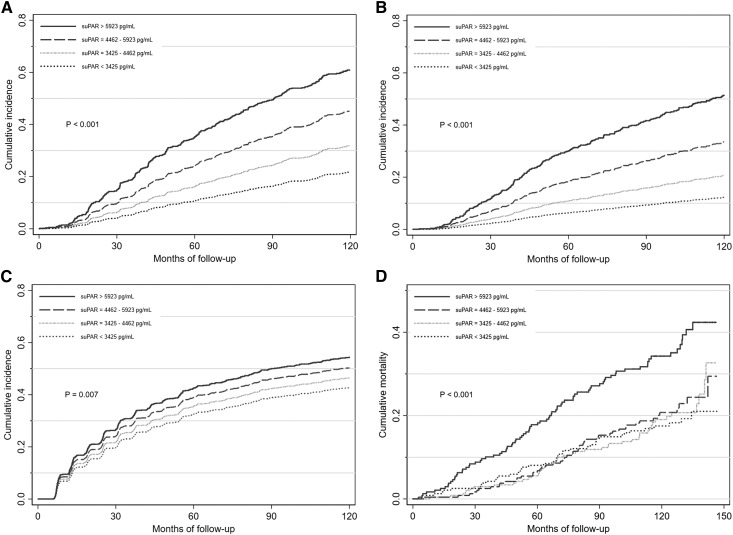
Figure 1.
The unadjusted cumulative incidences of CKD progression, ESKD, worsening proteinuria, and mortality were higher with higher suPAR quartiles in the African-American Study of Kidney Disease and Hypertension. (A) Levels of baseline serum suPAR concentration and cumulative incidence of CKD progression. (B) Levels of baseline serum suPAR concentration and cumulative incidence of ESKD. (C) Levels of baseline serum suPAR concentration and cumulative incidence of worsening proteinuria. (D) Levels of baseline serum suPAR concentration and cumulative incidence of all-cause mortality. CKD progression was defined as doubling of serum creatinine from baseline or ESKD (requiring dialysis or kidney transplantation). Worsening proteinuria was defined as pre-ESKD doubling of 24-hour UPCR to ≥220 mg/g.