Figure 2.
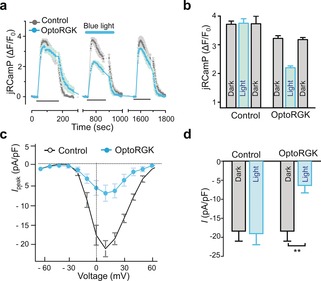
OptoRGK‐mediated photoswitchable inhibition of Ca2+ entry through CaV1.2 channels. a) Ca2+ influx in HEK‐CaV1.2 cells transiently expressing optoRGK and the red Ca2+ sensor jRCaMP1b with and without blue‐light stimulation. Cells transfected with the empty vector are used as control. Membrane‐depolarization‐induced Ca2+ entry was elicited by adding 50 mm KCl (black line below the curves; three repeated cycles) to transfected cells. Blue line represents light stimulation under 470 nm with a power density of 40 μW mm−2. b) Bar graphs showing the statistical results of mean Ca2+ entry for each cycle. c) The current–voltage relationships of CaV channels in HEK‐Cav1.2 cells transfected with optoRGK. Cells were either shielded from light or exposed to blue light prior to electrophysiological recording. d) Bar graphs showing the statistical results of peak whole‐cell currents induced by pulses of +10 mV depolarization (pA/pF) in HEK‐CaV1.2 cells before and after photo‐stimulation. All data were presented as mean±SEM. **P<0.01 (paired Student's t‐test).
