCF‐7 cells | Higher inhibition of NF‐κB than fumarate alone54 |
Olaparib‐vorinostat/PARP inhibitor–HDAC inhibitor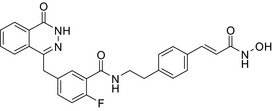
|
In vitro MDA‐MB‐231 and HCC1937 cells | Conjugate showed more potent activity than olaparib and vorinostat with 4.1‐fold less cytotoxicity to MCF‐10A123 |
Ruxolitinib‐vorinostat/Janus kinase‐HDAC inhibitor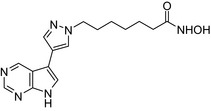
|
In vitro MCF‐7 cells | Conjugate was equipotent on MCF‐7 cells (IC50 = 0.84 μmol/L) to vorinosta (IC50 = 0.84 μmol/L) and more potent than ruxolitinib (IC50 = 10 μmol/L)121 |
Combretastatin‐cyclofenil/Antimitotic‐SERM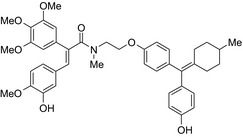
|
In vitro MCF‐7 cells | Cyclofenil‐combretastatin conjugate (IC50 = 187 nmol/L) showed potent antiproliferative activity to MCF‐7 cells56 |
Combretastatin endoxifen/Antimitotic‐SERM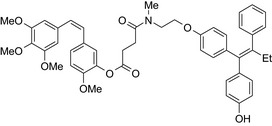
|
In vitro MCF‐7 cells | Endoxifen‐combretastatin conjugate (IC50 = 5.7 nmol/L) showed potent antiproliferative activity to MCF‐7 cells56 |
Endoxifen‐combretastatin/Antimitotic‐SERM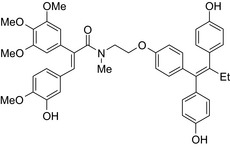
|
In vitro MCF‐7 and MDA‐MB‐231 cells | The conjugate showed potent antiproliferative activity (IC50 = 5 nmol/L) to MCF‐7 cells56 |
Vandetanib‐vorinostat/VEGFR‐HDAC inhibitor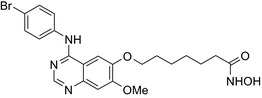
|
In vitro MCF‐7 cells | Conjugate was more potent on MCF‐7 cells (IC50 = 0.85 μmol/L) than vandetanib (IC50 = 18.5 μmol/L) and vorinostat (IC50 = 4.5 μmol/L)87 |
TBB‐triazole hydroxamic acid/Casein kinase 2–HDAC inhibitor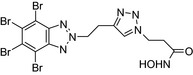
|
In vitro MCF‐7 cells | The conjugate showed cytotoxic activity (IC50 = 4.26 μmol/L) on MCF‐7 cells90 |
Oxabicycloheptene sulfonate‐vorinostat/ERα antagonist–HDAC inhibitor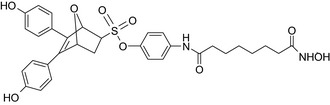
|
In vitro MCF‐7 cells | The conjugate showed higher potency than tamoxifen.107 |
ICI‐164,384‐N‐butylvorinostat/ER antagonist‐HDAC inhibitor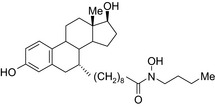
|
In vitro MCF‐7 and MDA‐MB‐237 cells | Conjugate was more potent on MCF‐7 cells (IC50 = 0.34 μmol/L) than ICI‐164,384 (IC50 = 0.93 μmol/L) and vorinostat (IC50 = 0.32 μmol/L)76 |
Semaxanib‐vorinostat / VEGFR‐HDAC inhibitor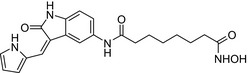
|
In vitro MDA‐MB‐237 cells | Conjugate was equipotent on MDA‐MB‐237 cells (IC50 = 117 nmol/L) to vorinostat (IC50 = 118 nmol/L)86 |
Melatonin‐tamoxifen/SERM–melatonin receptor agonist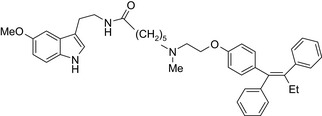
|
In vitro BC cells In vivo ovariectomized FVB/n mice | Hybrid conjugate did not increase uterus weight compared to tamoxifen, and showed efficacy against different BC cells including tamoxifen‐resistant MCF‐7 cells, to be published,116 US patent no. ‐ 08785501) |
Colchicin‐pironetin/Β‐tubulin inhibitor–α‐tubulin inhibitor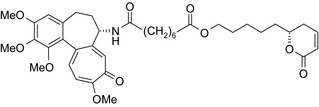
|
In vitro MCF‐7 cells | All conjugates showed lower cytotoxicity values than the parental molecules, whereas the binding of the conjugates to tubulin depends on the length of the linkers113 |
