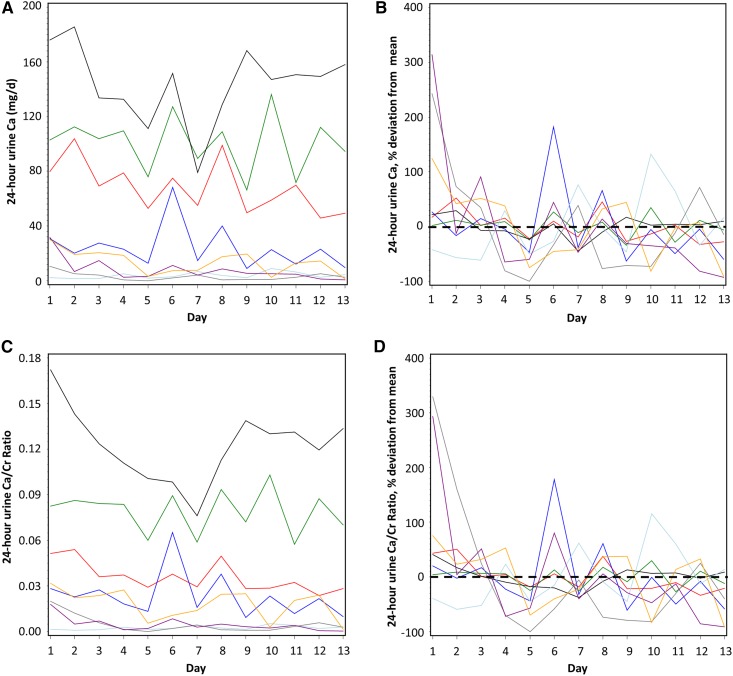
Figure 4.
Twenty four-hour urine calcium was generally low and showed high percent coefficients of variation, but low absolute variation in CKD patients. Daily variation in subjects in (A) 24-hour urine calcium (absolute values) and (B) 24-hour urine calcium (% variation above and below the mean [set at zero] for each subject); (C) 24-hour urine calcium-to-creatinine ratio (absolute values) and (D) 24-hour urine calcium-to-creatinine (% variation above and below the mean [set at zero] for each subject). In (B and D), the mean for each subject is set at zero and the percentage fluctuation each day above or below the mean is shown; zero is indicated by a horizontal black dashed line. In all panels, different color lines represent individual subjects. Ca, calcium; Ca/Cr, calcium-to-creatinine.