c‐Src kinase inhibitor vorinostat/c‐Src‐HDAC inhibitor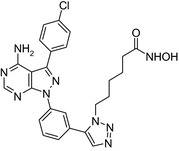
|
In vitro SK‐BR‐3 cells | Conjugate was more potent on SK‐BR‐3 (IC50 = 0.2 μmol/L) than vorinostat (IC50 = 1.2 μmol/L)59 |
Platinum‐acridin‐endoxifen/DNA intercalation & platination–SERM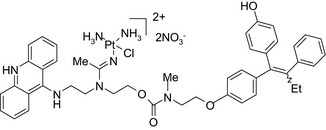
|
In vitro MCF‐7 and MDA‐MB‐231 cells | One conjugate showed higher potency on MCF‐7 cells compared to cisplatin or tamoxifen23 |
Endoxifen‐endoxifen/Bivalent SERM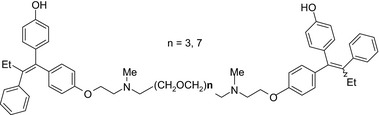
|
In vitro MCF‐7 and MDA‐MB‐231 cells | Bivalent ligands showed higher potency than 4OH tamoxifen98 |
Tamoxifen‐vorinostat/SERM‐HDAC inhibitor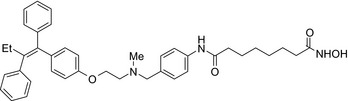
|
In vitroMCF‐7 and MDA‐MB‐231 cells | The conjugate showed higher cytotoxicity on MCF‐7 (IC50 = 3.8 μmol/L) and on MDA‐MB‐231 cells (IC50 = 8.1 μmol/L) than tamoxifen and vorinostat40 |
Doxorubicin‐RU 39411/Topoisomerase inhibitor–ER antagonist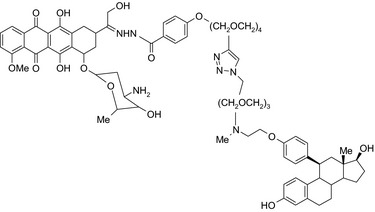
|
In vitro MCF‐7 and MDA‐MB‐231 cells | The conjugate was about 70‐fold more potent than doxorubicin to inhibit MCF‐7 cell proliferation18 |
Erlotinib‐vorinostat CUDC‐101/EGFR‐HER2‐HDAC inhibitor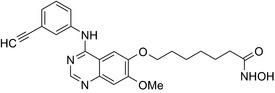
|
In vitro MCF‐7 and MDA‐MB‐231 cellsIn vivo xenograft mice | Conjugate was more potent on MCF‐7 cells (IC50 = 0.55 μmol/L) than erlotinib (IC50 = 20 μmol/L) and vorinostat (IC50 = 2.8 μmol/L) and the combination of the parent drugs (IC50 = 2.7 μmol/L)64 |
Lapitanib‐panobinostat/EGFR‐HER2‐HDAC inhibitor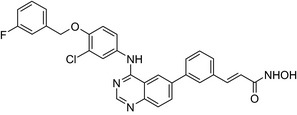
|
In vitroSKBR3 cells | Conjugate is more potent on SMBR3 cells than lapitanib and vorinostat70 |
Estradiol‐cisplatin/ER agonist–antineoplastic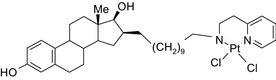
|
In vivoMCF‐7 and MDA‐MB‐468 mouse xenografts | The conjugates decreased tumor volume compared to cisplatin in ER‐positive mice111 |
Retinoic acid‐butyric acid/RAR & RXR agonist–HDAC inhibitor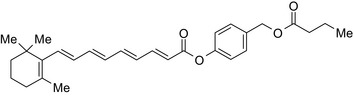
|
In vitroMCF‐7 andMDA‐MB‐231 cells | The conjugate showed 1085‐fold higher potency than parent retinoic acid and 100000‐fold higher potency than butyric acid38 |
Tamoxifen‐ferrocene/SERM–organometallic complex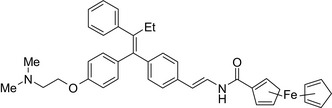
|
In vitroMCF‐7 cells | Increased apoptotic events compared to tamoxifen/ferrocene117 |
Doxorubicin‐4OH tamoxifen/Topoisomerase inhibitor–SERM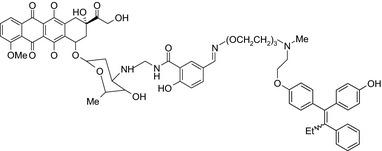
|
In vitroMCF‐7, MCF‐7 resistant,MDA‐MB‐231, MDA‐MB‐435 cells | The conjugates showed 4‐ to 140‐fold higher potency than doxorubicin10 |
Aniline mustard‐estradiol/DNA‐alkylating agent–ER agonist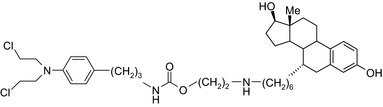
|
In vitroMCF‐7 and MDA‐MB‐231 cells | The conjugate showed higherpotency compared to chlorambucil79 |
Aniline mustard‐phenylindole/DNA‐alkylating agent–SERM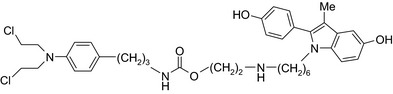
|
In vitroMCF‐7 and MDA‐MB‐231 cells | Two conjugates showed higher toxicity to MCF‐7 than to MDA‐MB‐231 cells94 |
SERM, Selective estrogen receptor modulator, GPCR, G protein‐coupled receptor.
